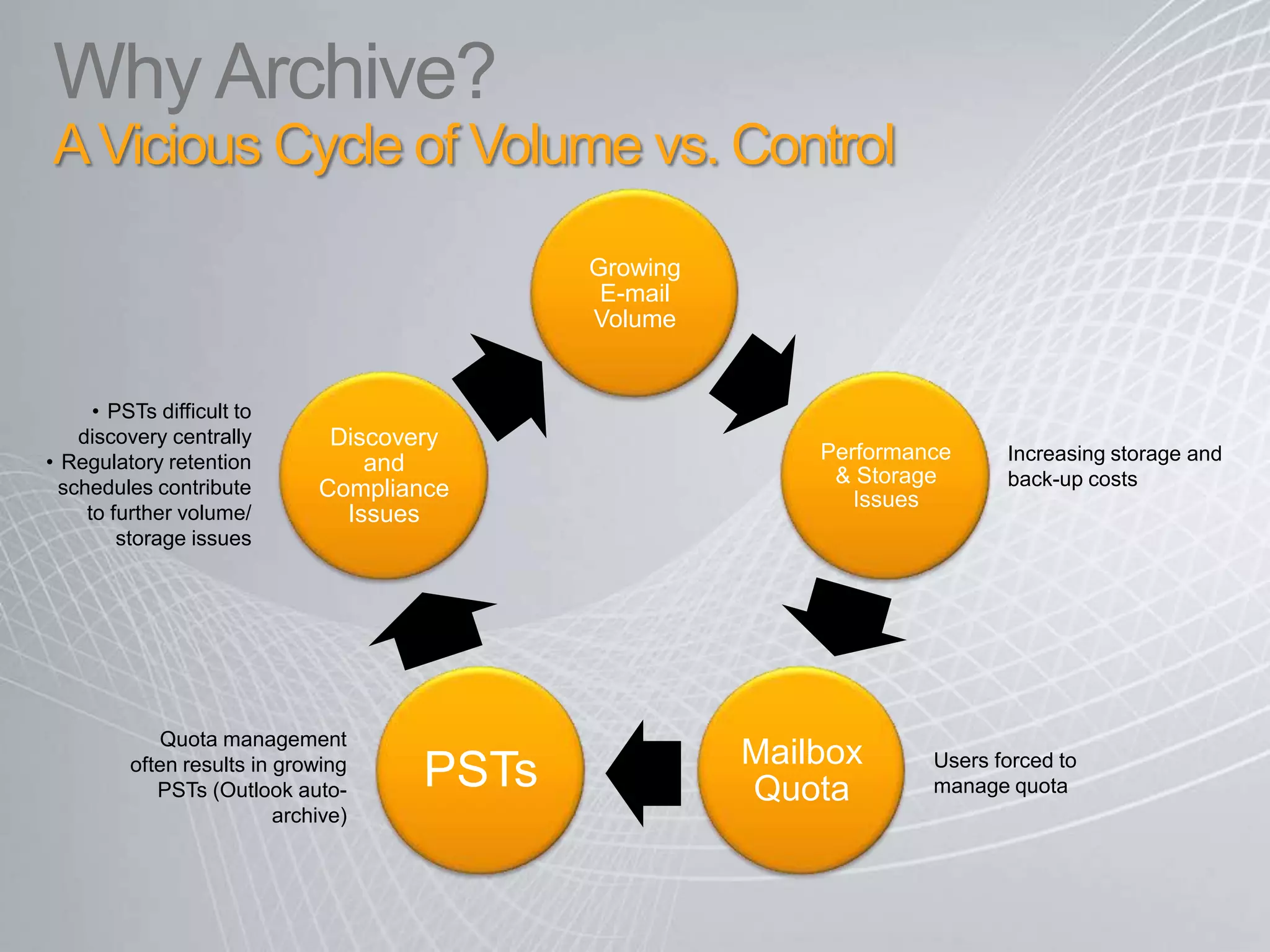
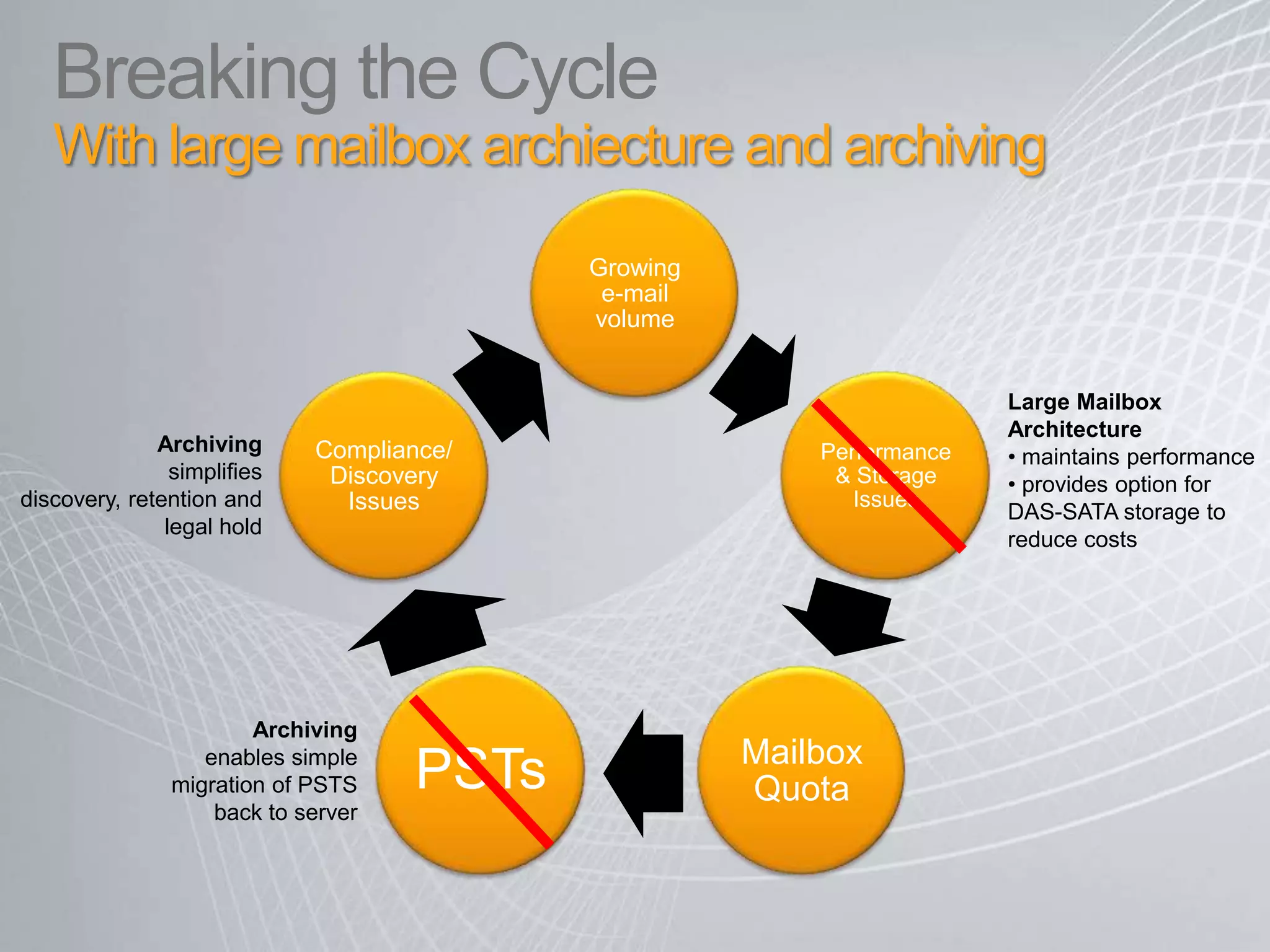
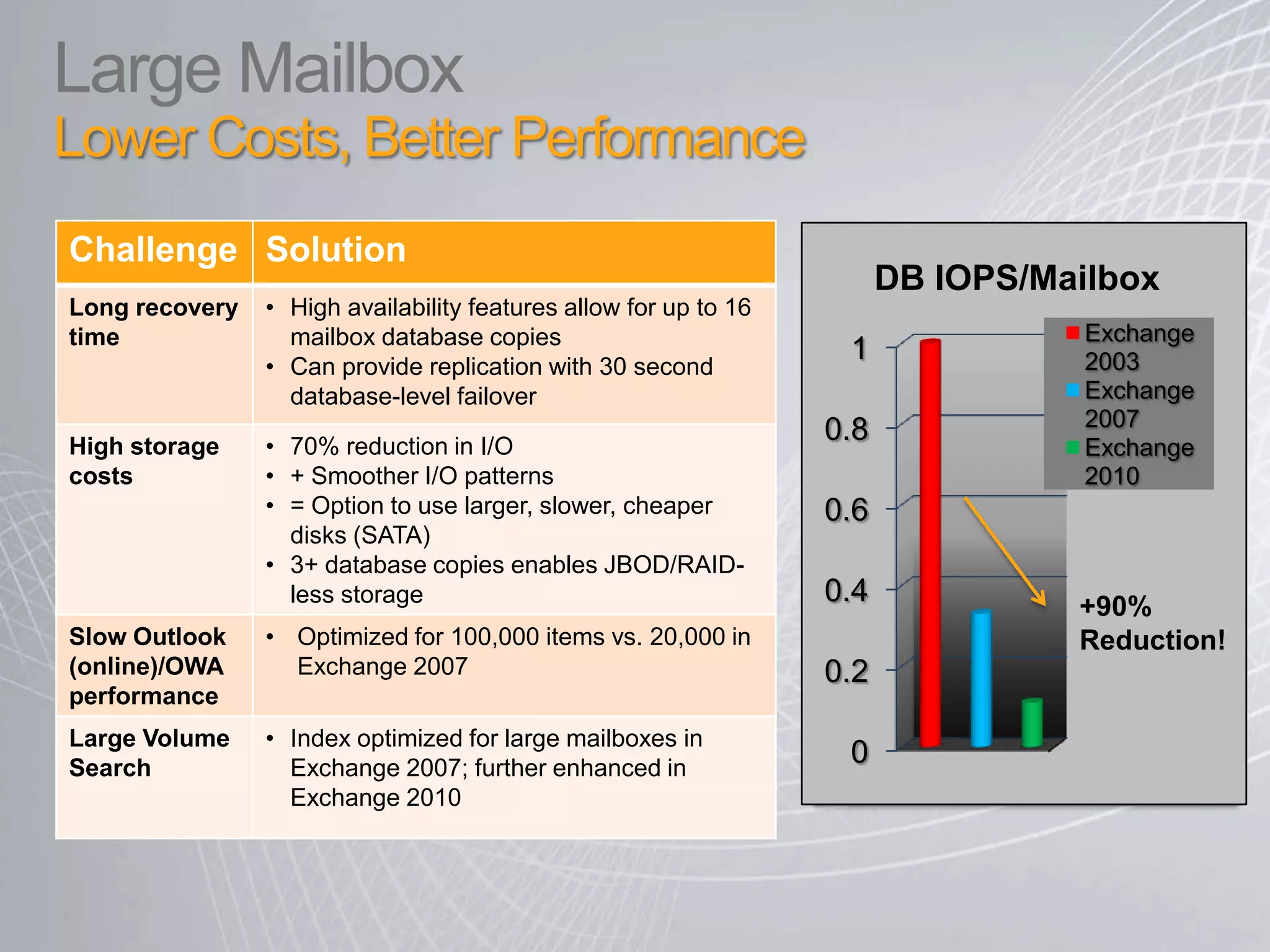
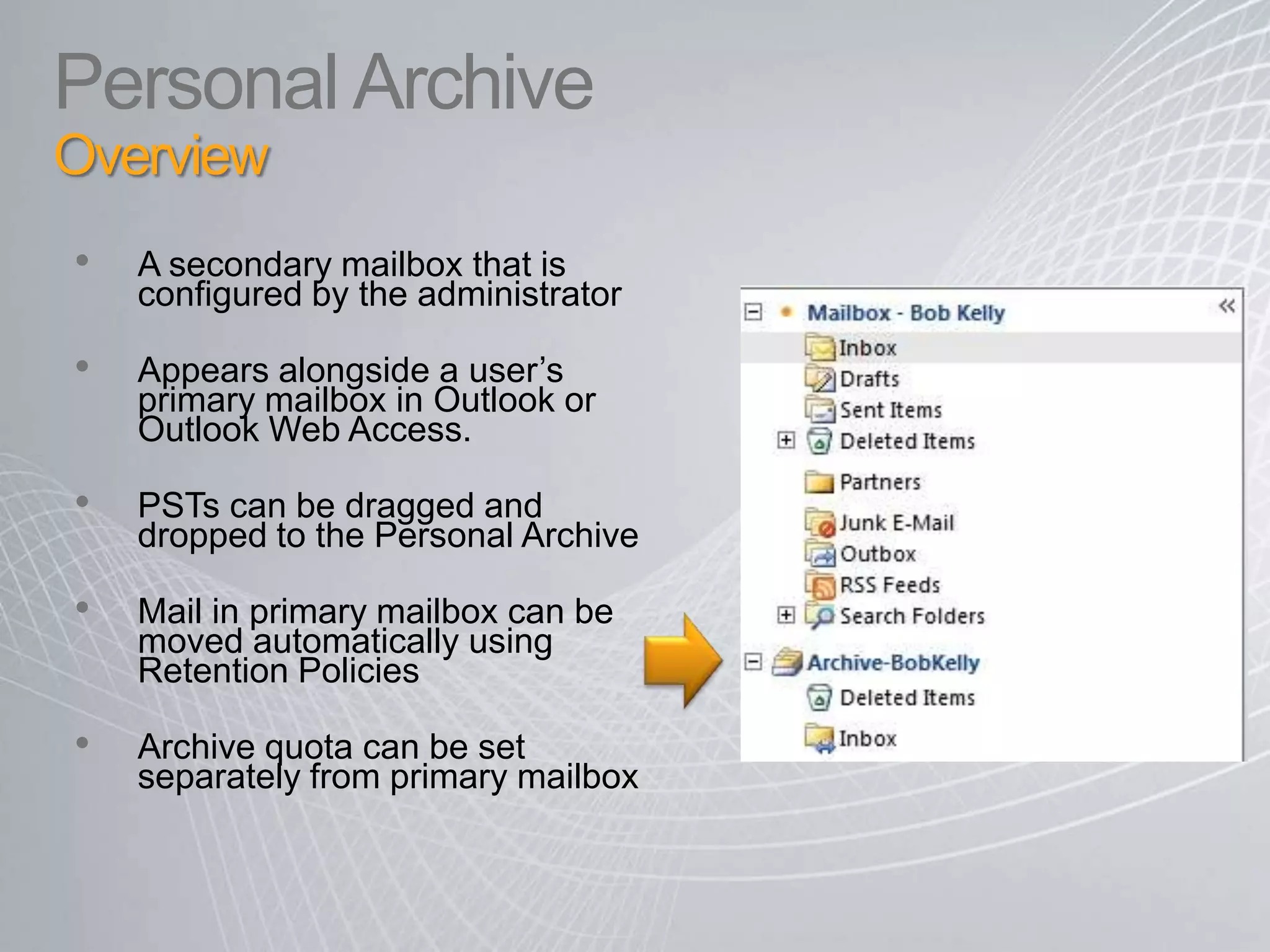
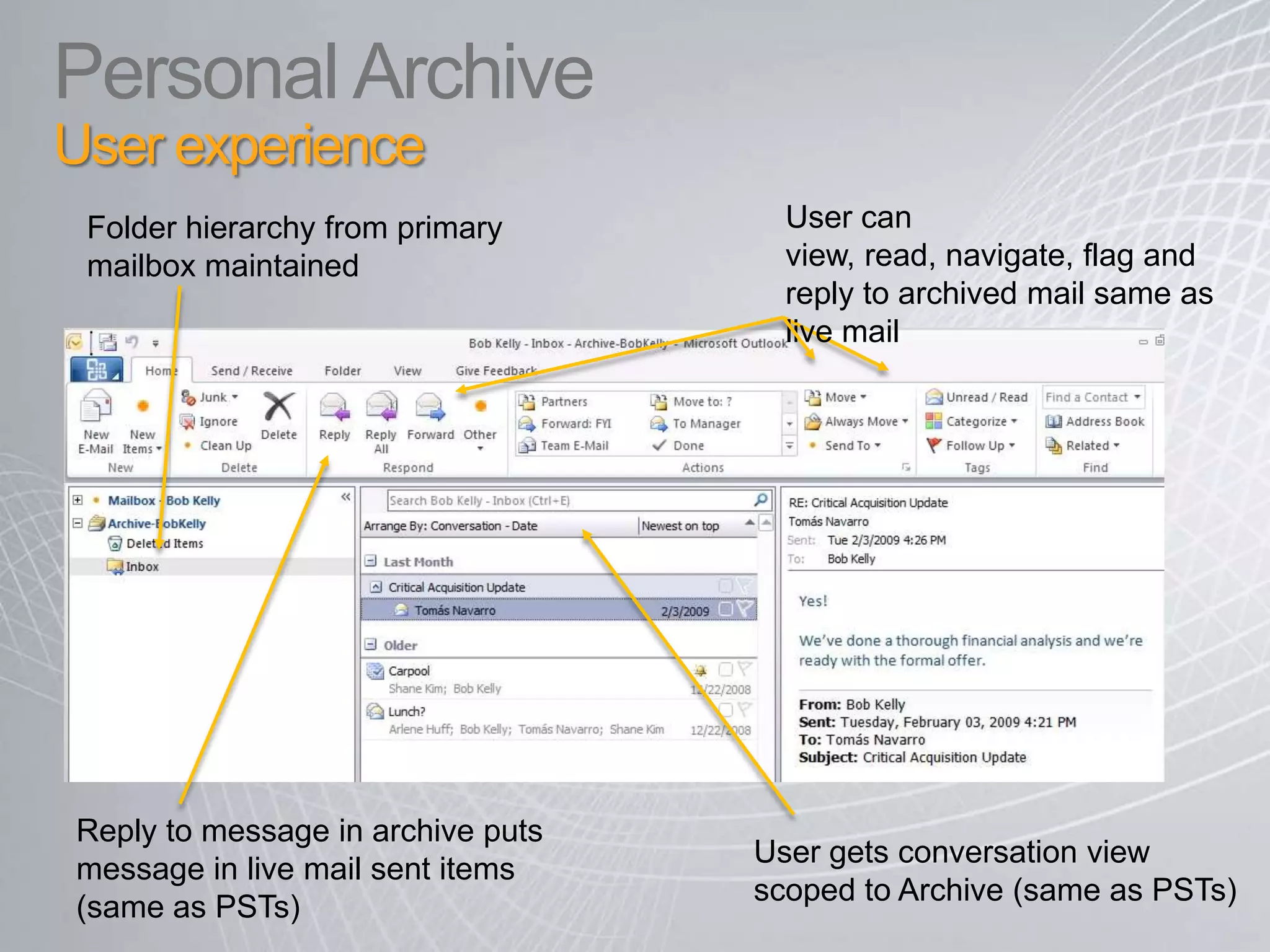
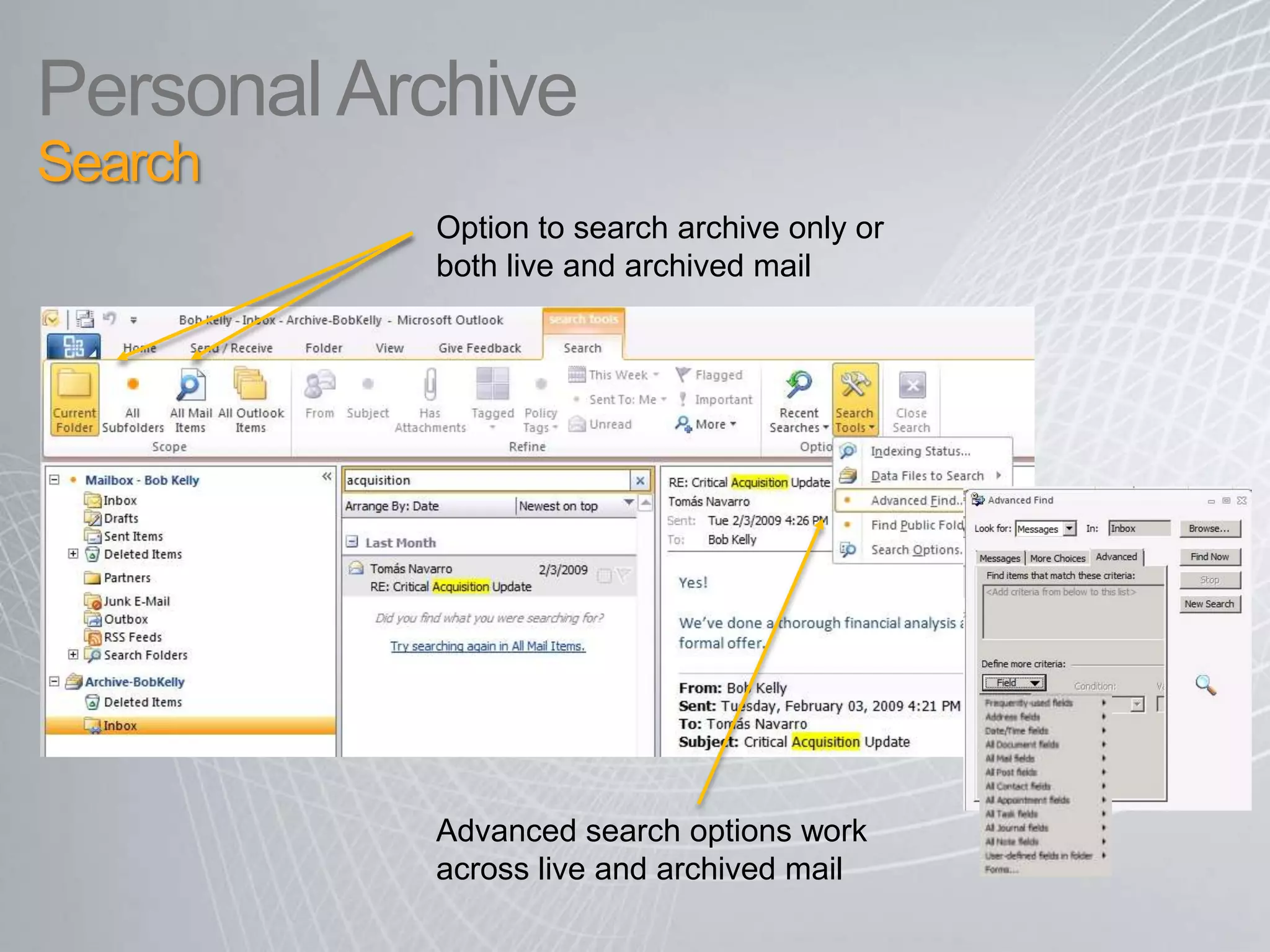
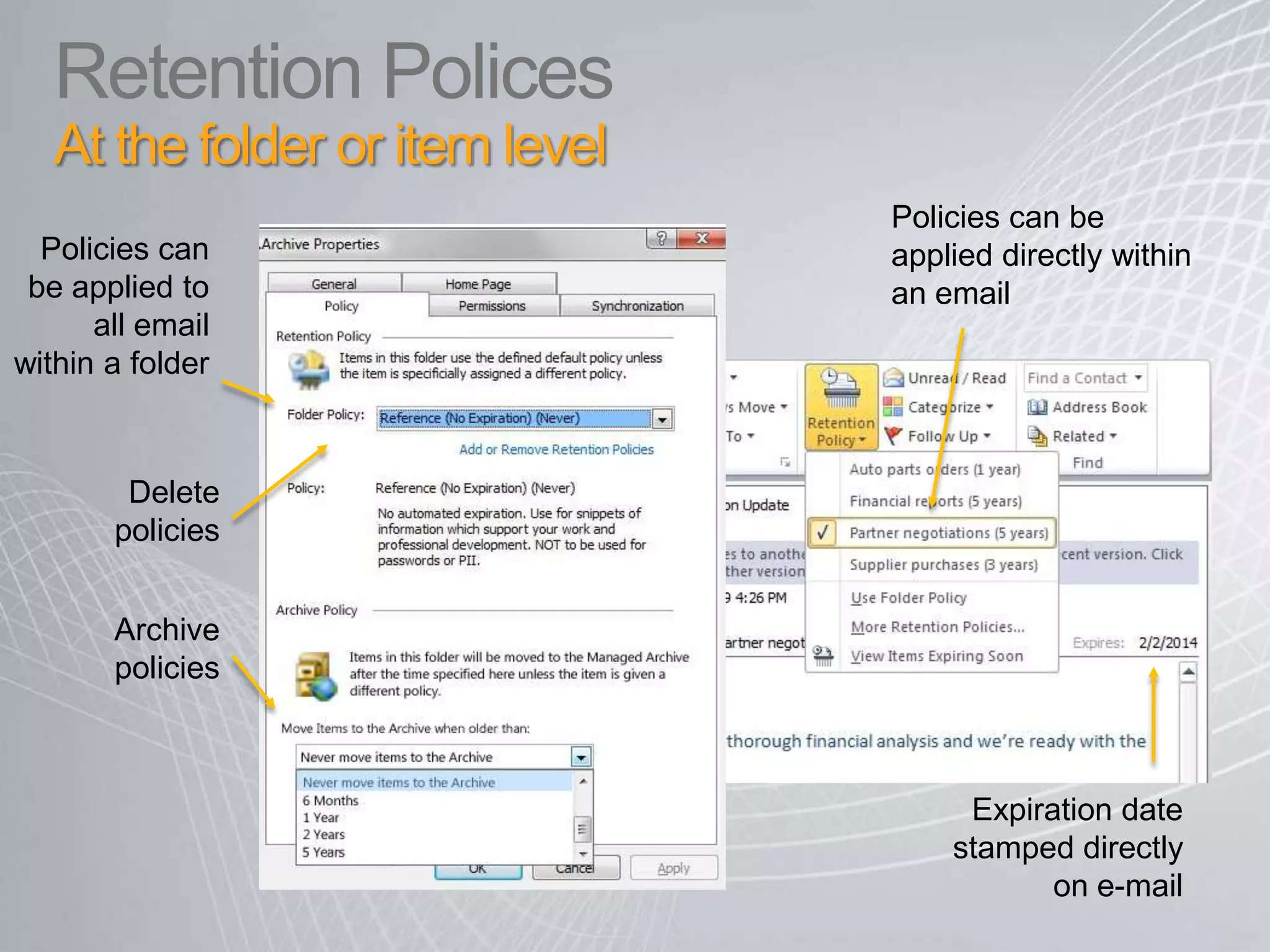
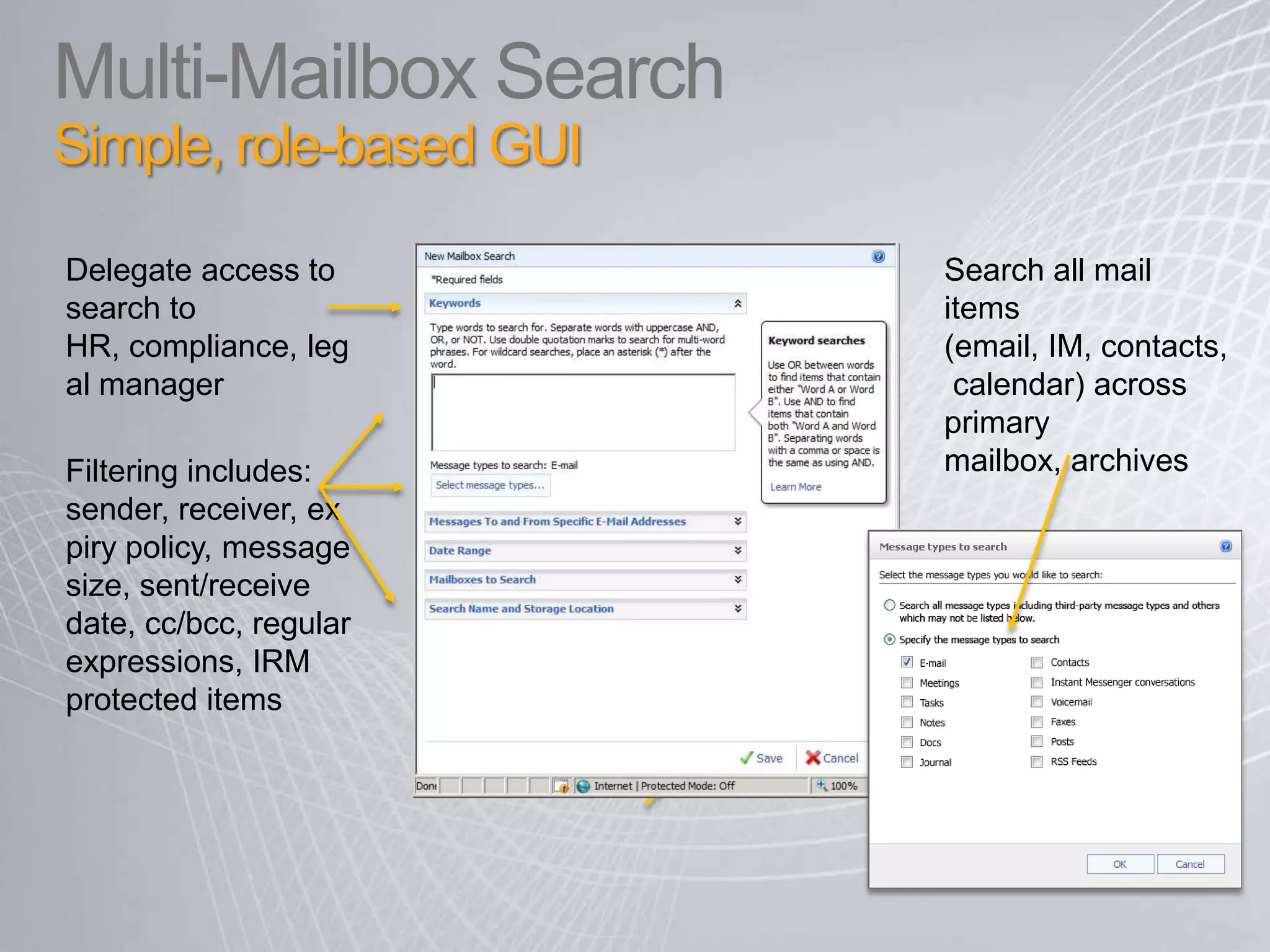
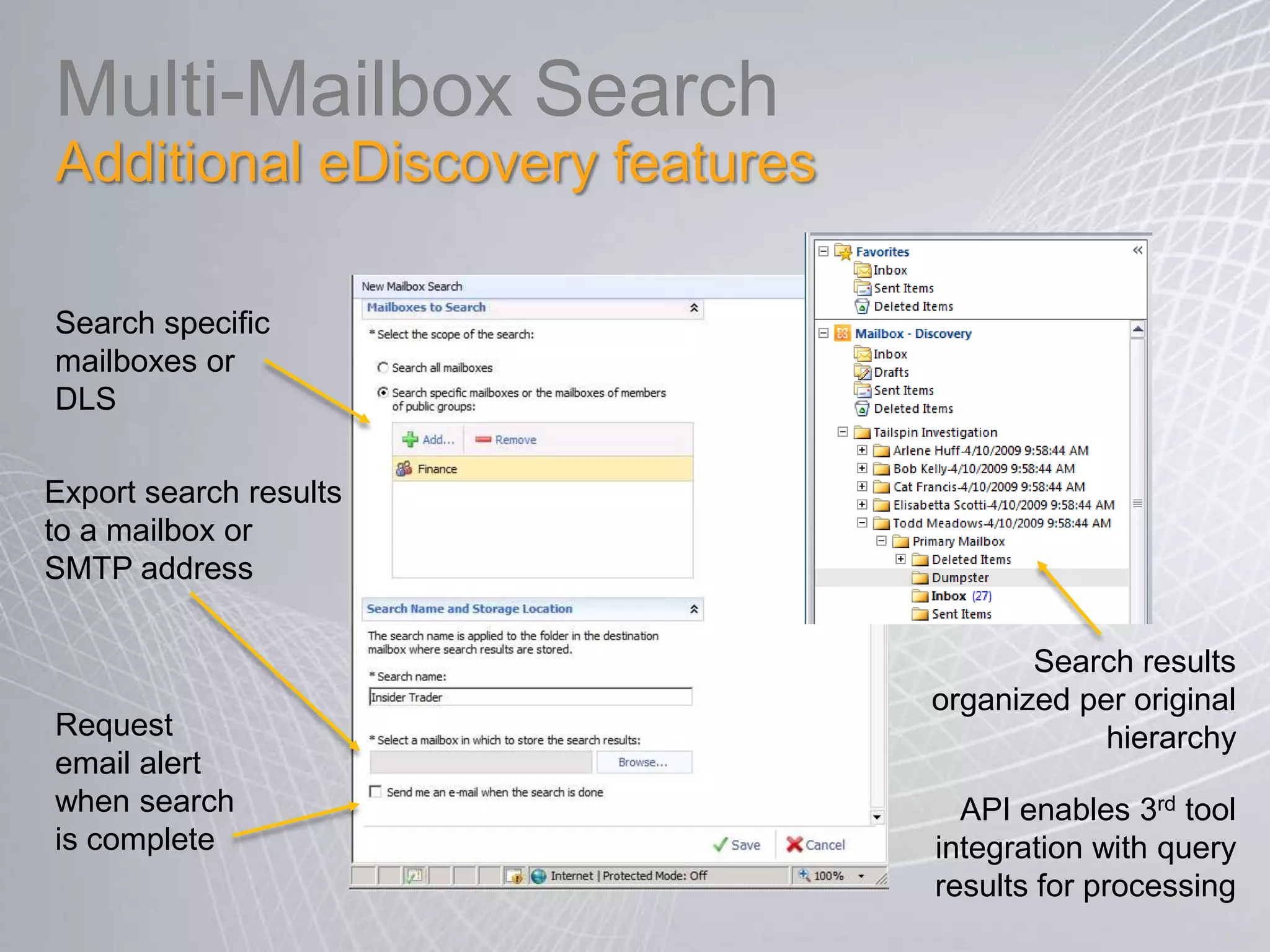
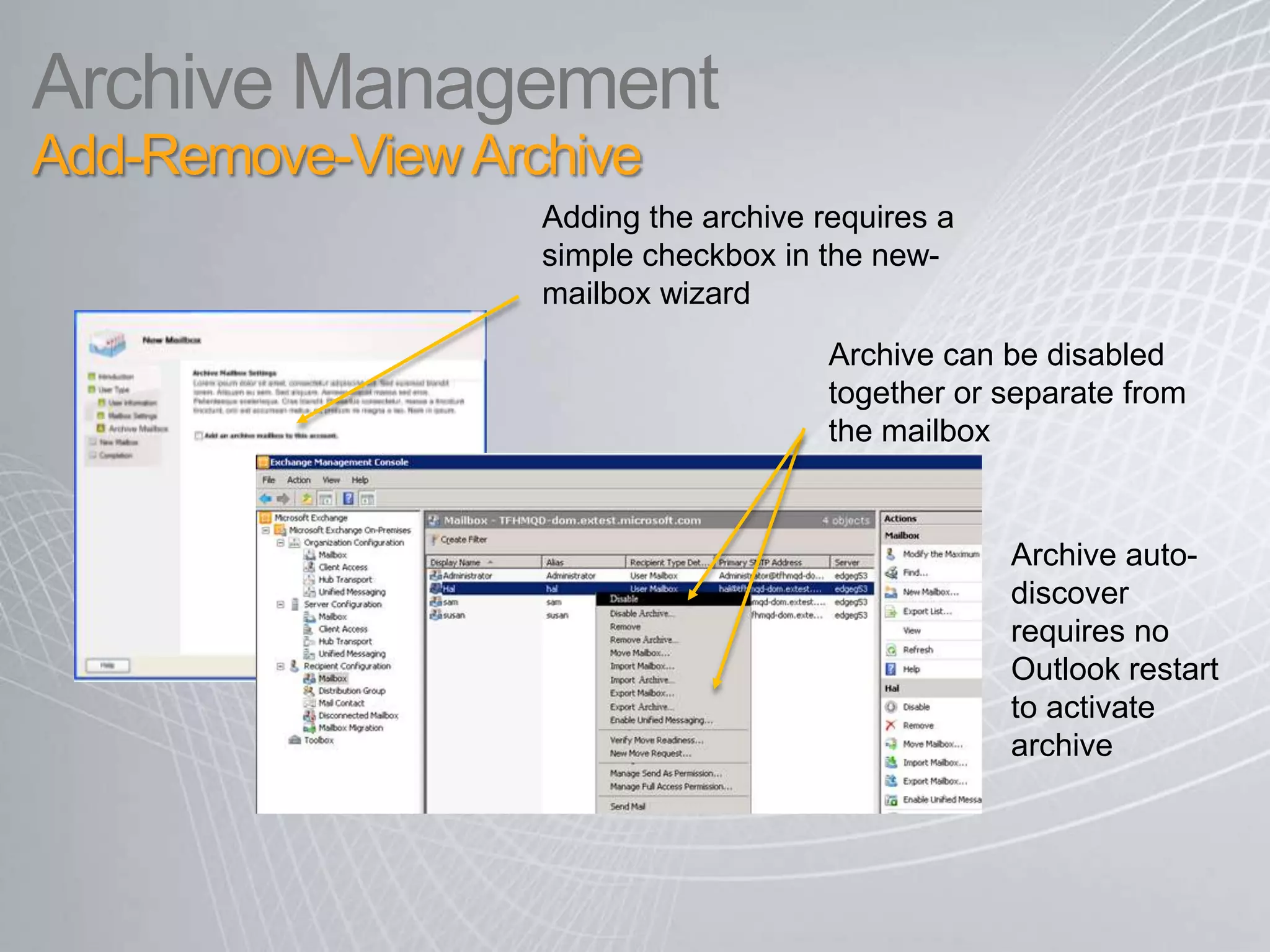
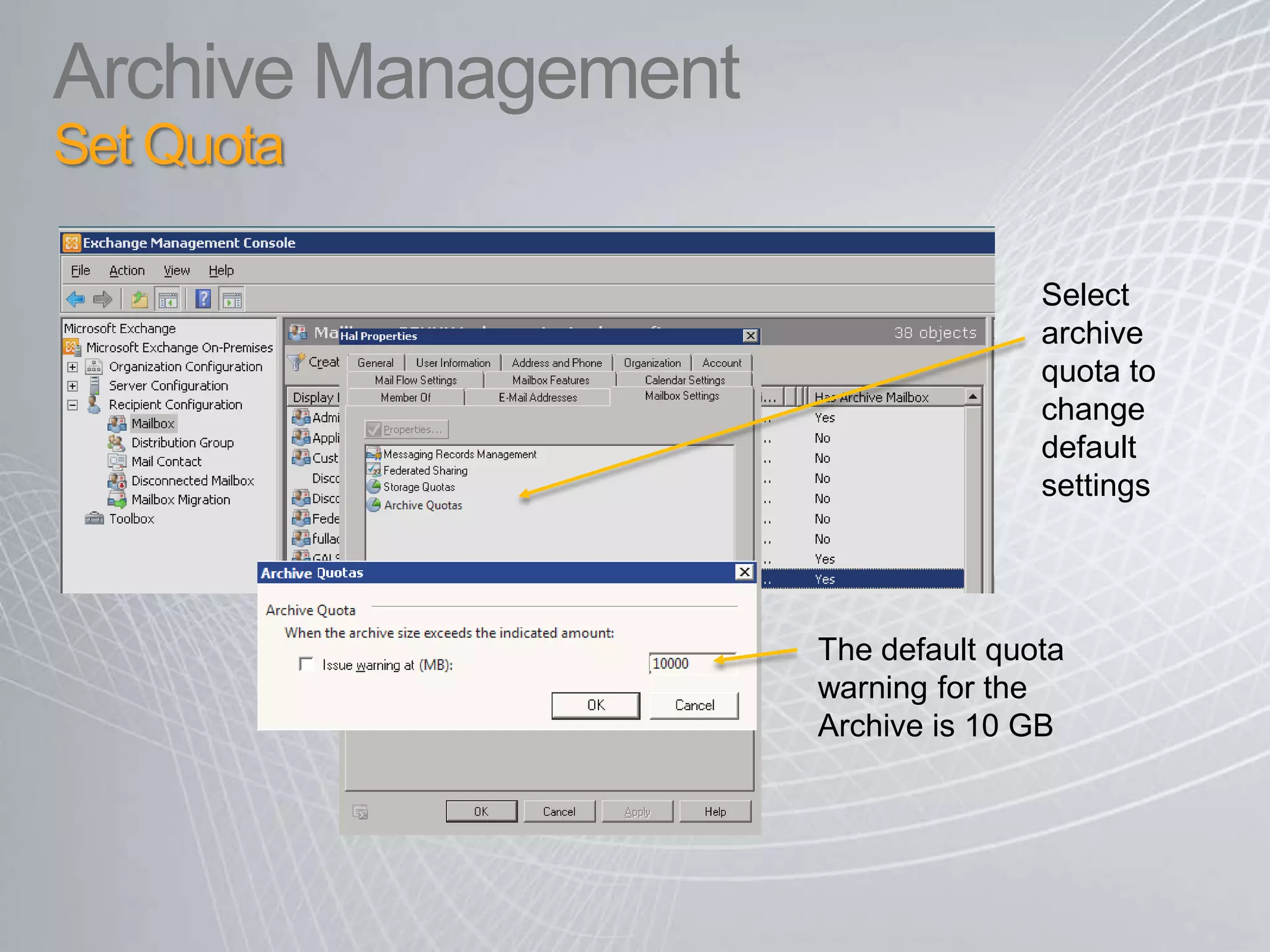
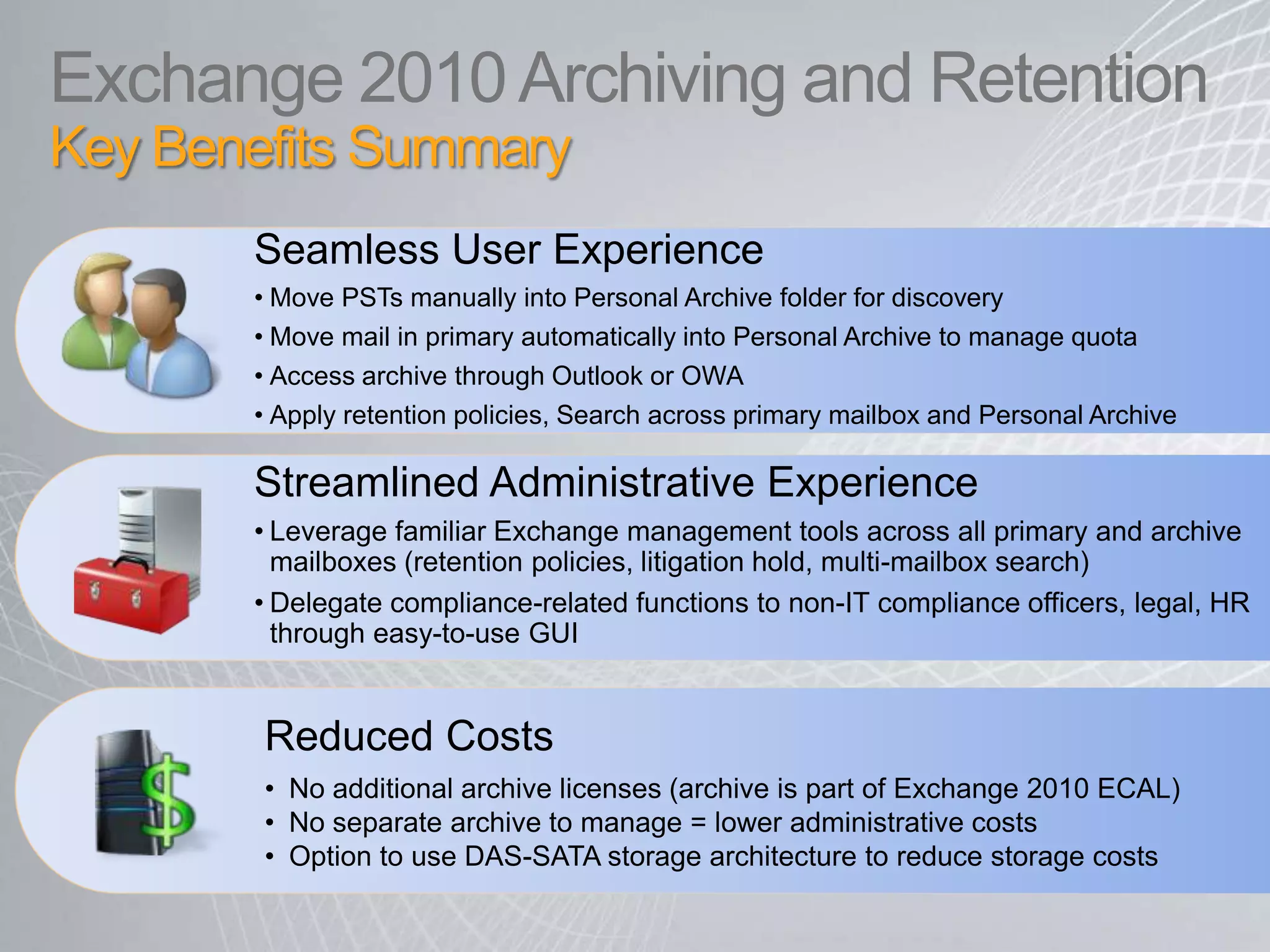
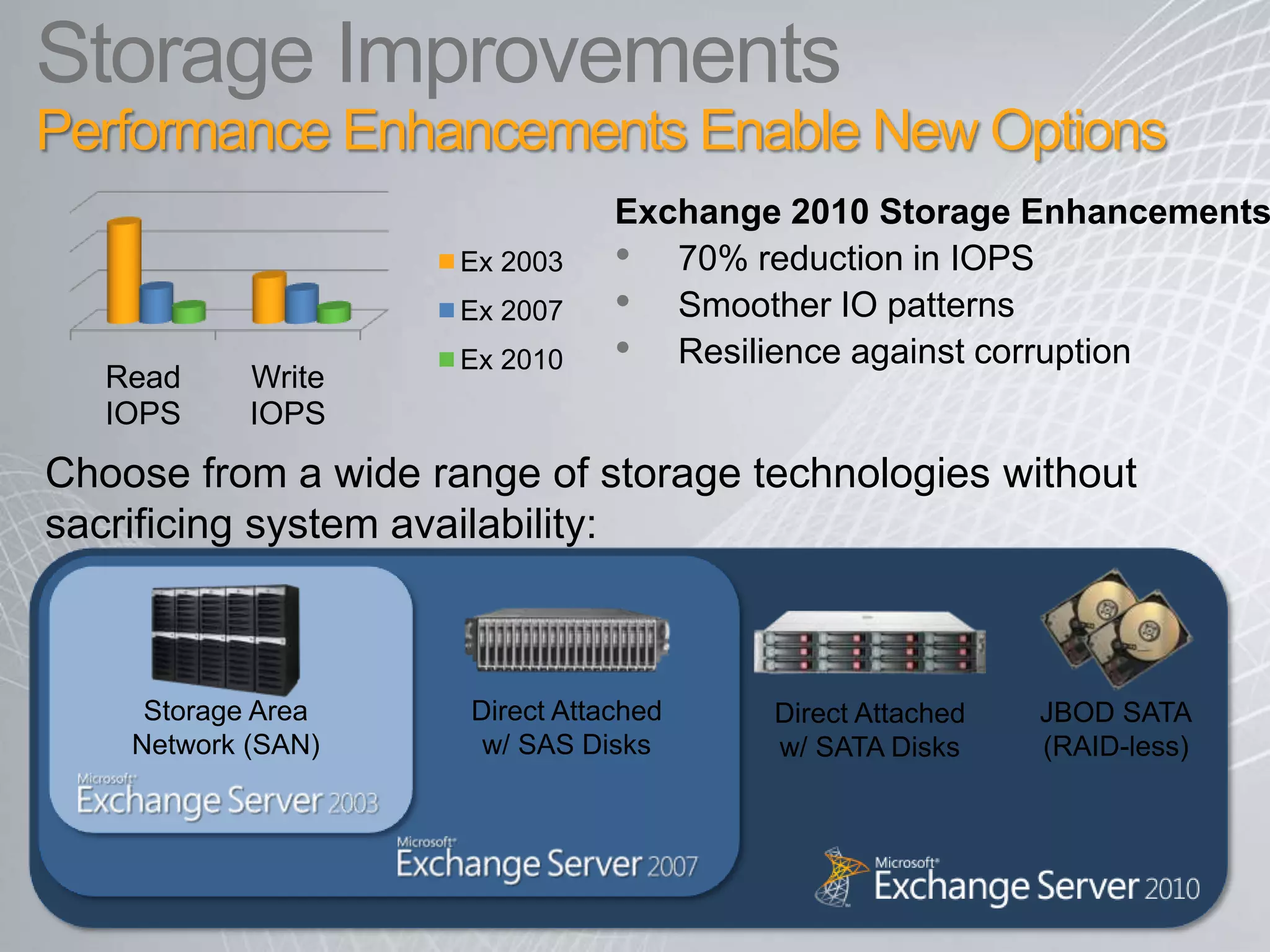
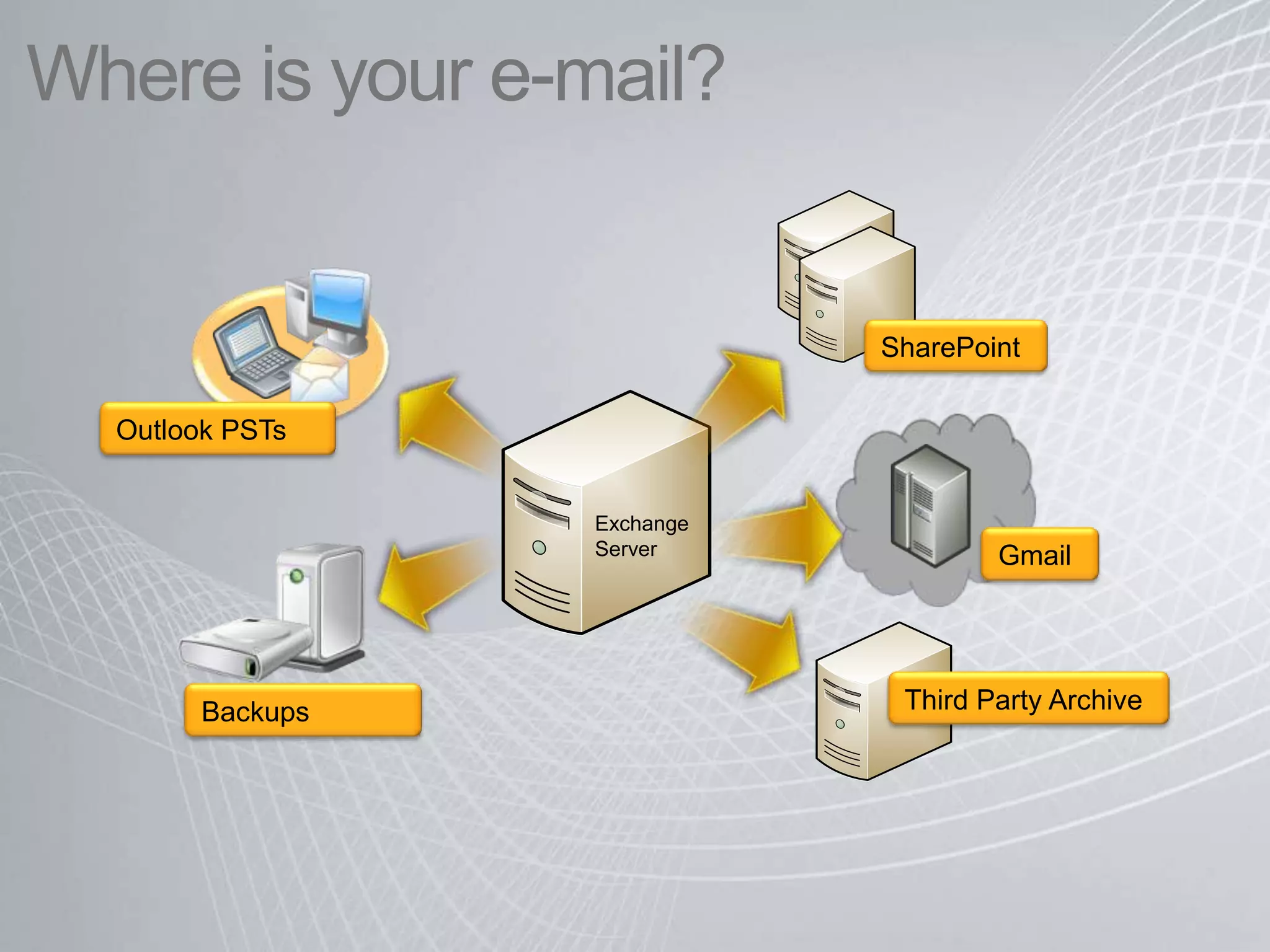
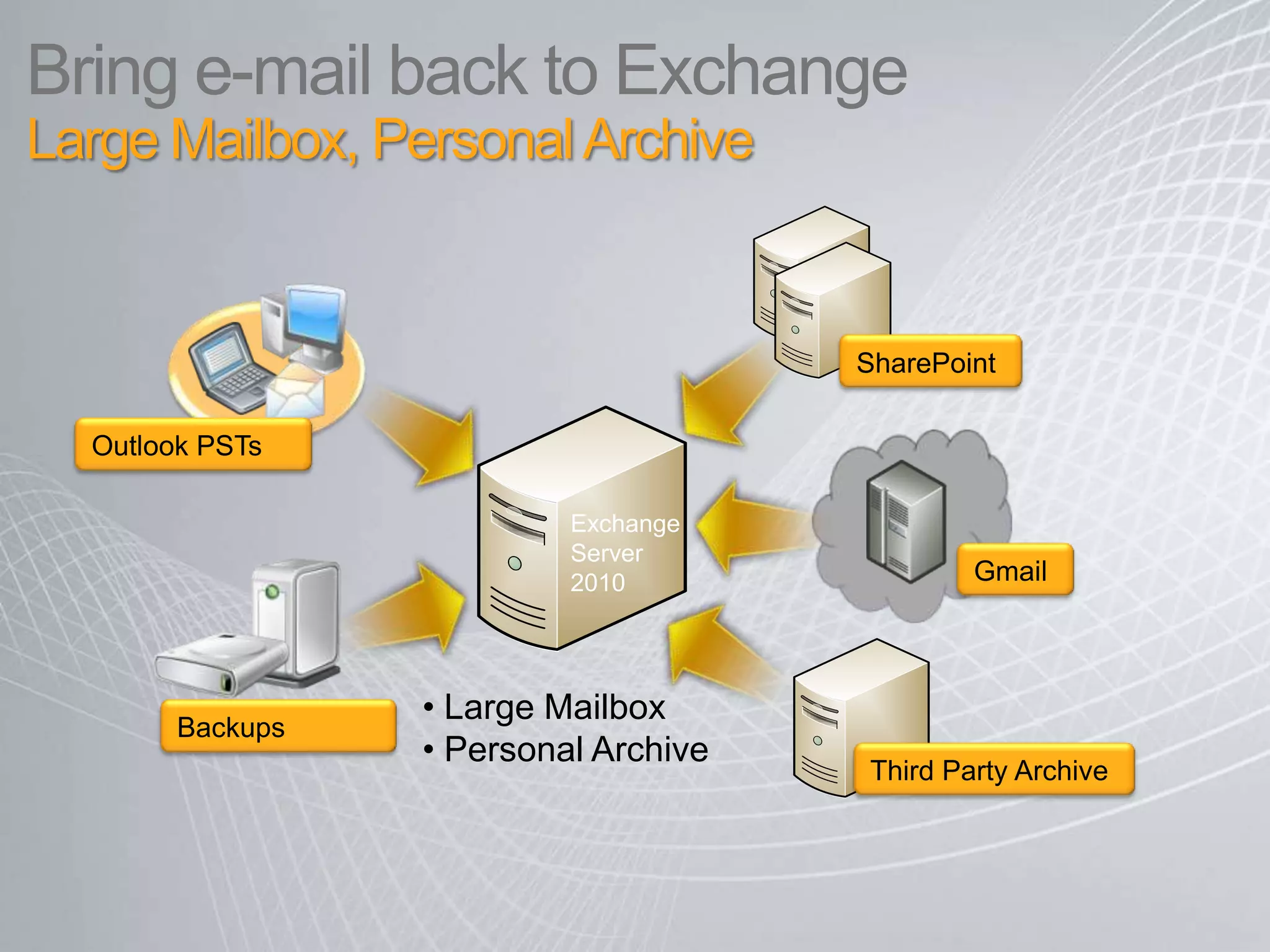
Exchange 2010 includes features that help break the cycle of growing mailbox volumes and storage costs. It provides large mailbox architecture and personal archiving to move older emails out of the primary mailbox automatically according to retention policies. This simplifies discovery, retention, and legal holds while lowering costs. Users can access archived emails through Outlook or OWA and IT administrators can leverage familiar tools to manage policies and search across mailboxes and archives.