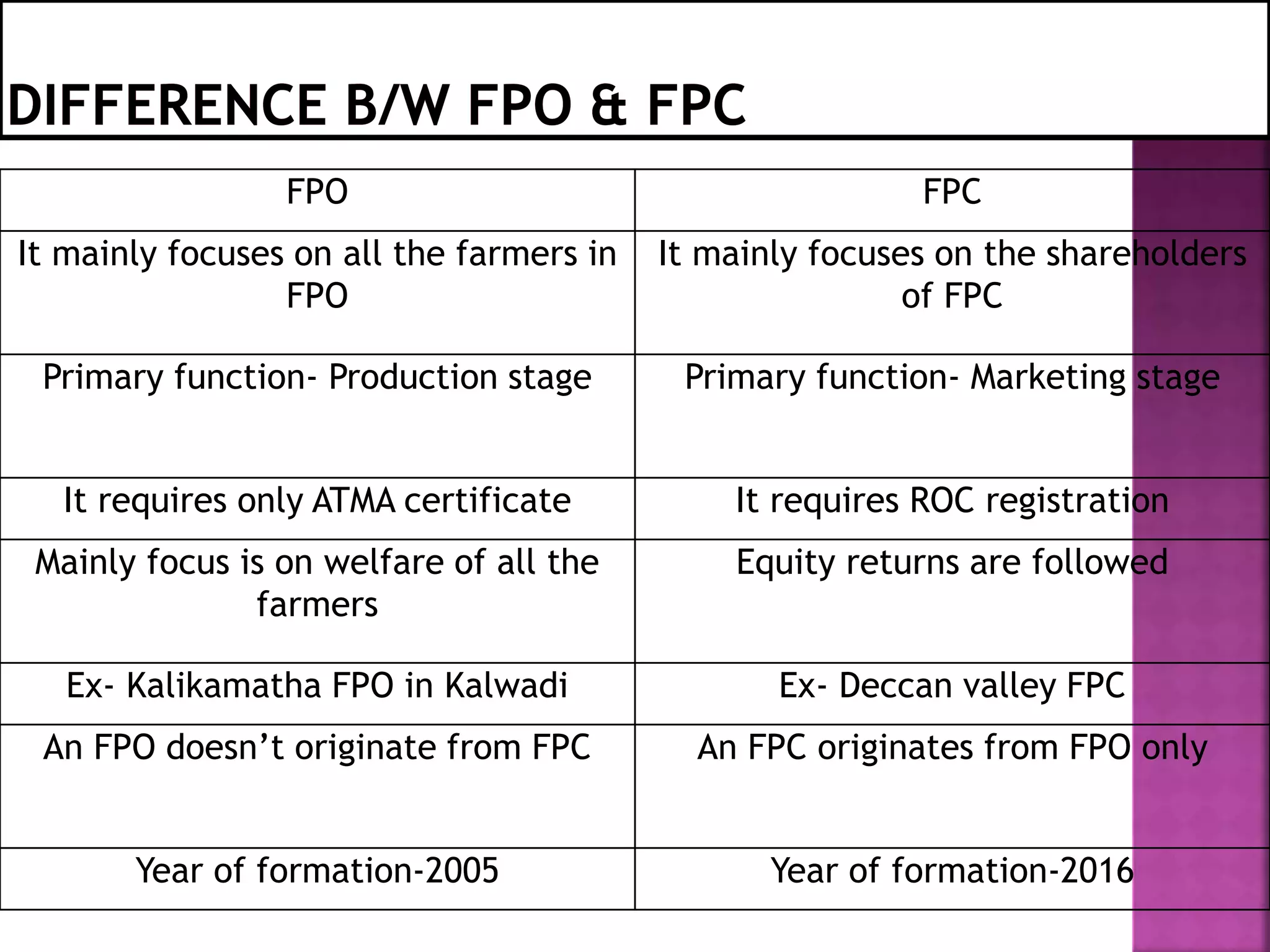
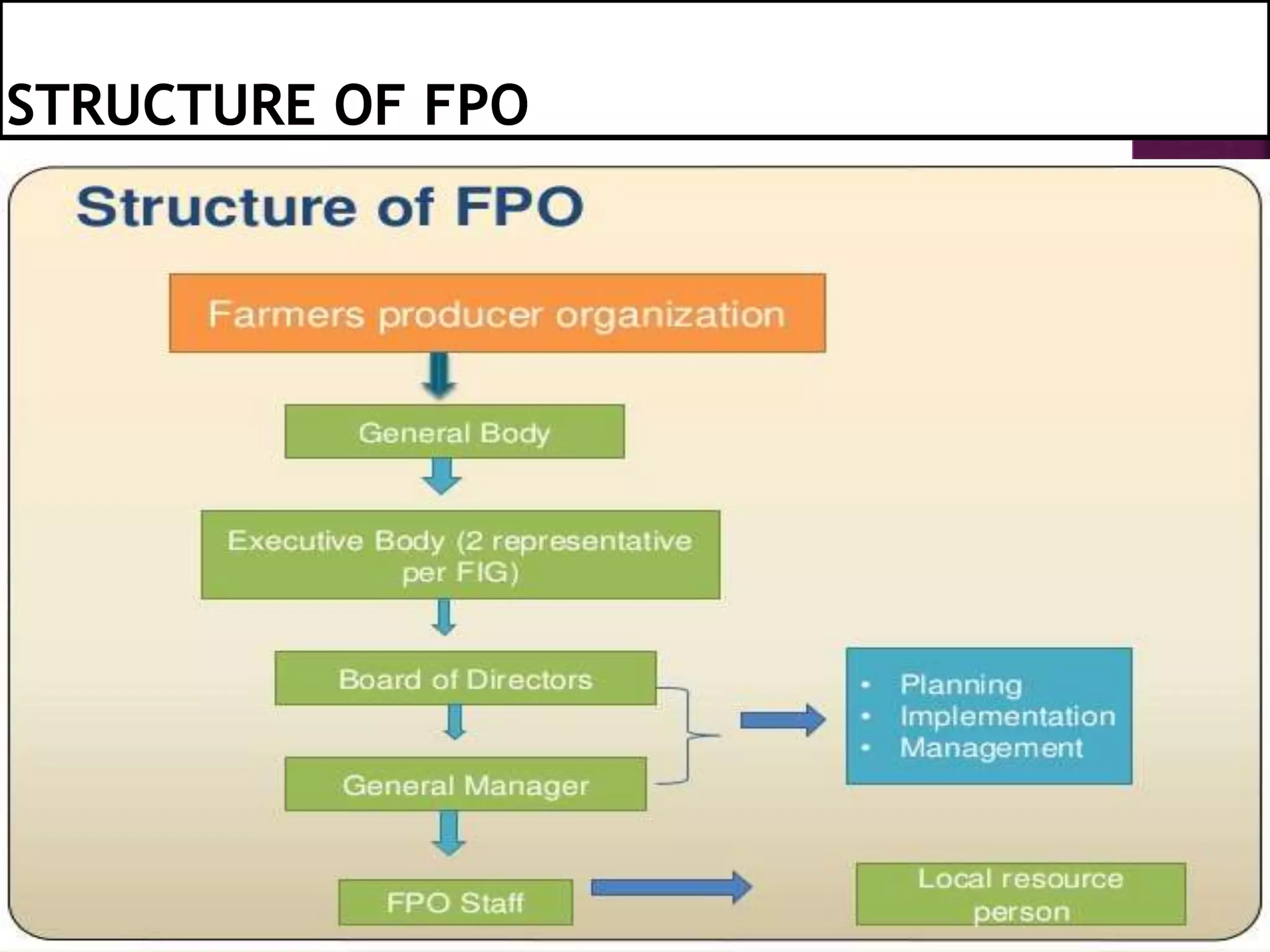
This document discusses farmer producer organizations (FPOs). It defines an FPO as a farmer group with a formal structure and bylaws to benefit its members. FPOs have a hybrid structure of cooperatives and private companies. They provide production services, insurance, inputs, procurement, packaging, marketing, financing, and technical services to farmers. FPOs give farmers better prices, access to markets and technology, and influence over policies. They are supported by organizations like NABARD, SFAC, and NGOs. The conclusion states that FPOs ensure higher incomes for farmers by giving them collective bargaining power and economies of scale.