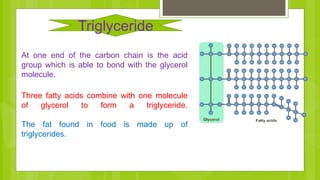
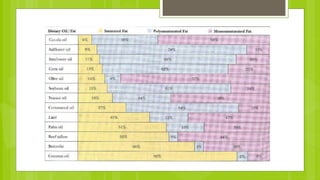
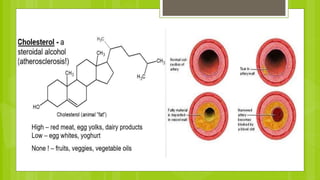
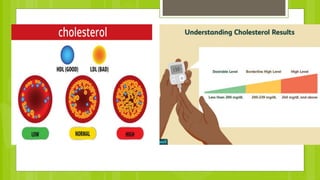
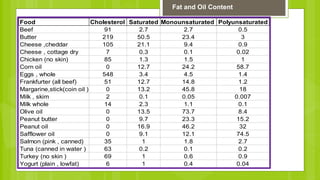
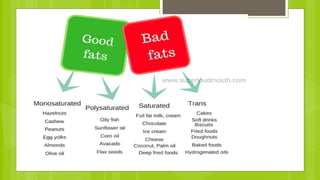
The document discusses different types of dietary fats, including saturated, trans, monounsaturated, and polyunsaturated fats. It notes that saturated and trans fats tend to be solid at room temperature while monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats tend to be liquid. The document provides examples of foods that are high in different types of fats and notes the health impacts of consuming too much saturated and trans fats, which can raise LDL cholesterol and risk of heart disease. It recommends limiting saturated fat intake and choosing sources of monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats like olive oil instead of hydrogenated oils.