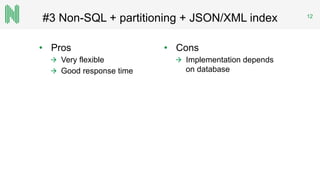
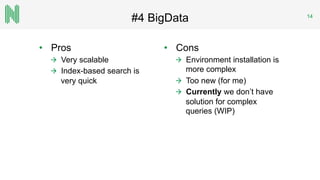
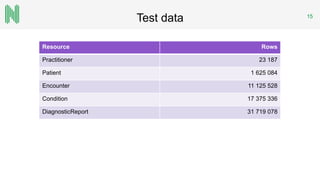
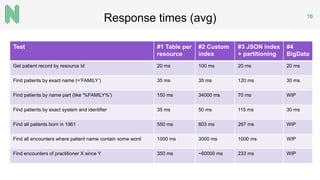
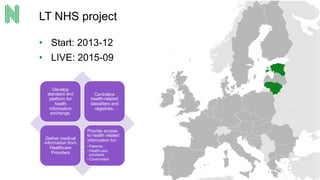
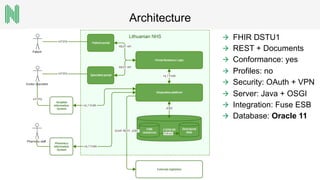
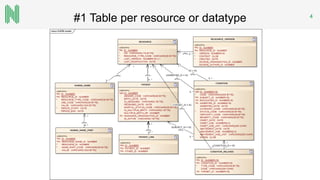
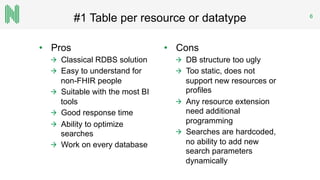
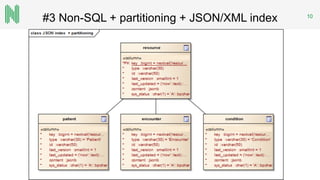
The document discusses the implementation of a FHIR server for health information exchange in Lithuania, detailing various database approaches including traditional RDBMS, resource store with custom indexing, non-SQL methods, and big data solutions. It evaluates each approach based on flexibility, response time, and scalability, providing specific query examples and their performance metrics. Overall, the study highlights the trade-offs between different database structures while addressing requirements for healthcare data accessibility.





![#3 PostgreSQL JSONB query examples 11
select id from fhir.patient
where content @> '{"name":[{"use":"official", "family":[”XXX"]}]}'
select c.id
from practitioner p
inner join condition c on
c.content -> 'asserter' ->> 'reference' = p.id
where p.content ->> 'name' ~ '"family":[ []*”XXX"*[ ]]'](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fhirdevdays2015-151119110200-lva1-app6891/85/FHIR-Developer-Days-2015-Study-on-db-implementations-for-FHIR-server-11-320.jpg)