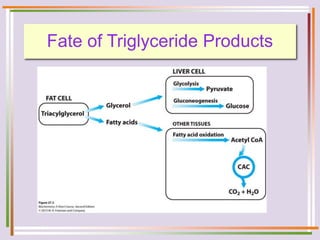
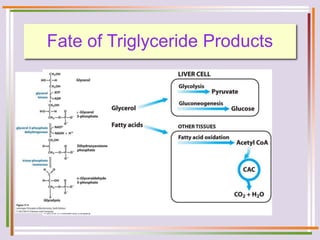
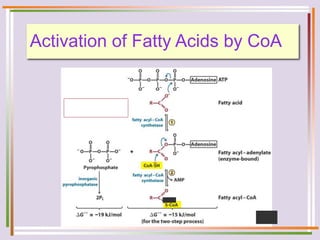
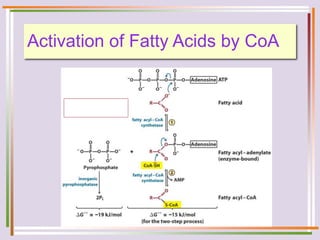
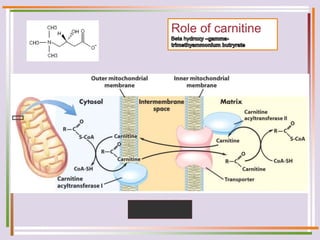
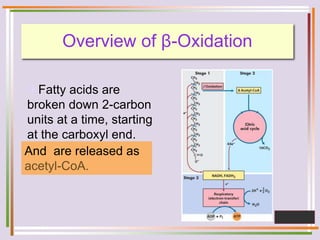
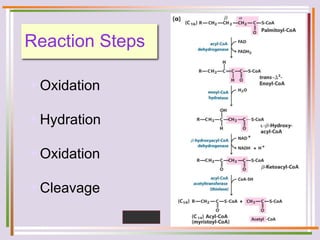
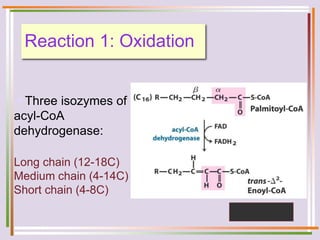
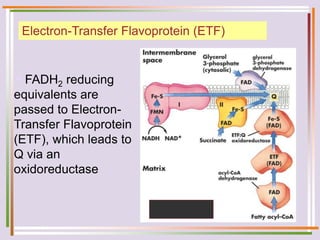
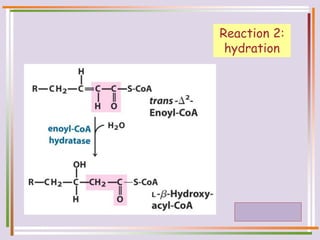
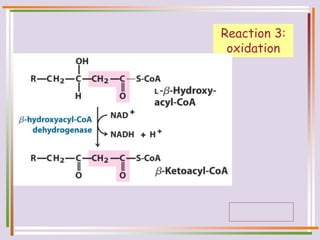
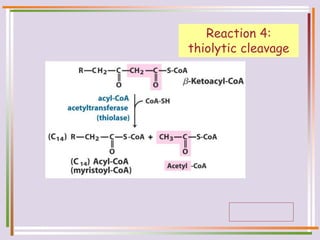
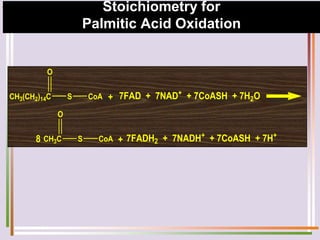
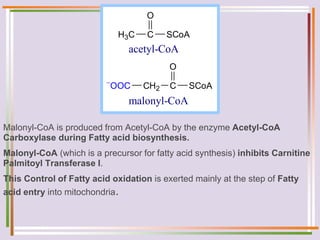
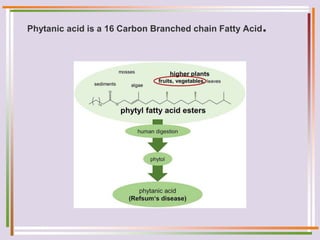
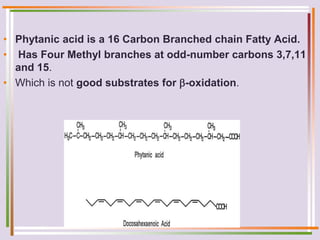
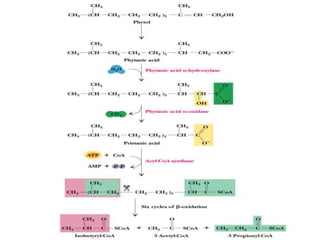
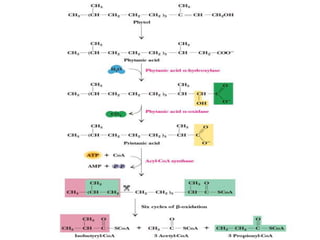
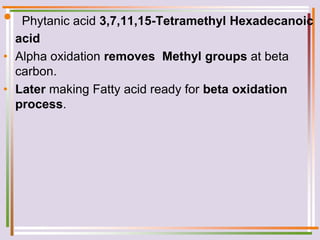
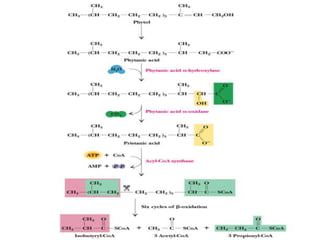
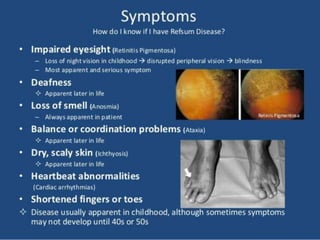
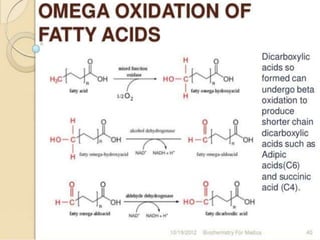
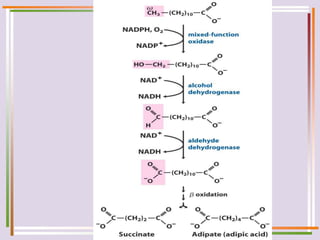
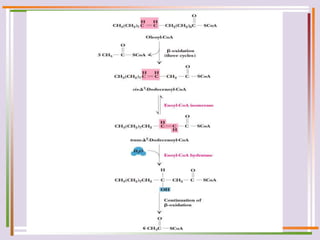
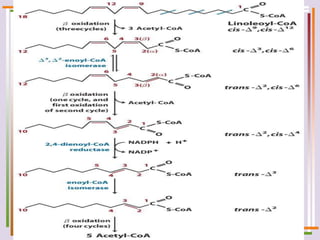
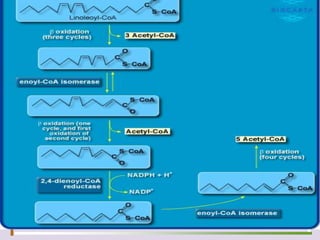
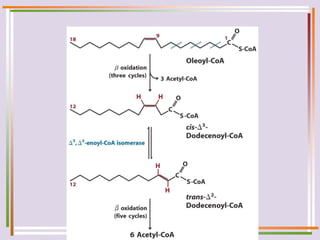
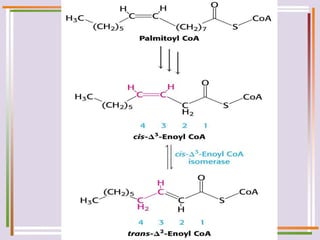
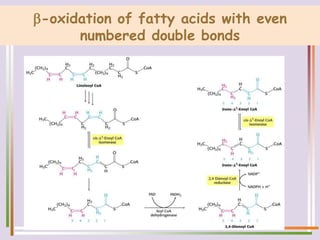
The document discusses fatty acid oxidation, including the pathways of beta oxidation and alpha oxidation. Beta oxidation occurs in the mitochondria and involves activating fatty acids with CoA, transport into the mitochondrial matrix via carnitine shuttle, and breaking the fatty acid down into two-carbon units through four reactions: oxidation, hydration, oxidation, and thiolytic cleavage. The products are acetyl-CoA which enter the TCA cycle. Alpha oxidation occurs with branched fatty acids like phytanic acid in peroxisomes or ER and removes methyl branches to allow beta oxidation. Defects can cause diseases like Refsum's disease.