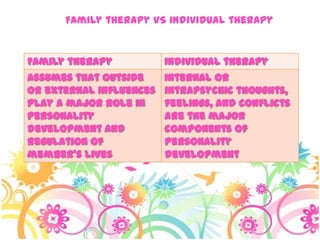
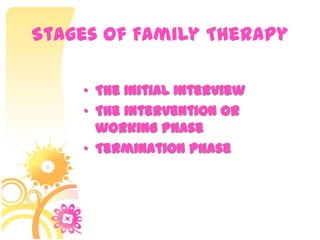
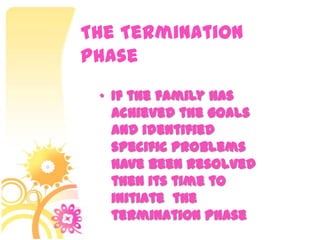
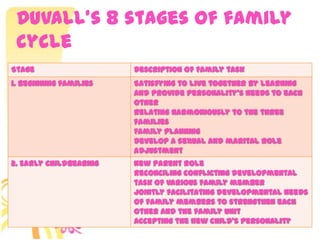
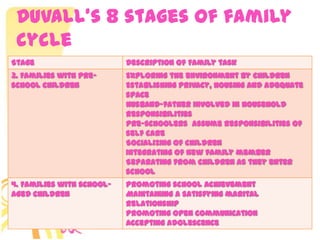
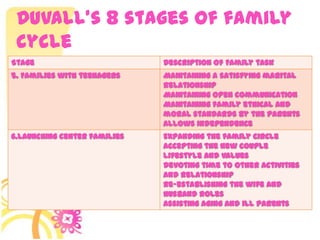
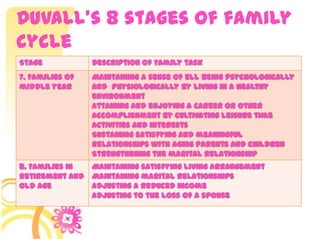
This document discusses family systems theory and approaches to family therapy. It defines the family as a system and discusses how family therapists view problems arising from dysfunctional relationships and interactions within the family system. Several major approaches to family therapy are summarized, including psychoanalytic, structural, strategic, and behavioral. The document also covers stages of the family life cycle, characteristics of healthy vs unhealthy families, types of family therapy interventions, and goals and techniques of the initial, working, and termination phases of family therapy.