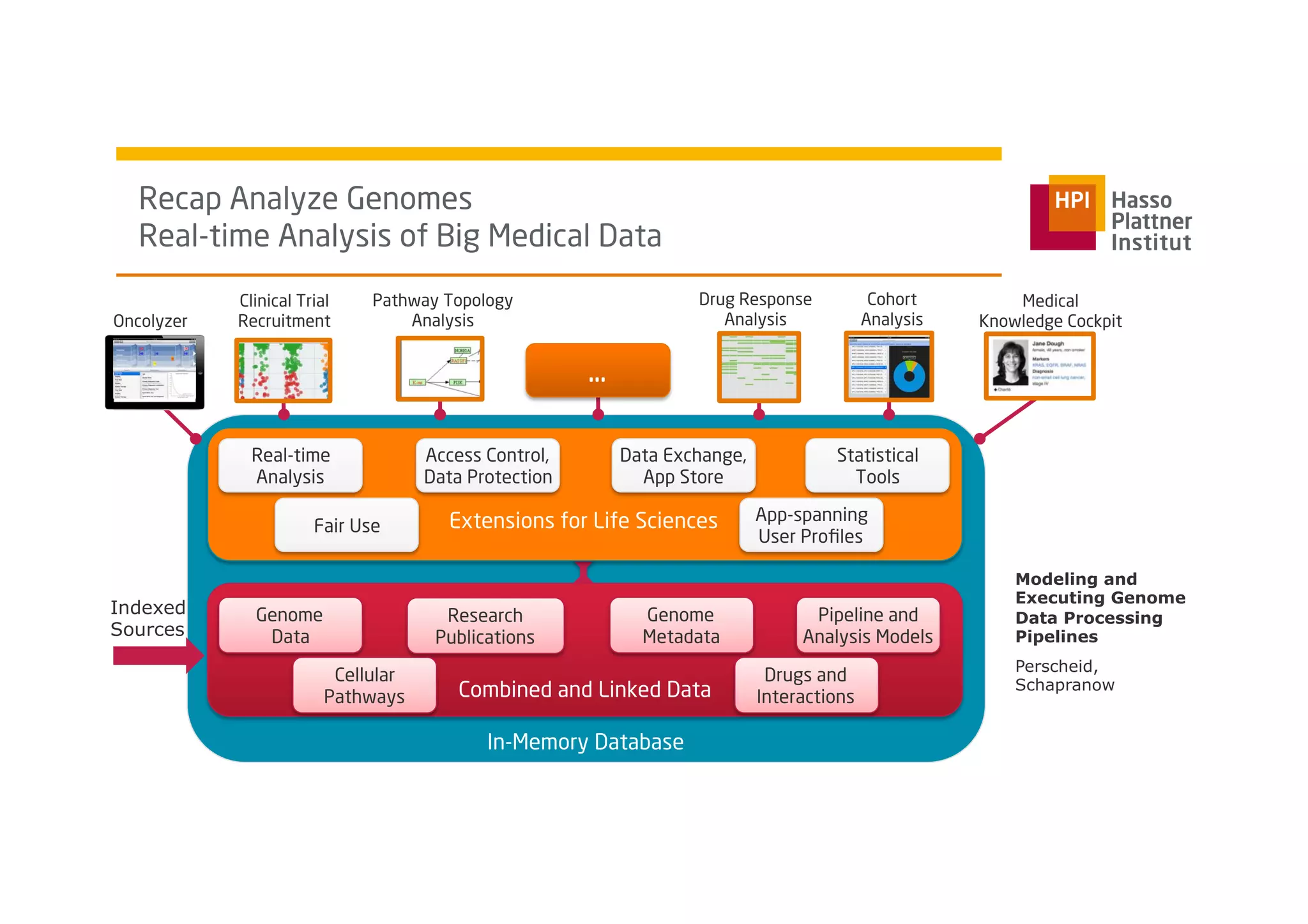
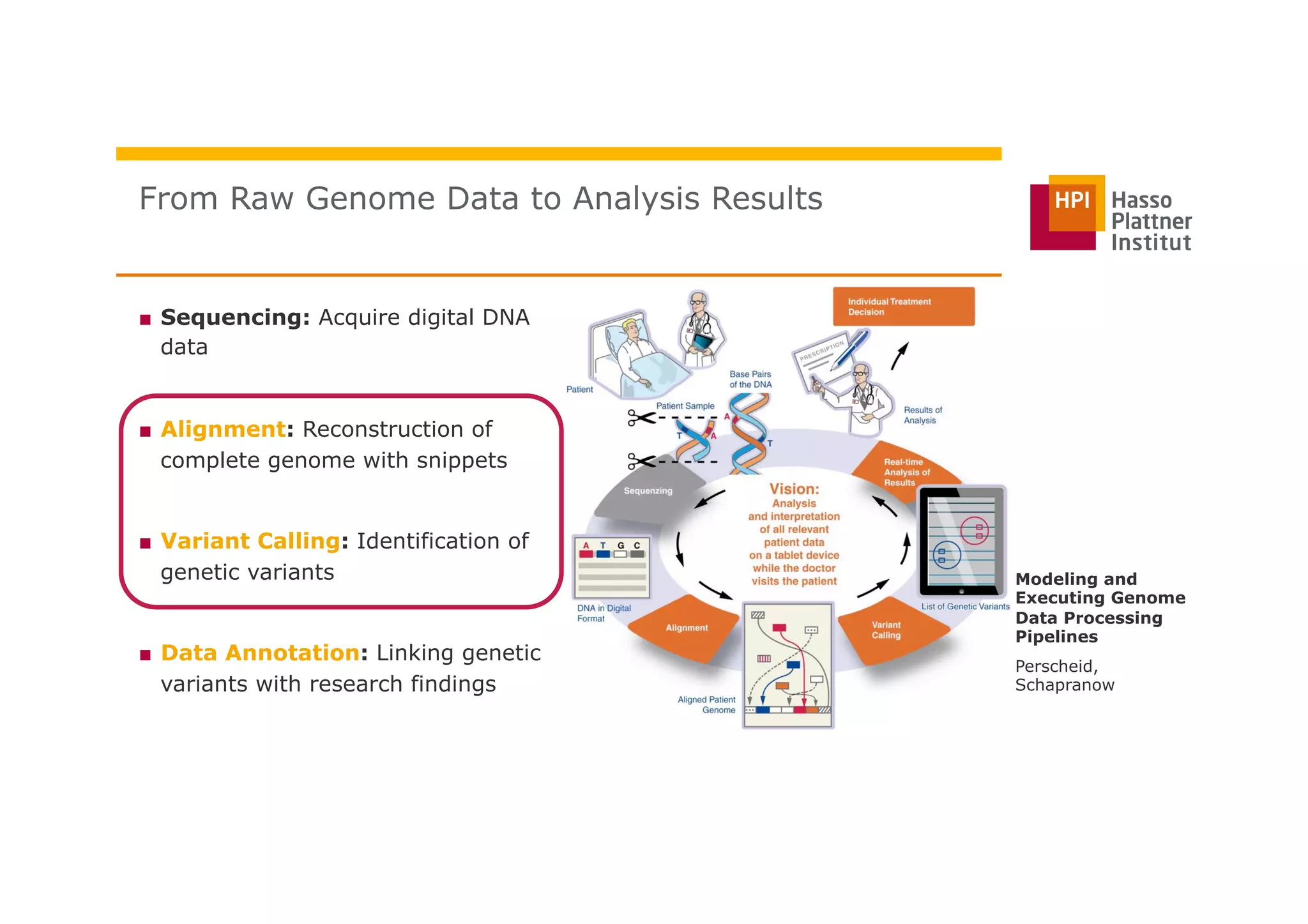
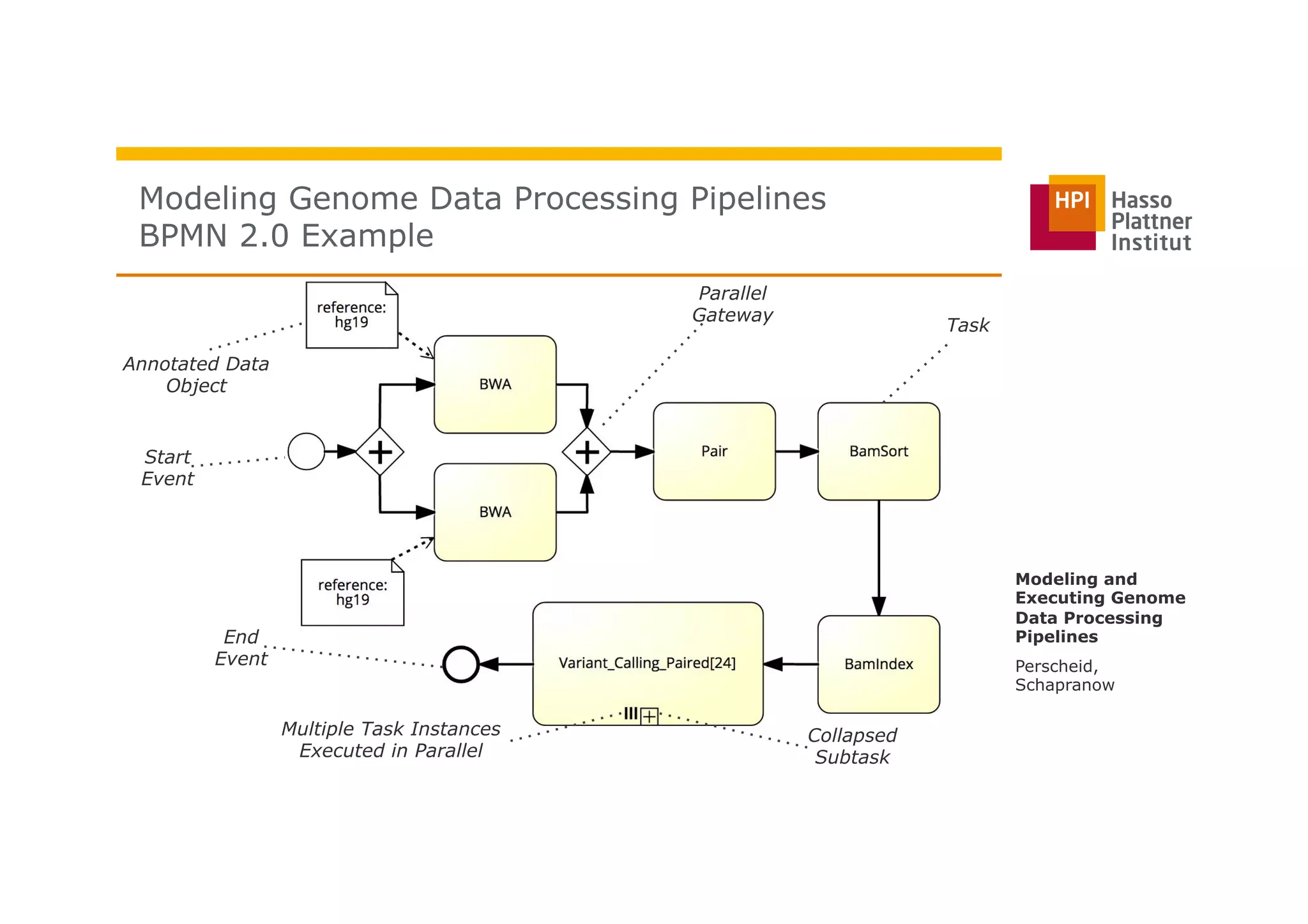
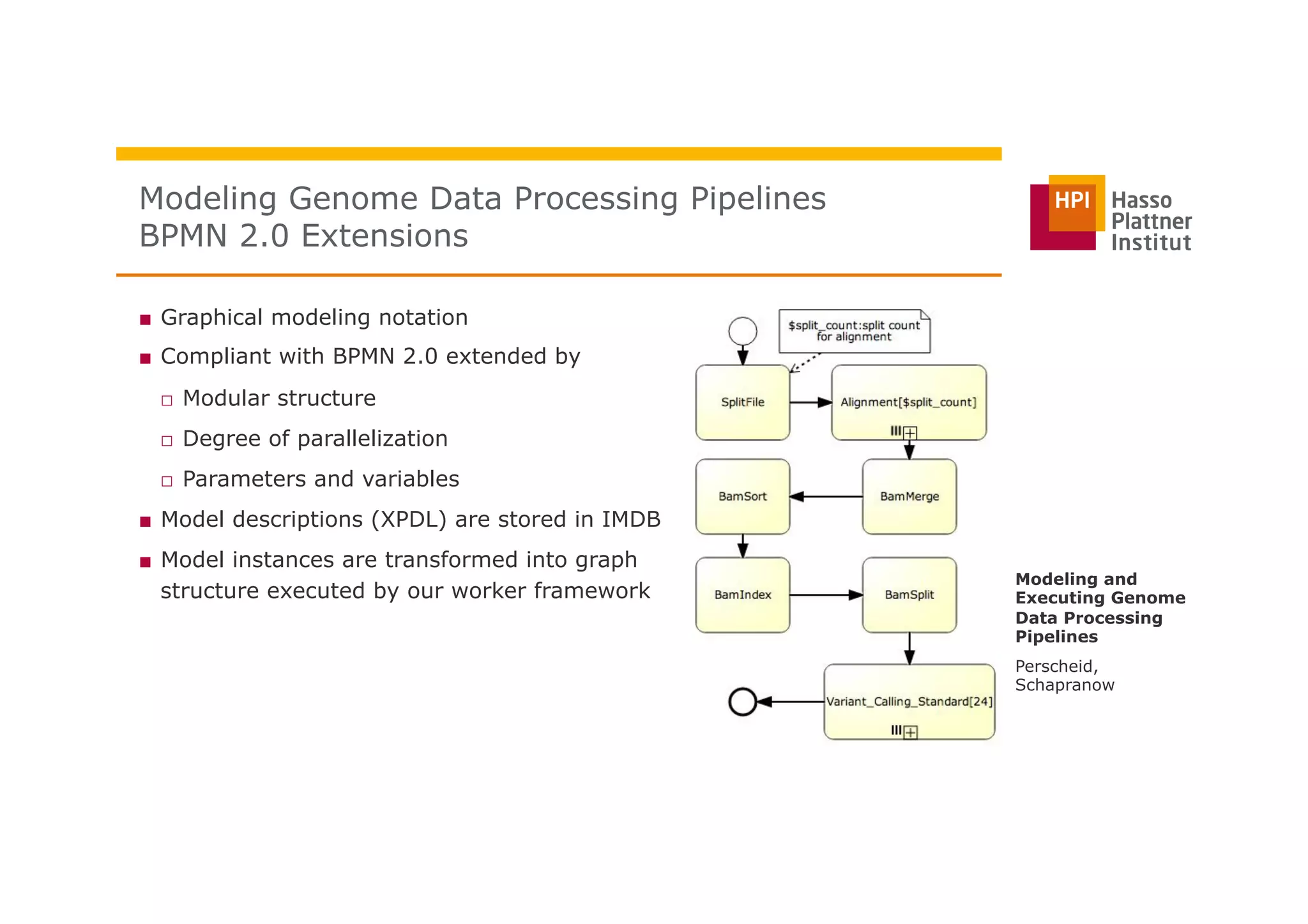
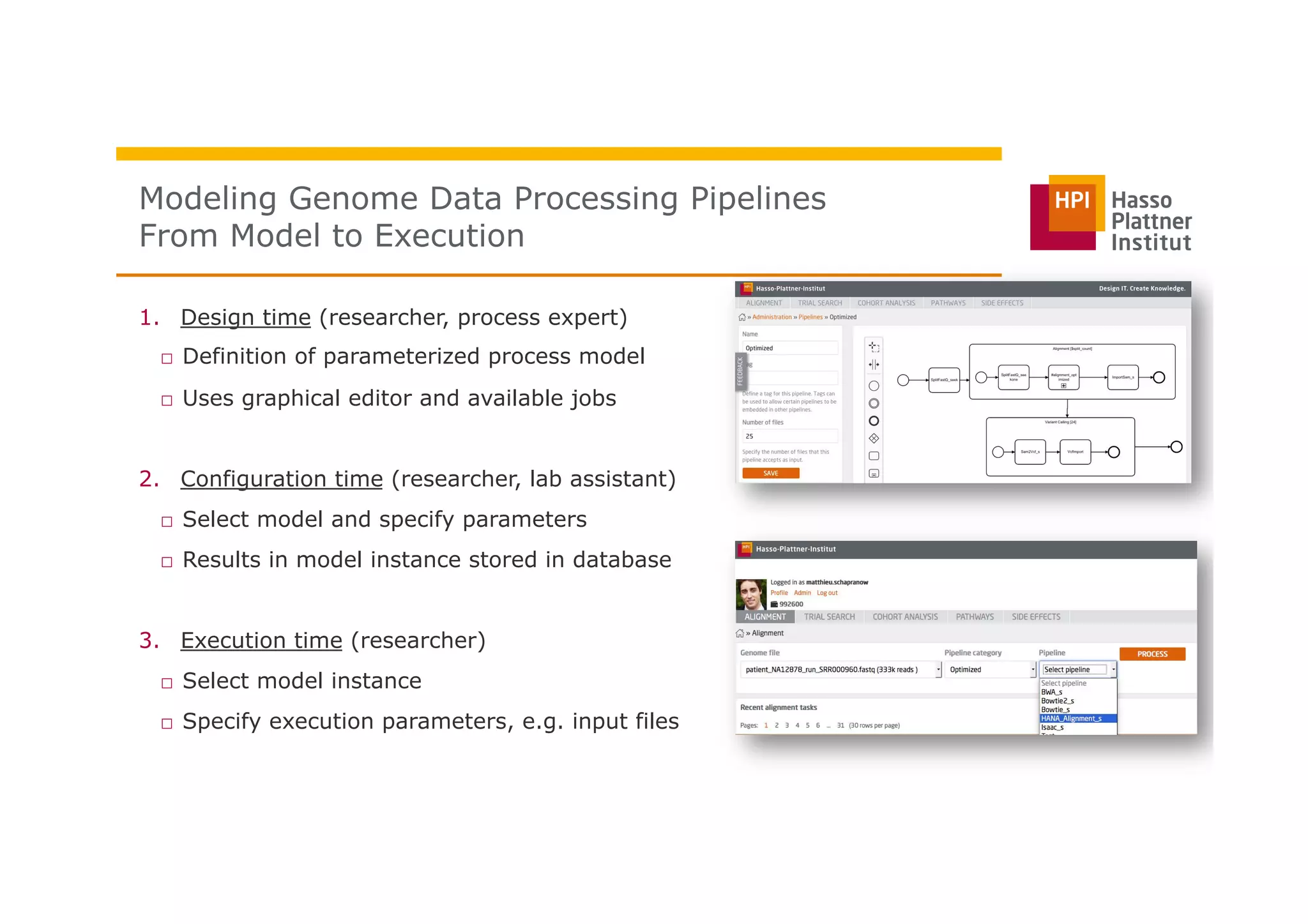
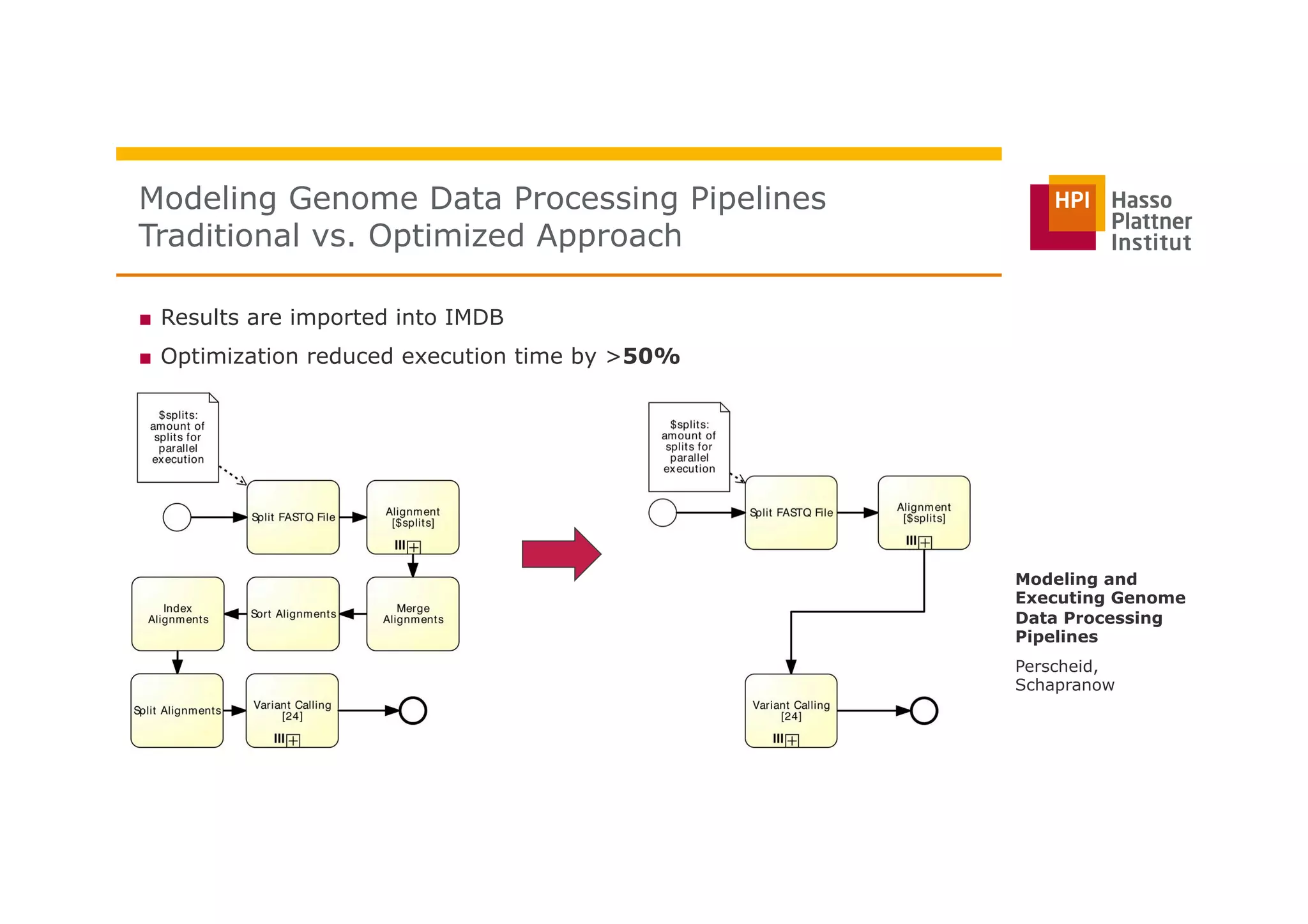
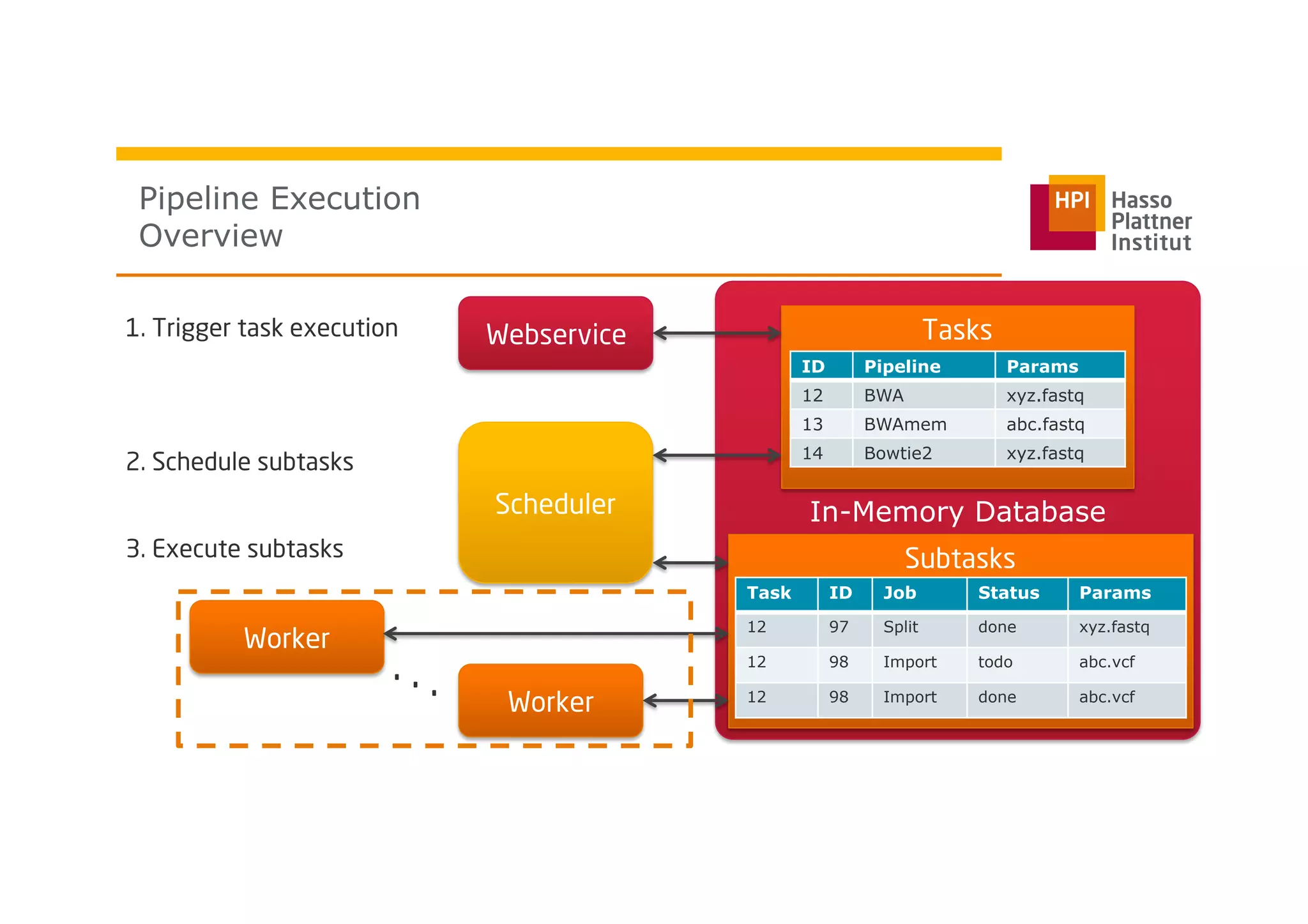
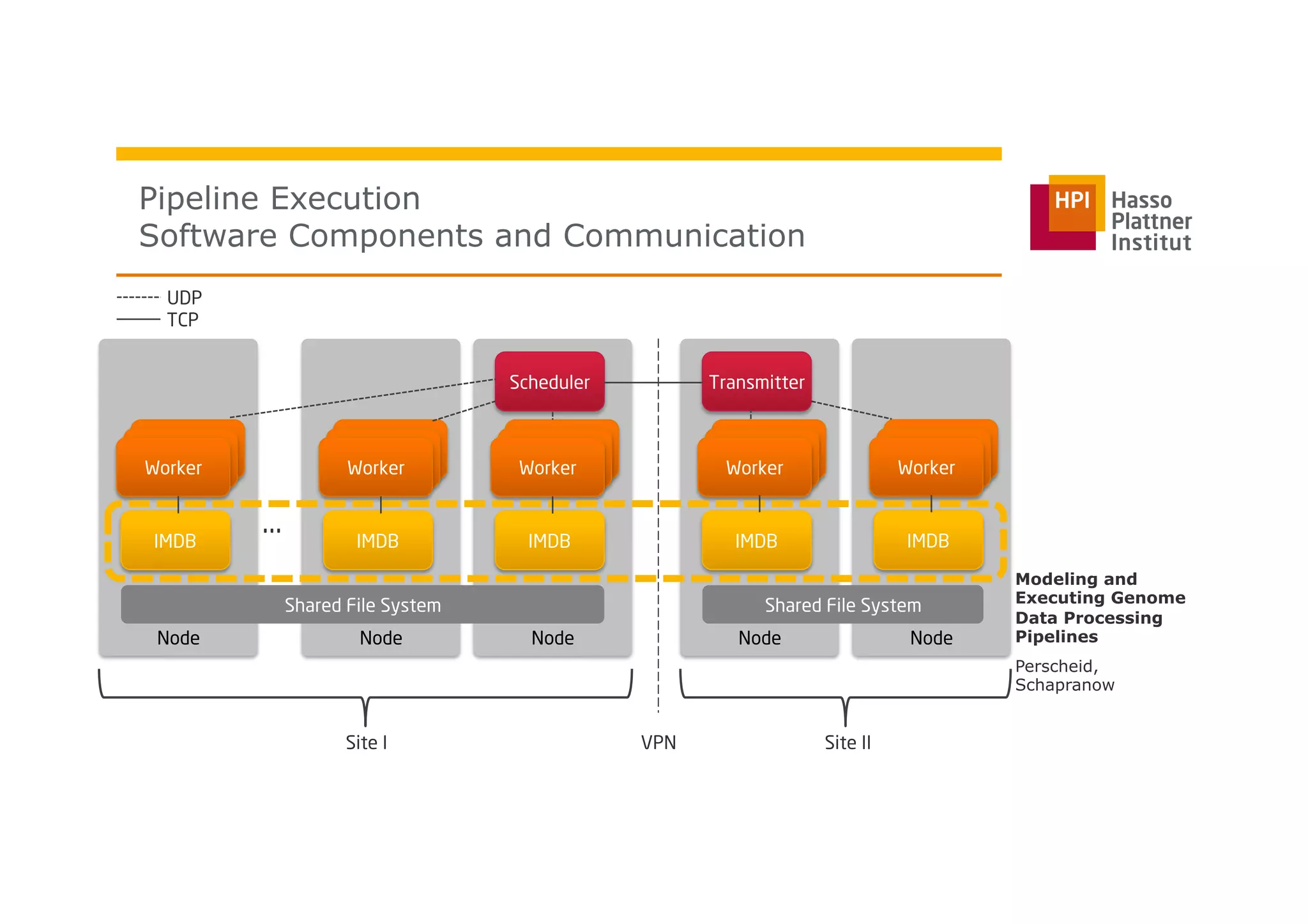
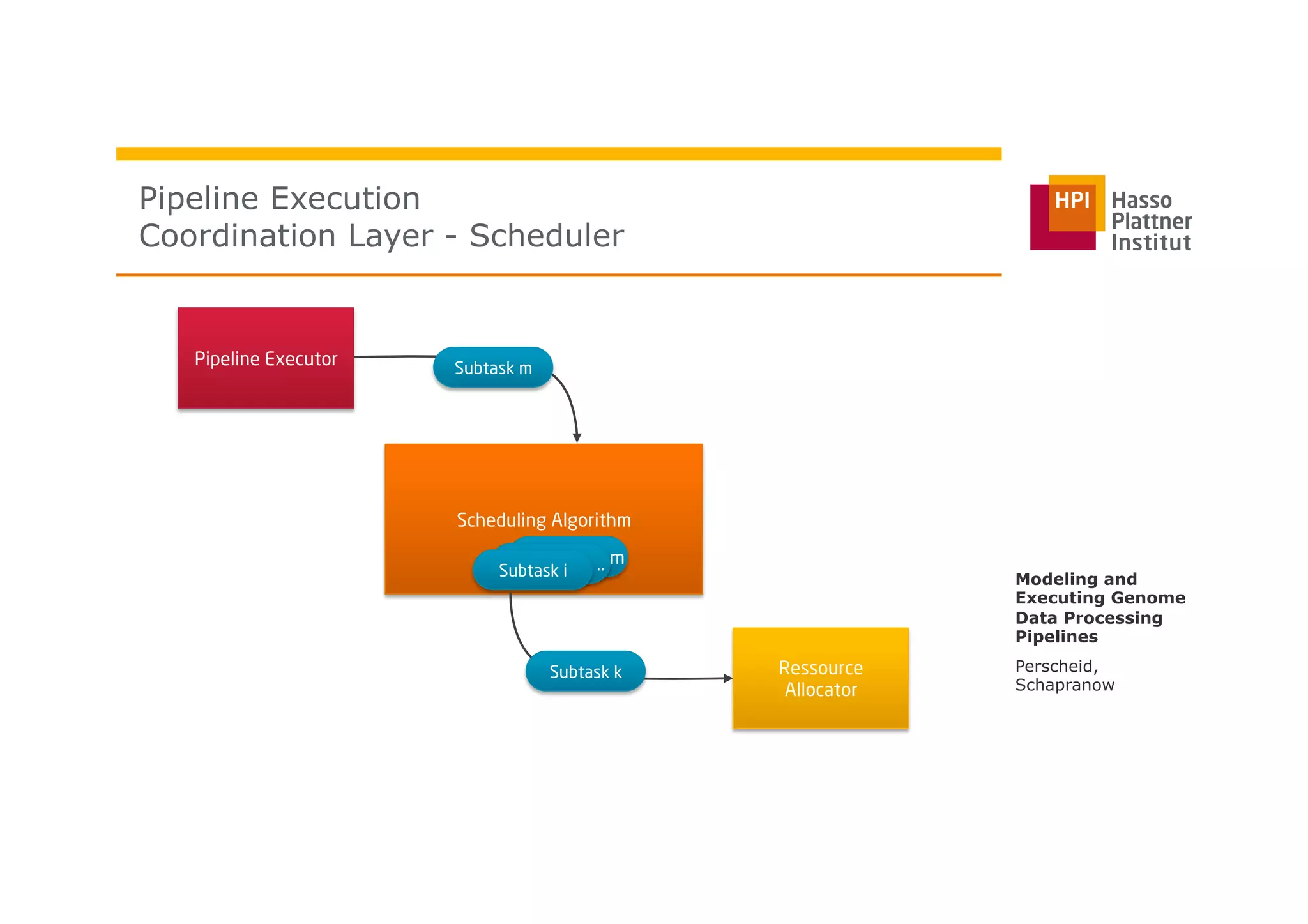
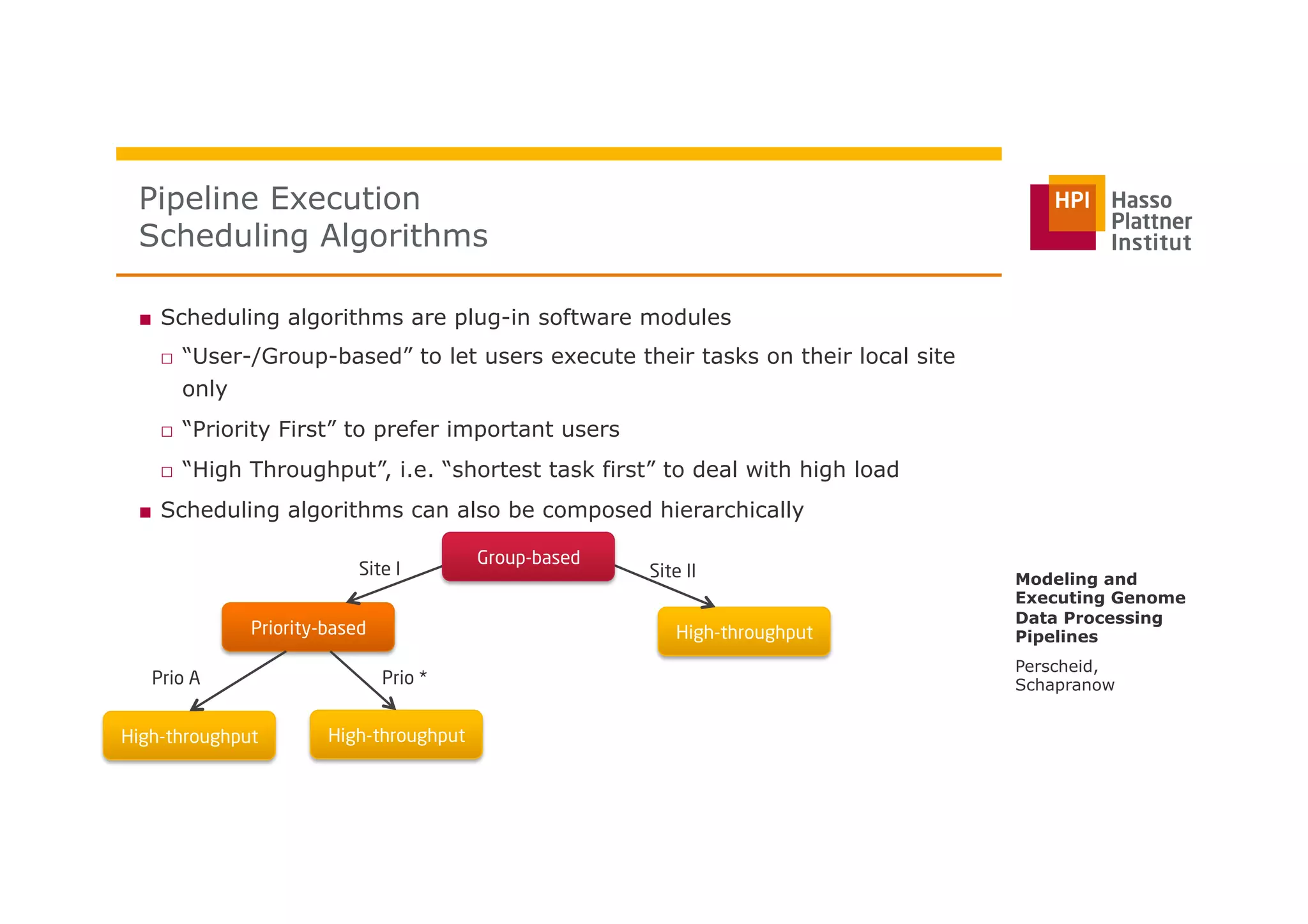
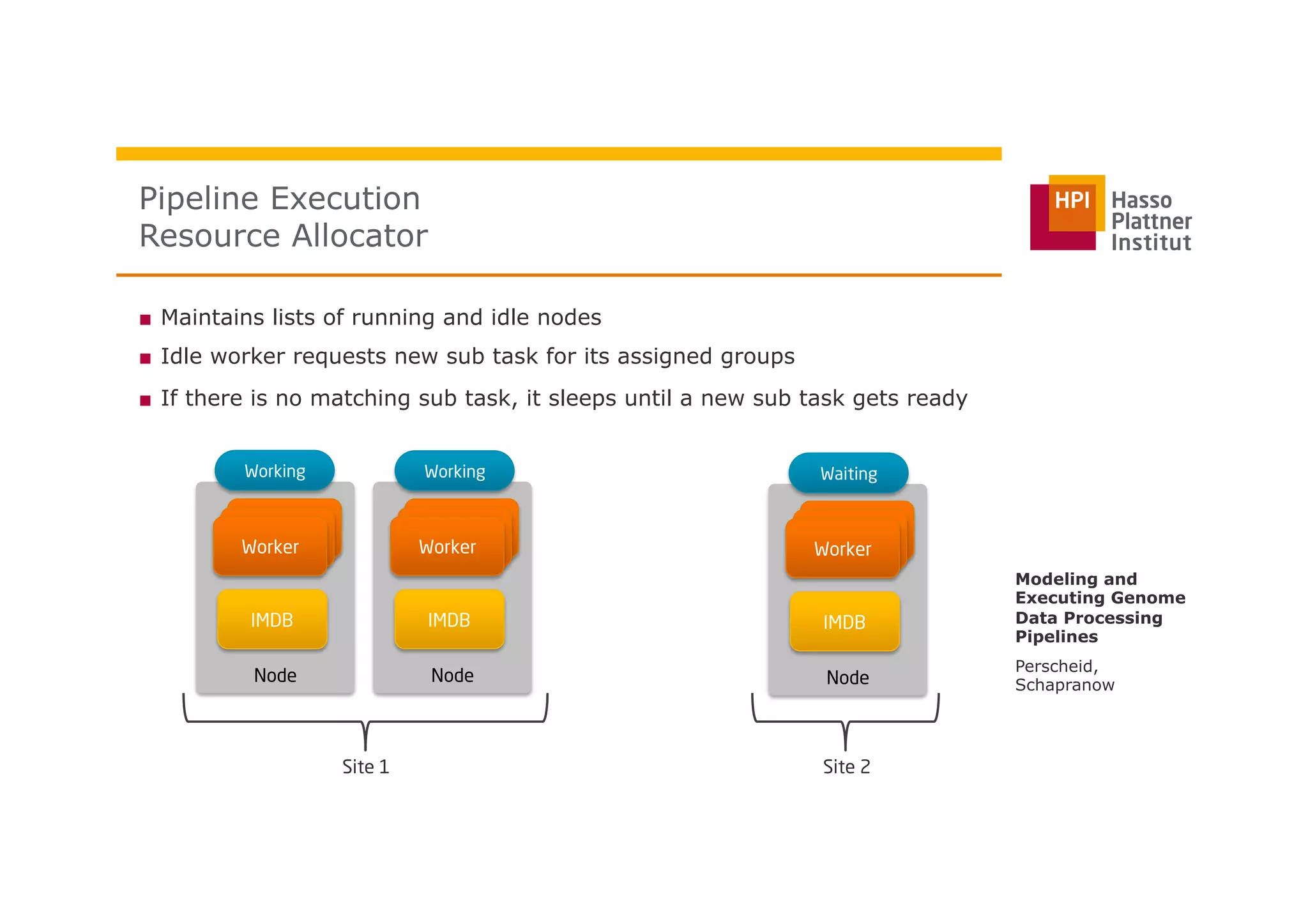
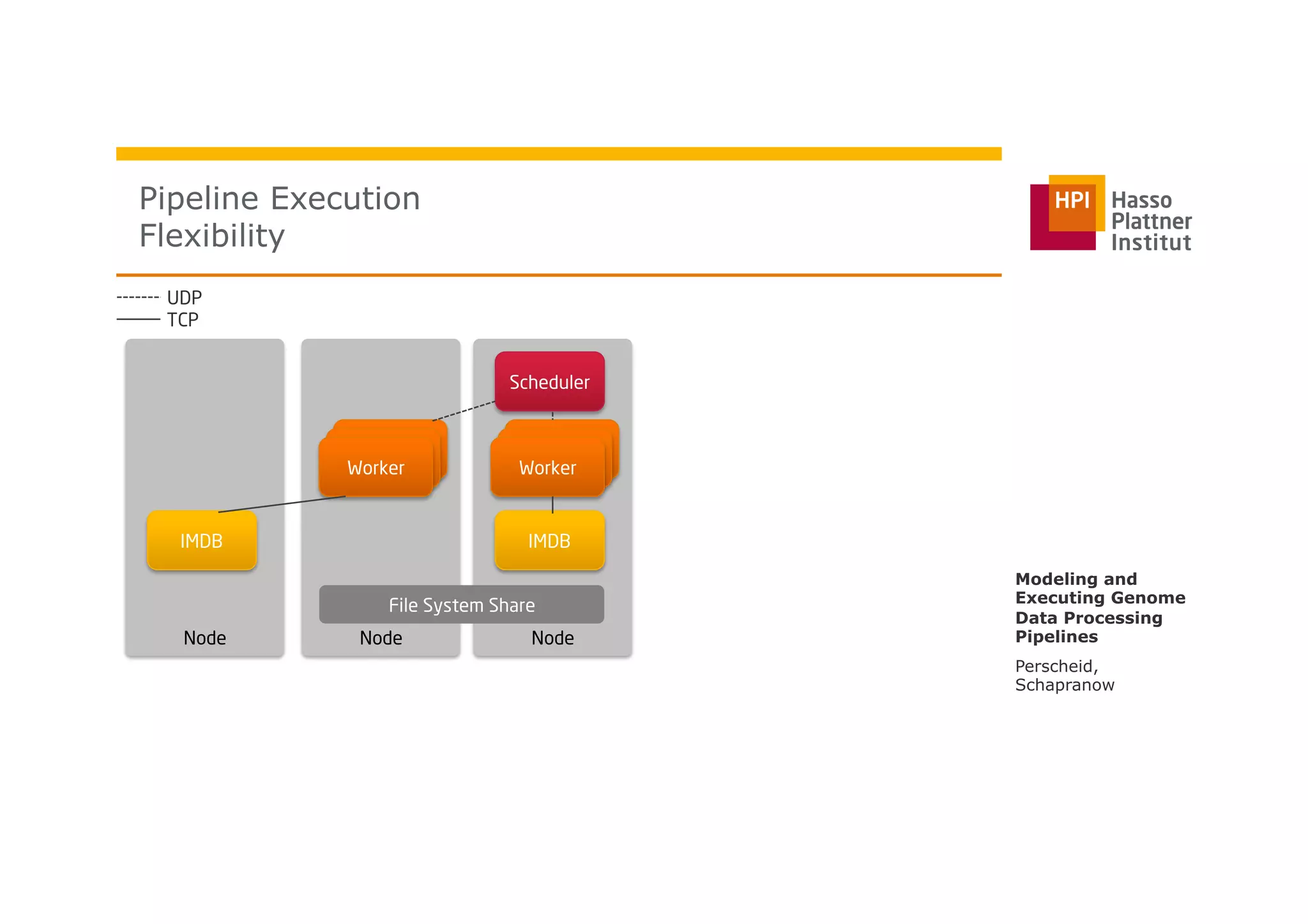
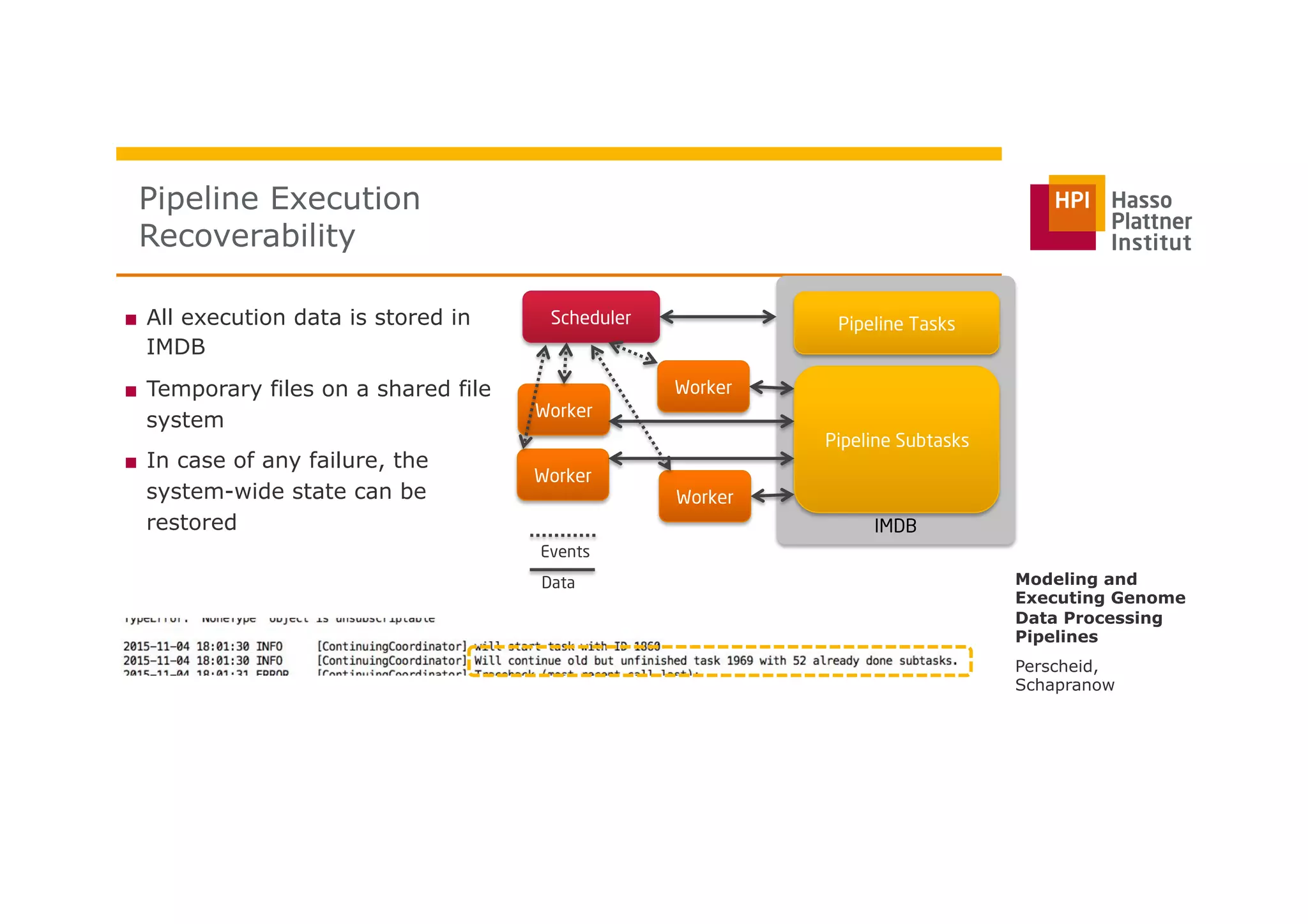
The document discusses a framework for modeling and executing genome data processing pipelines, focusing on real-time analysis of genomic data and the challenges of integrating large datasets. It emphasizes the necessity of efficient processing and parallelization, illustrating how the framework can optimize execution time by over 50%. Key features include a graphical modeling notation compliant with BPMN 2.0, a robust worker framework for task execution, and advanced scheduling algorithms for efficient resource allocation.