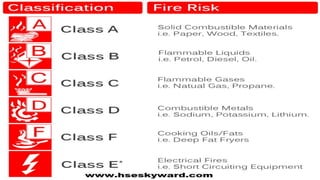
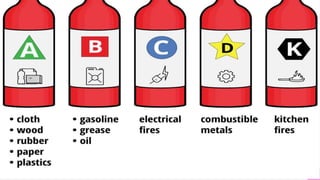
Here are two measures that could have prevented the fire incident:
1. Proper storage and handling of flammable materials like chemicals, fuels, etc. Flammables should be stored safely away from potential ignition sources.
2. Regular maintenance of electrical wiring and appliances to prevent short circuits or overheating that could spark a fire. Damaged or faulty wiring should be repaired immediately.