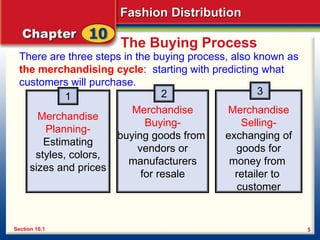
1. Fashion buyers are responsible for purchasing merchandise from vendors for stores. They must predict consumer demand six months to a year in advance based on sales records, vendor information, and fashion trends. Inaccurate predictions can lead retailers like Walmart and Goodys to have unsold inventory.
2. The three steps in the buying process, or merchandising cycle, are merchandise planning, merchandise buying, and merchandise selling. Planning involves estimating styles, colors, sizes and prices based on past sales and vendor advice.
3. Retailers include department stores like Macy's, specialty stores like PacSun that target specific groups, boutiques with limited trendy items, designer stores that are vertically integrated, outlets