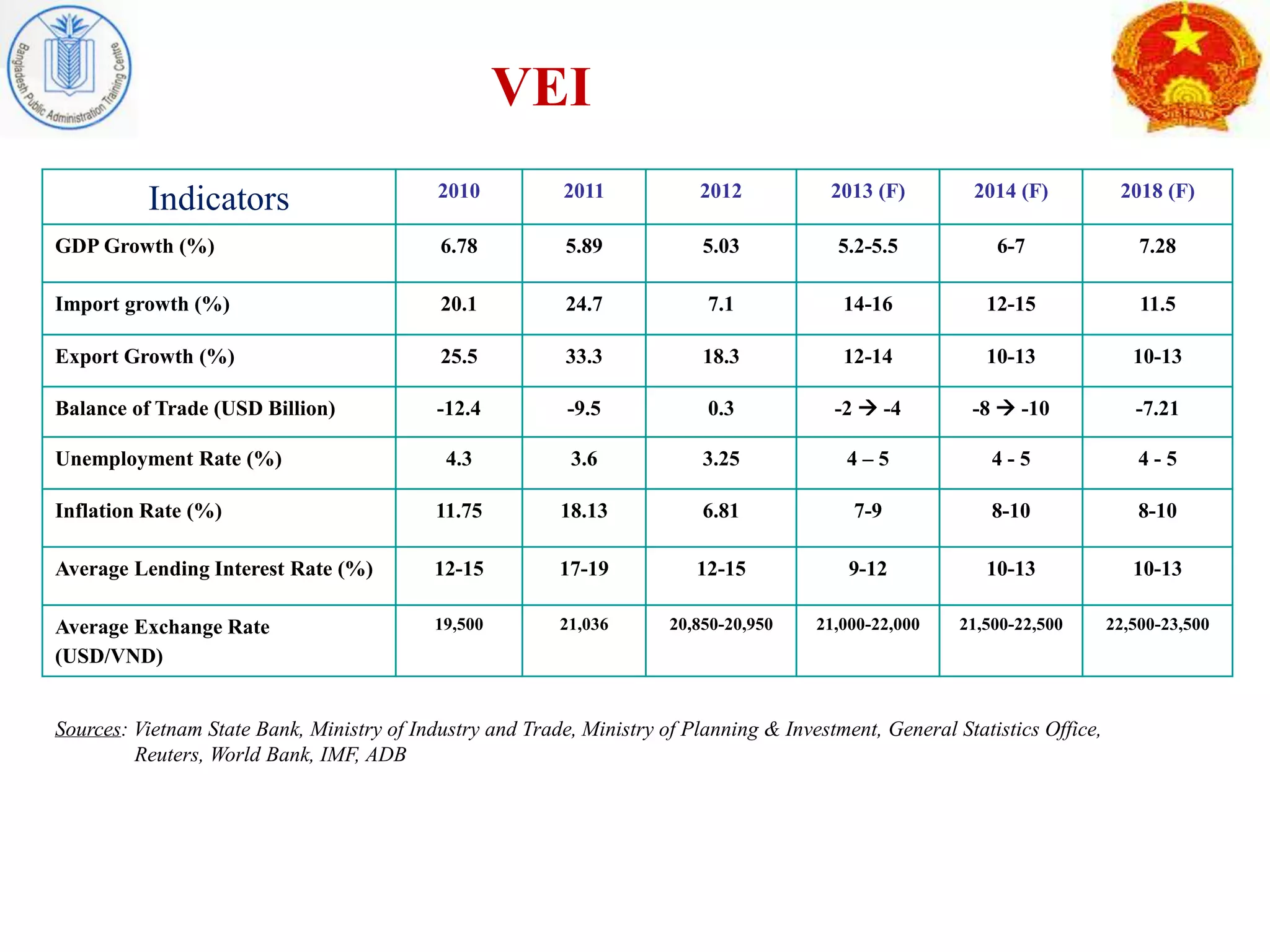
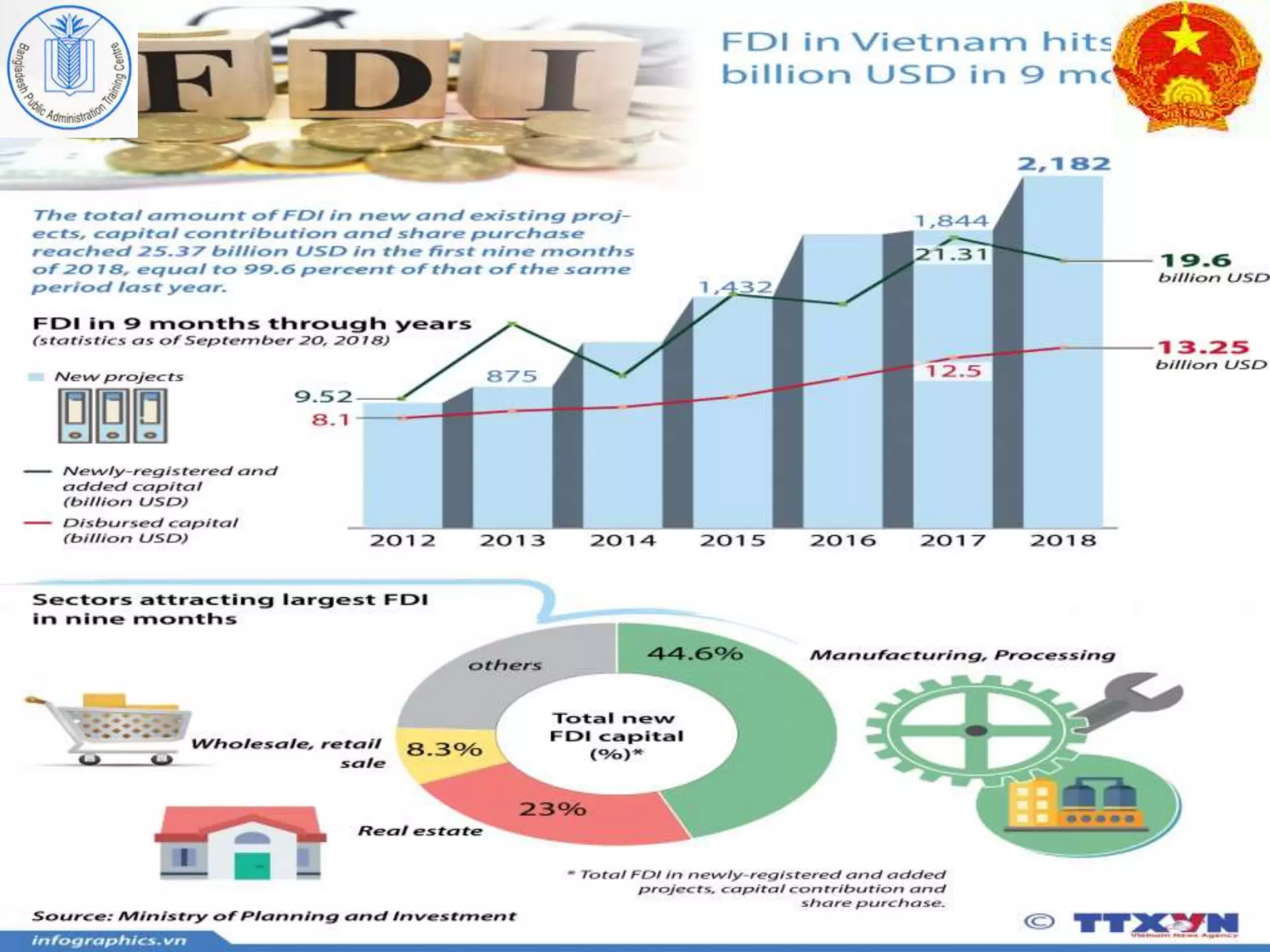
After adopting economic reforms in the 1980s, Vietnam pursued foreign direct investment (FDI) to support its transition to a market economy. It passed laws in 1987 and 1990 to liberalize FDI inflows and establish special economic zones. These policies were successful in attracting substantial FDI, which contributed significantly to Vietnam's rapid economic growth and integration into the global economy by providing capital, technology, skills, and management expertise. However, Vietnam still faces challenges like corruption and environmental issues to further improve its business environment and ensure sustainable development. Learning from Vietnam's pro-market reforms, policy coordination between government and citizens, and steady approach to development could help Bangladesh achieve its own development goals.