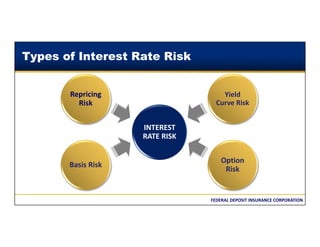
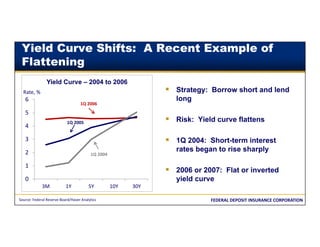
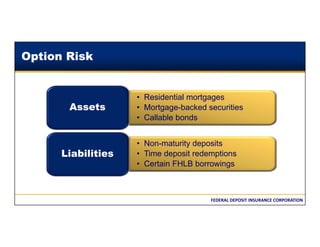
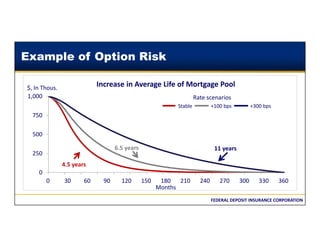
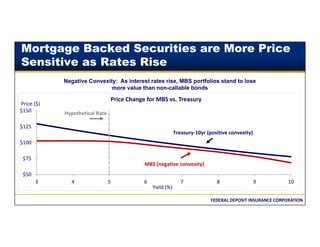
This document discusses the different types of interest rate risk that financial institutions face: repricing risk, which is the risk from timing differences in rate changes of assets and liabilities; yield curve risk, which is the risk of non-parallel shifts in the yield curve; option risk, which includes the risk of changes in cash flows due to embedded options like prepayments; and basis risk, which is the risk that different indices do not move together. It provides examples and definitions for each type of interest rate risk. Effective management of these various risks is important for financial institutions.