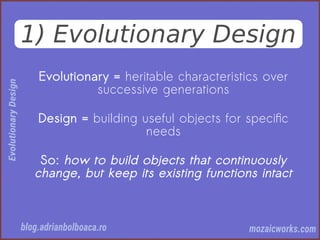
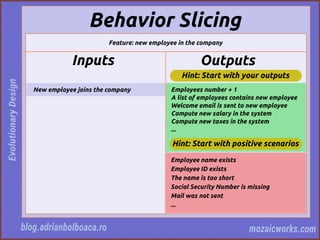
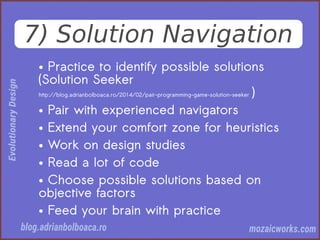
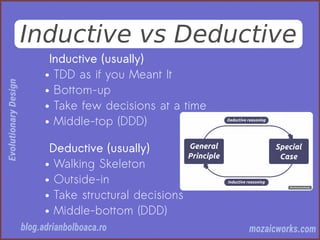
This document discusses evolutionary design in software development, emphasizing the importance of creating adaptable and resilient systems. It highlights principles such as focusing on problem-solving over solution-driven design, using simplicity, and incorporating feedback mechanisms for continuous improvement. The author, Adrian Bolboacă, advocates for various techniques including test-driven design and collaboration to foster the evolution of software projects.