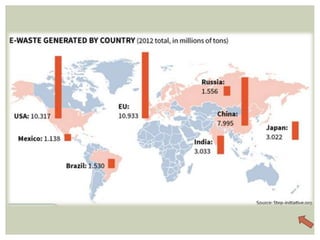
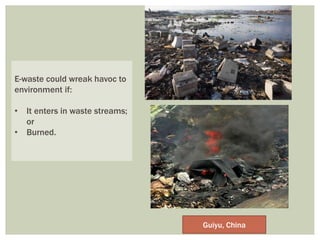
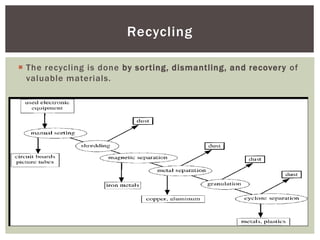
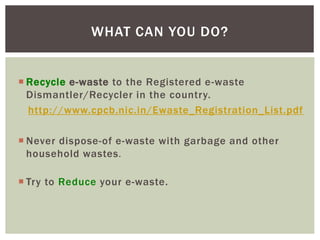
E-waste is rapidly growing worldwide, posing significant health and environmental risks due to hazardous components found in discarded electronic devices. In India, e-waste generation is projected to increase drastically, with poor disposal practices noted in both developed and developing nations, often resulting in hazardous conditions for workers. Improved recycling and bioremediation techniques are needed, along with public awareness on responsible disposal to mitigate the risks associated with e-waste.