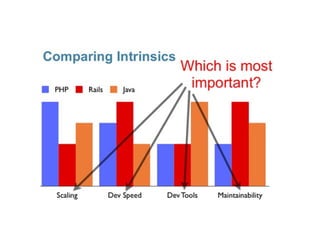
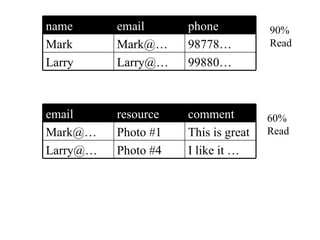
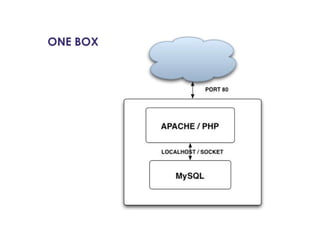
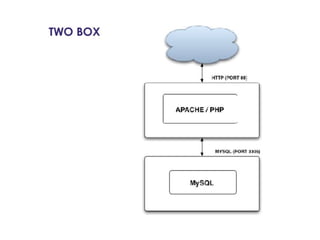
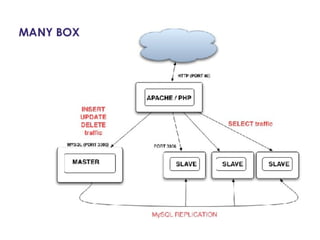
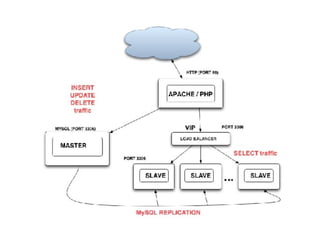
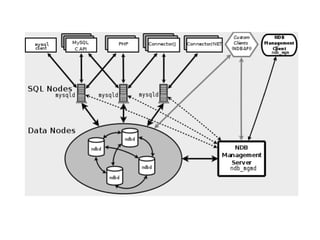
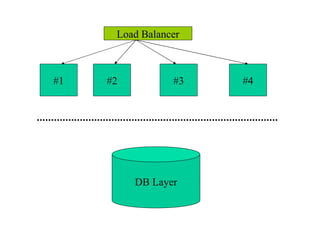
This document provides an overview of PHP, discussing why it is popular for web development, how to scale PHP applications, and caching strategies. It introduces PHP basics and arrays. It then explains that PHP is popular because its array syntax can be directly passed to JavaScript, avoiding the need for object mapping. The document discusses scaling by moving to multiple servers ("scaling out") rather than increasing resources on one server ("scaling up"). It covers database replication and load balancing across database slaves. It also recommends scaling the web tier by storing sessions in a database. Finally, it discusses caching frequently accessed data in memory caches like APC or Memcached to improve performance.






![<?php $arr = array( "foo" => "bar" , 12 => true ); echo $arr [ "foo" ]; // bar echo $arr [ 12 ]; // 1 ?>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-090622071649-phpapp02/85/Everyone-loves-PHP-7-320.jpg)