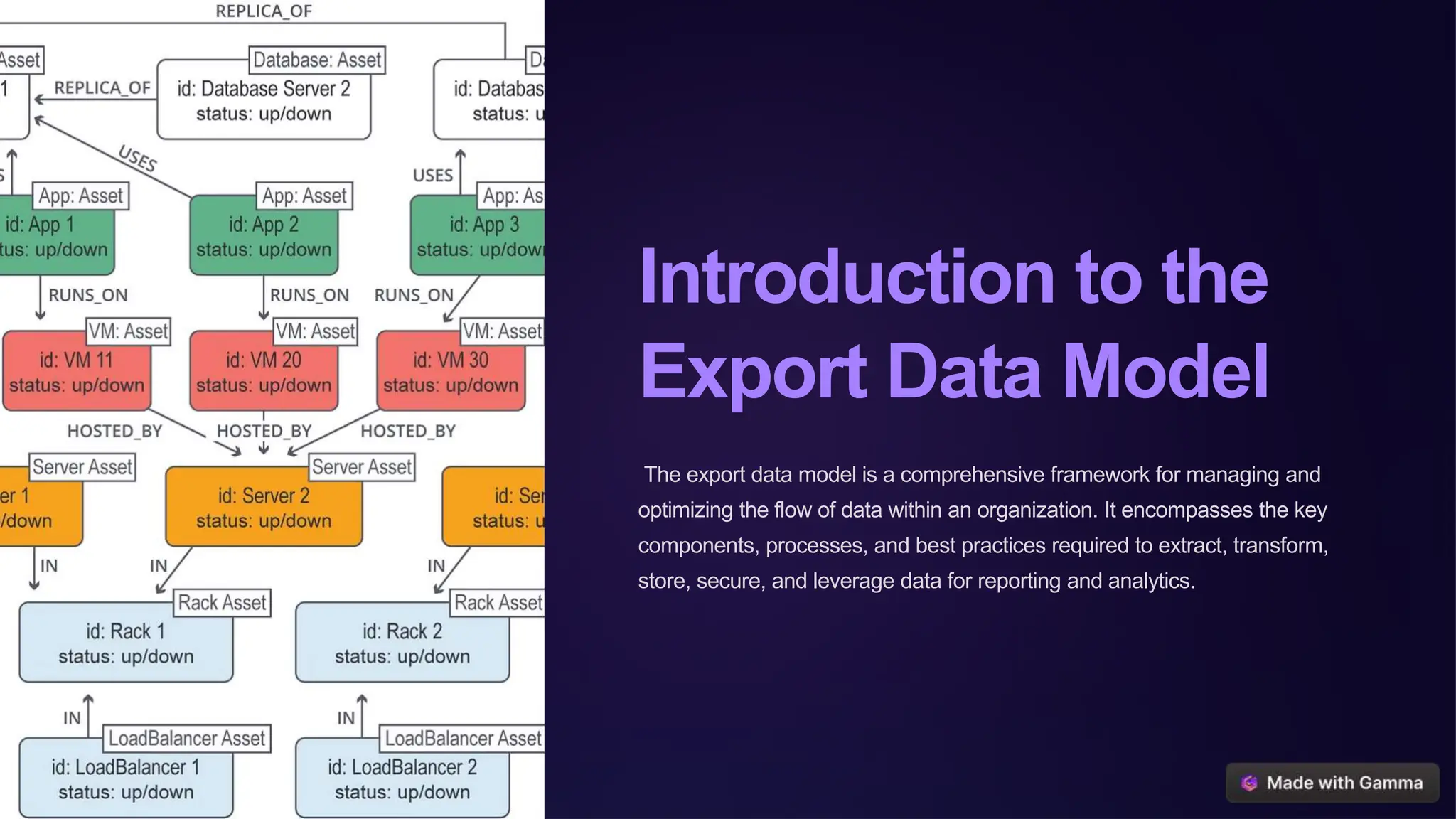
The export data model is a structured framework designed for effective data management within organizations, focusing on data extraction, transformation, storage, and security. It emphasizes integrating diverse data sources, maintaining data quality, and enabling reporting and analytics through various techniques like dashboards and predictive analytics. Implementing this model allows businesses to gain insights, enhance decision-making, and foster growth by evaluating and improving their current data management practices.