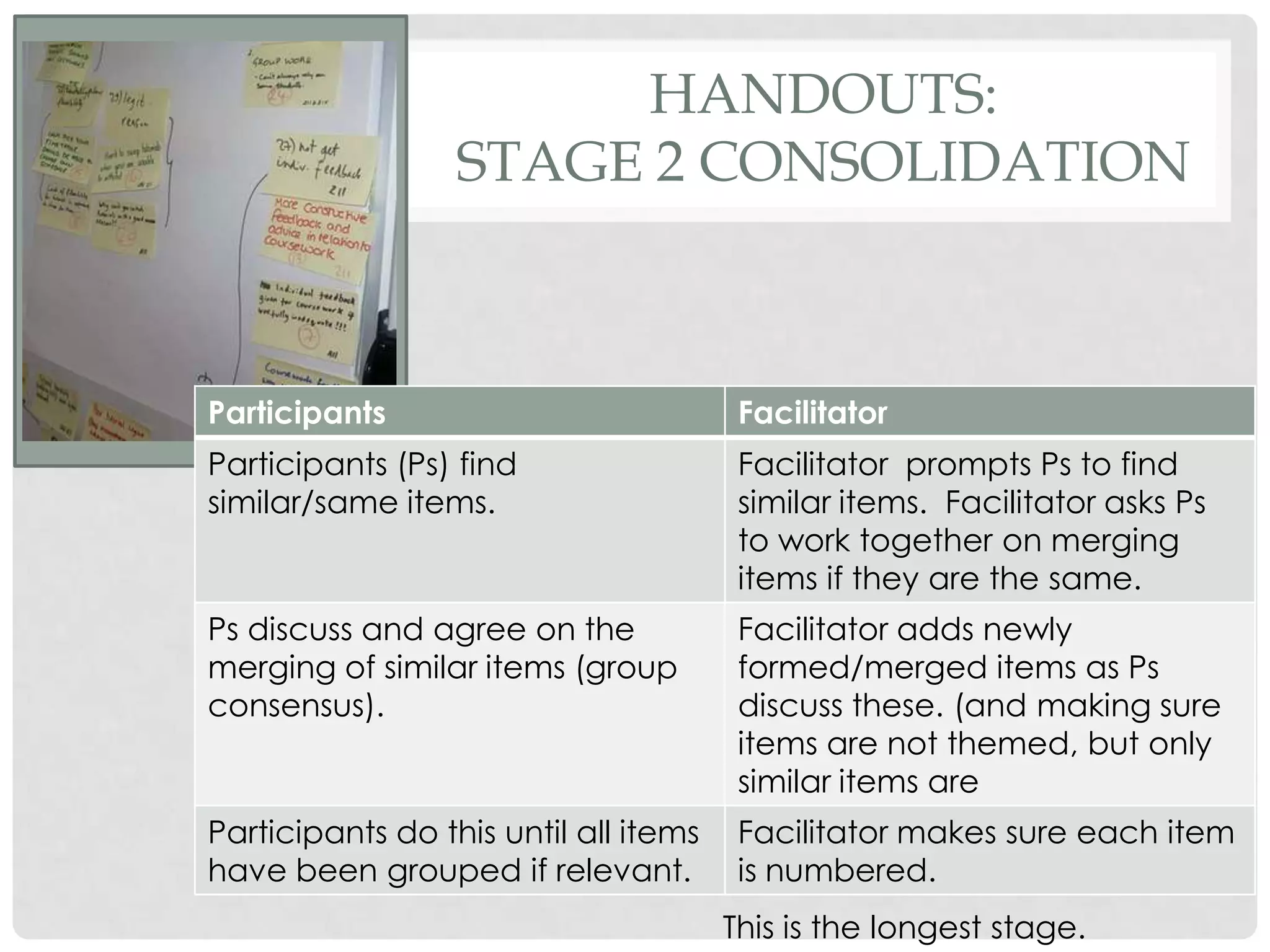
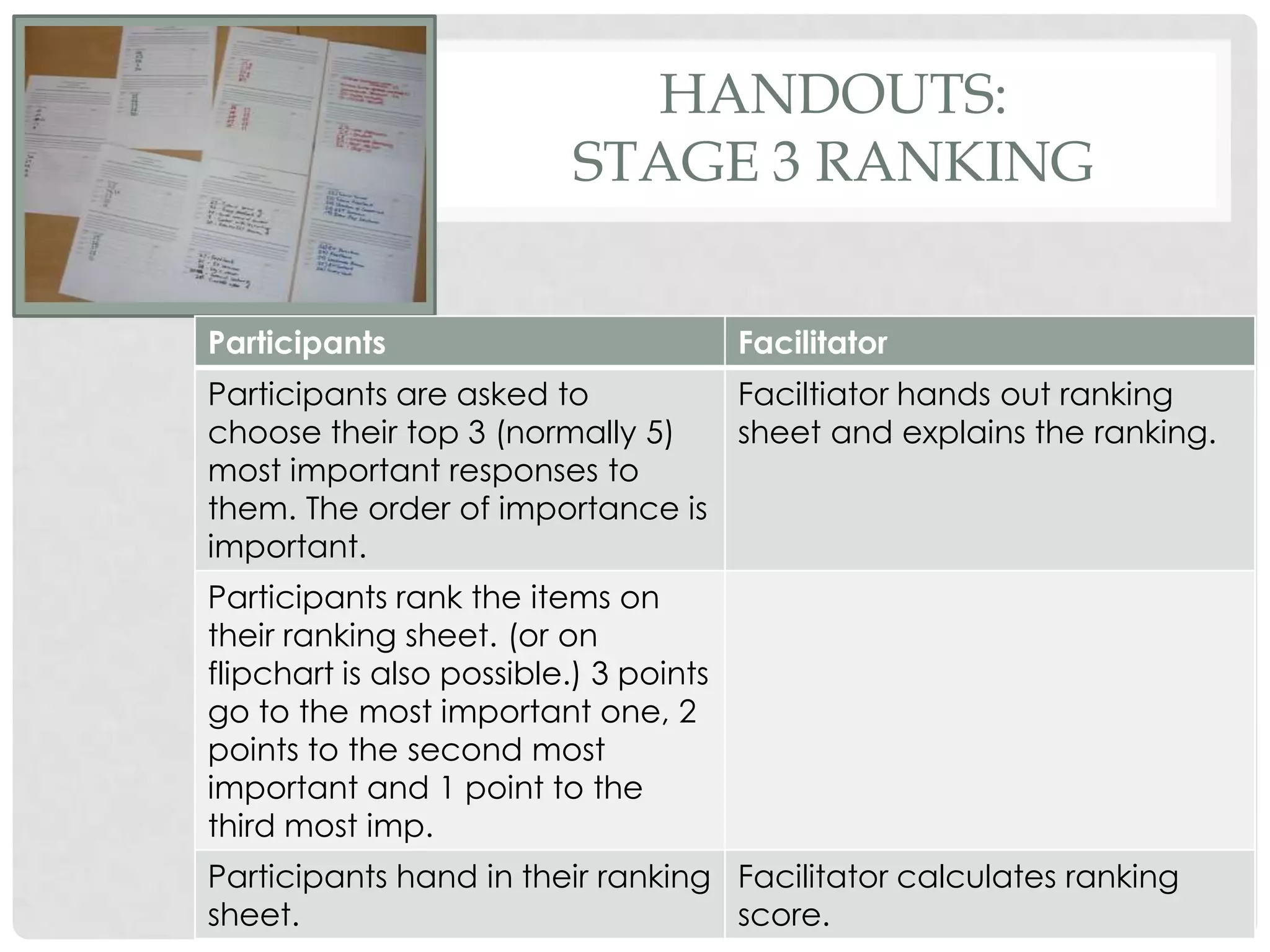
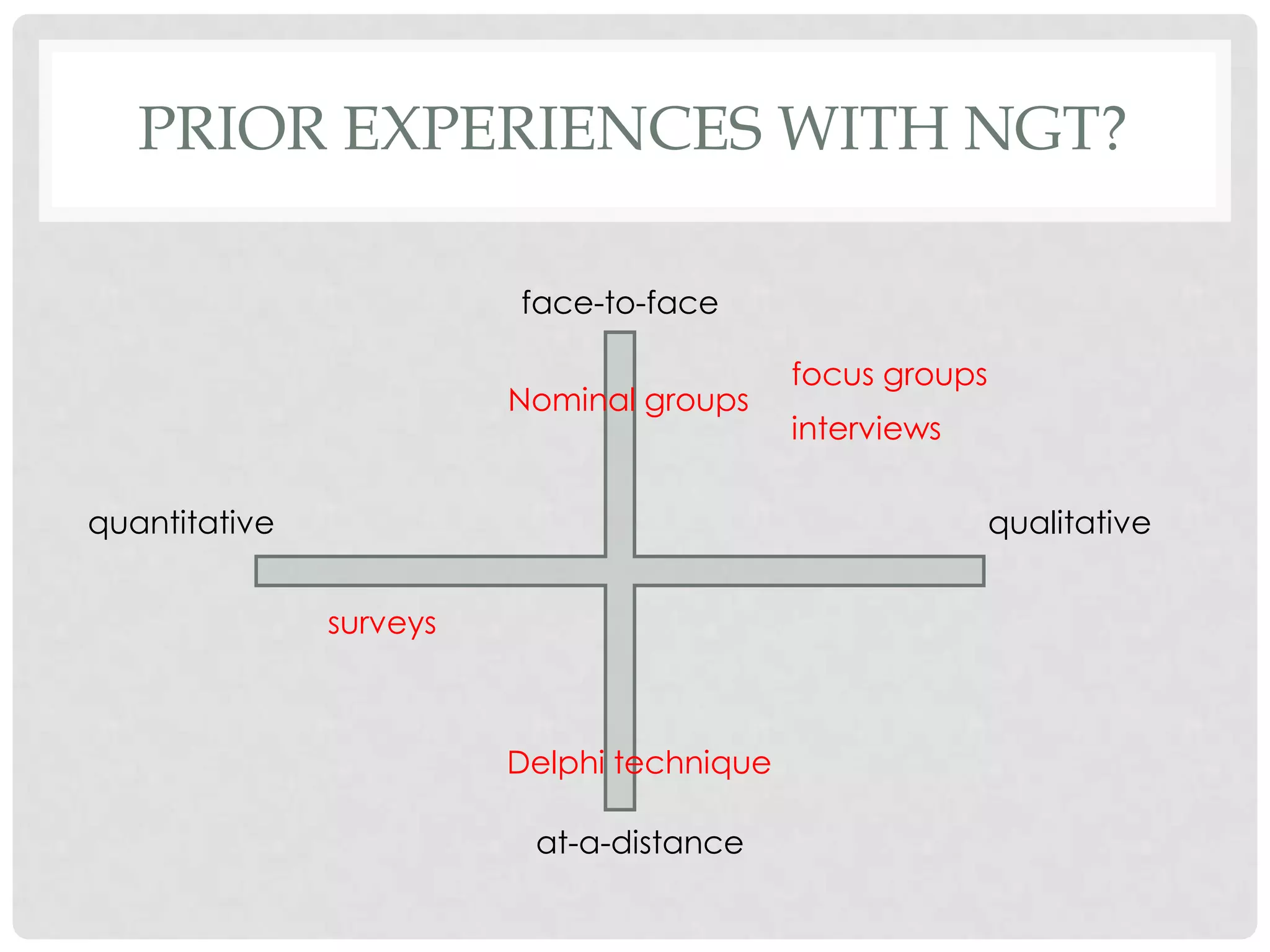
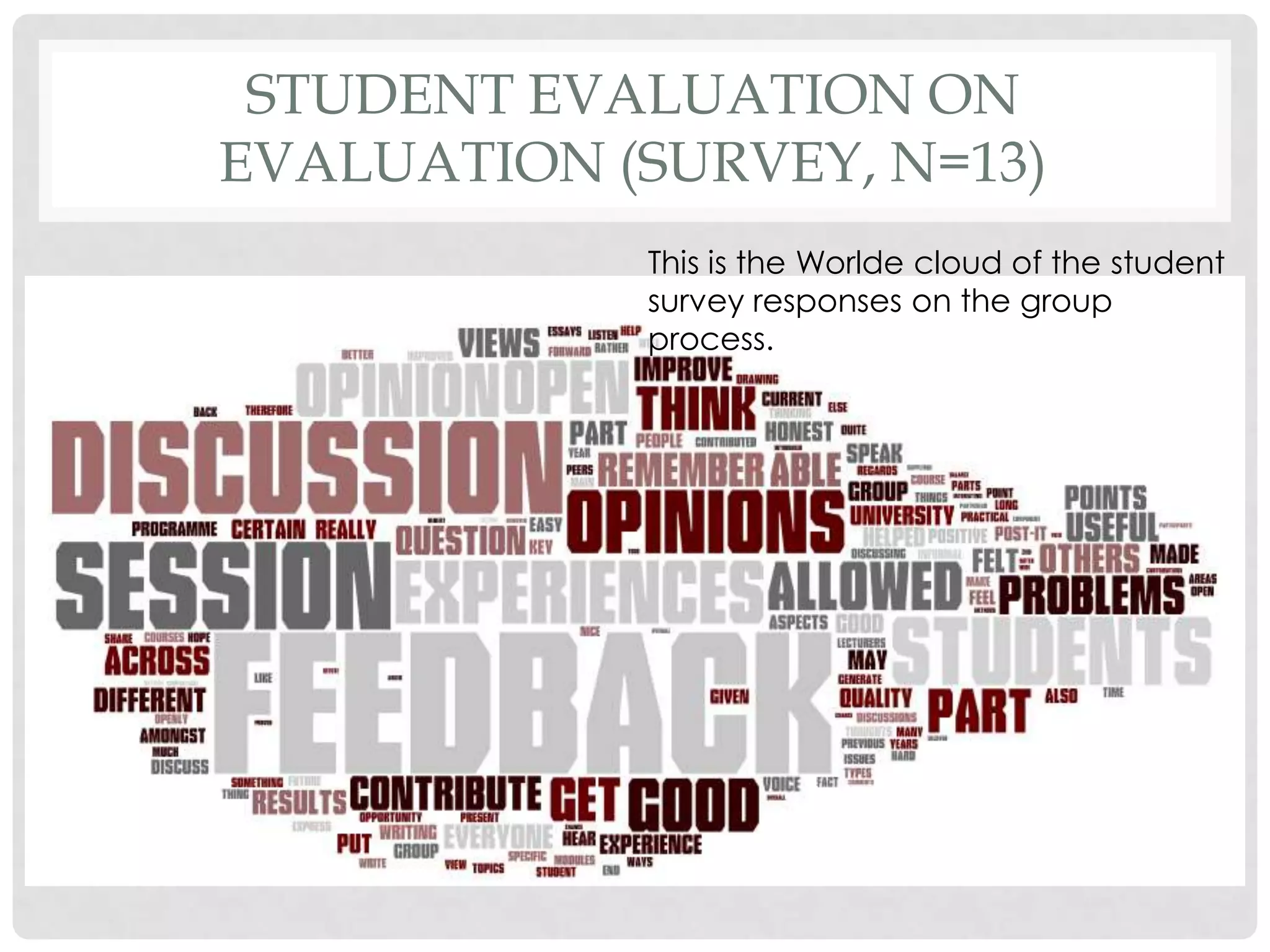
The document discusses evaluation techniques of teaching, particularly focusing on the Nominal Group Technique (NGT) and its combined two-staged approach with focus groups. It highlights the benefits and challenges of NGT and how these methods can improve group decision-making and curriculum development. The document includes insights from educational developers on utilizing these techniques effectively in various contexts.




![LISTENING TO THE EXPERIENCE?
survey face-to-face groups
Wood-peckers?
Wolves?
Dinosaurs? “I found it extremely
…. helpful to have not just an
idea what is going on,
but to hear what is said
“with the questionnaire, by students.”(staff)
you never know if [you]
give the right question
out.”(staff)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/evaluationtechniquesofteachingsedaworkshop2012-11-15slideshare-121116032430-phpapp01/75/Evaluation-techniques-of-teaching-focus-groups-and-Nominal-Group-Technique-5-2048.jpg)


![AND NOW: LET’S HAVE A GO...
THE QUESTION IS:
In your current role as
educational developer
what is one
key challenging issue
you are facing?
[purpose: identifying top 3 key ones to tackle together]
[normally we would ask participants to write 2-3 – but
shortening the task here due to time constraints]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/evaluationtechniquesofteachingsedaworkshop2012-11-15slideshare-121116032430-phpapp01/75/Evaluation-techniques-of-teaching-focus-groups-and-Nominal-Group-Technique-10-2048.jpg)

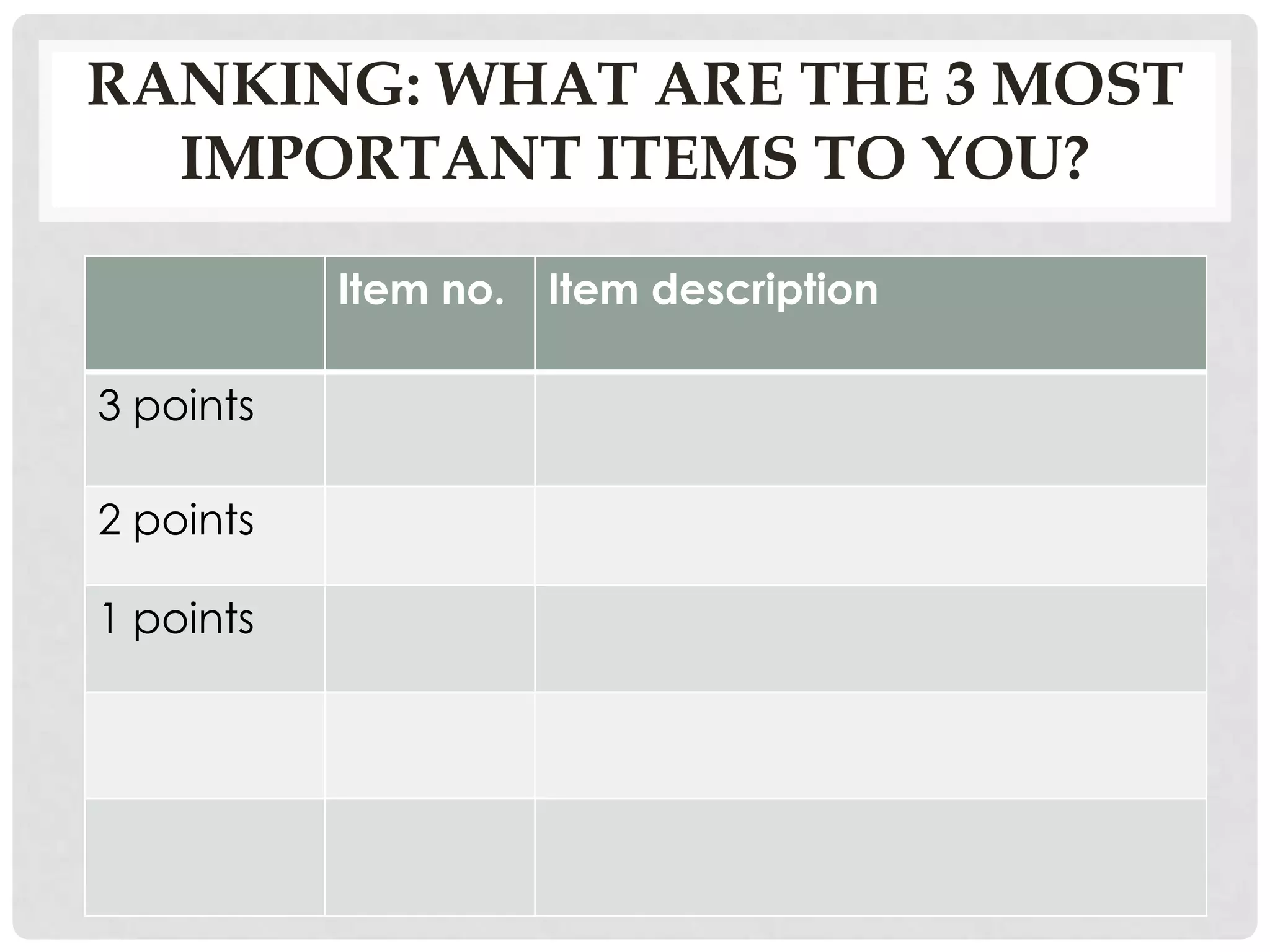
![STAGE 3 RANKING:
YOUR TOP 3 KEY CHALLENGES
that you want the group/SEDA etc. to tackle…
Item no. Item description
3 points 1
2 points 2
1 points 4
[normally top 5 but for brevity
only doing 3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/evaluationtechniquesofteachingsedaworkshop2012-11-15slideshare-121116032430-phpapp01/75/Evaluation-techniques-of-teaching-focus-groups-and-Nominal-Group-Technique-13-2048.jpg)





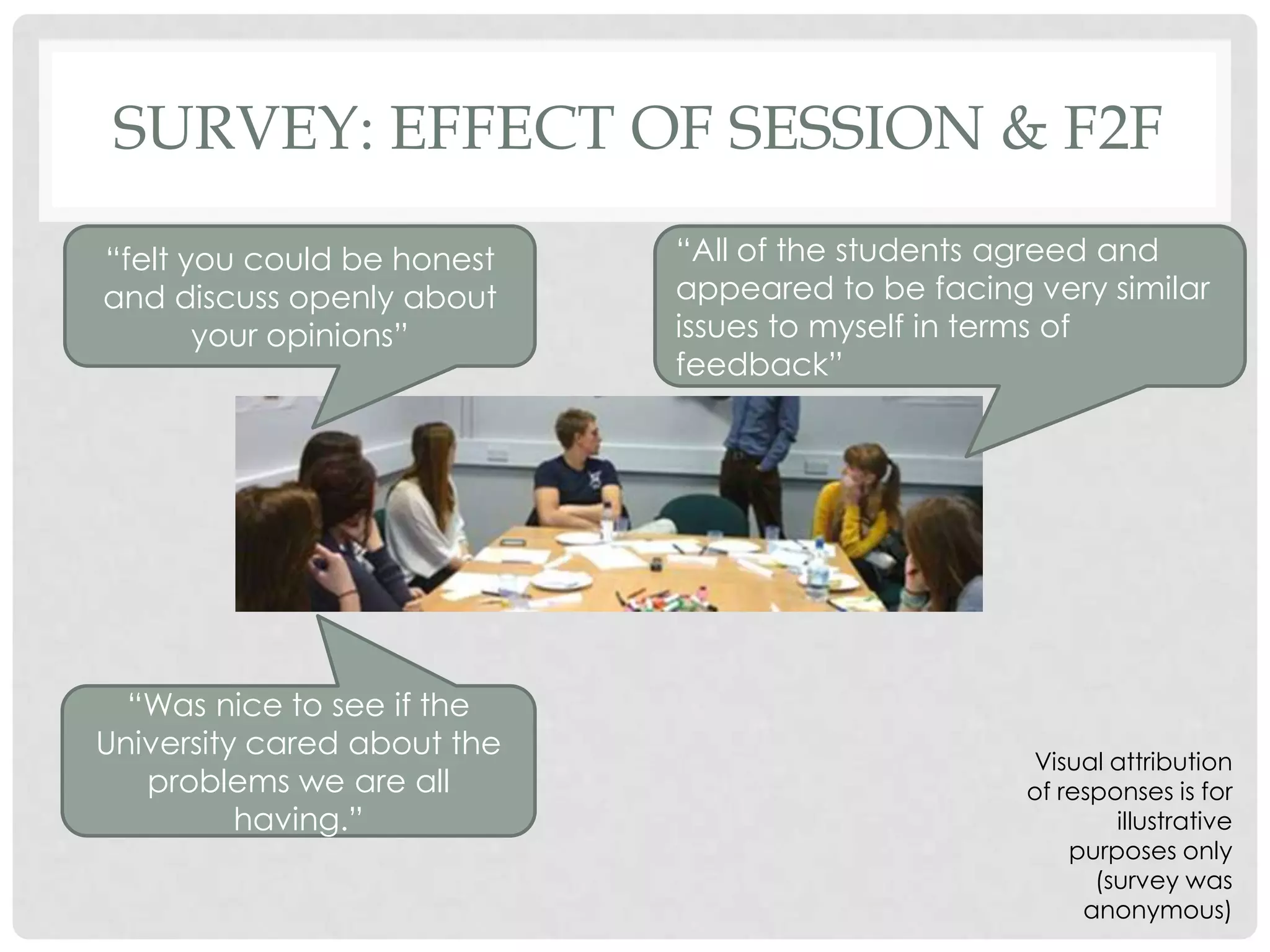

![VIEWS ON STAGE 2: ‘NOMINAL’ BIT
“outlined the main
problems with feedback “[gave] more time to
and made it clear what is think about answers.”
needed to improve.”
“if individuals didn‟t contribute
much in the open discussion, their
views were still taken in to account Visual attribution
[in stage 2]” of responses is for
illustrative
purposes only
(survey was
anonymous)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/evaluationtechniquesofteachingsedaworkshop2012-11-15slideshare-121116032430-phpapp01/75/Evaluation-techniques-of-teaching-focus-groups-and-Nominal-Group-Technique-24-2048.jpg)


![STAFF PERCEPTION ON THE
‘NOMINAL FOCUS GROUP’
“dealing with basically a bullet
point, … you might get the
meaning wrong. You might
not understand, really what
they meant. Whereas [the
Focus Group the citations from
students] explained a bit more
of what they meant. ”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/evaluationtechniquesofteachingsedaworkshop2012-11-15slideshare-121116032430-phpapp01/75/Evaluation-techniques-of-teaching-focus-groups-and-Nominal-Group-Technique-27-2048.jpg)

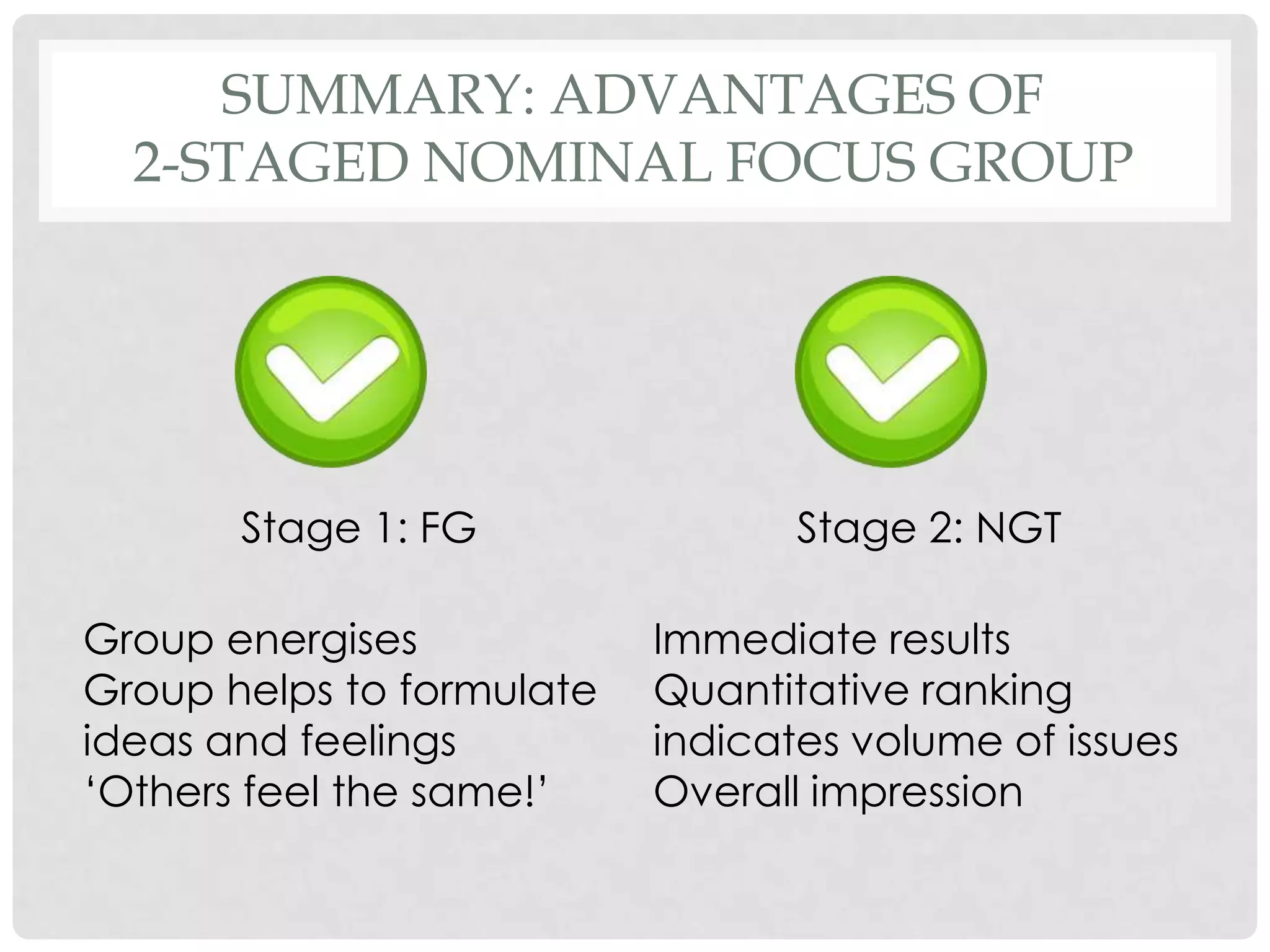

![KEY MESSAGE
We have found the two-staged
„Nominal Focus Group‟ to be
an efficient and useful method
for
evaluation of teaching &
curriculumalldevelopment.
[It is a technique to add to your repertoire of evaluation
methods. It may not suit contexts, and the full evaluation
cycle is the most important including a feedback loop and
action on results! ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/evaluationtechniquesofteachingsedaworkshop2012-11-15slideshare-121116032430-phpapp01/75/Evaluation-techniques-of-teaching-focus-groups-and-Nominal-Group-Technique-32-2048.jpg)
![[OUTCOMES] YOU:
• Are now familiar with the NGT and its
stages.
• Discussed benefits and potential
challenges of NGT.
• Contrasted focus groups & NGT.
• Considered a combined approach of
FG&NGT.
• Reflected on methods in own context.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/evaluationtechniquesofteachingsedaworkshop2012-11-15slideshare-121116032430-phpapp01/75/Evaluation-techniques-of-teaching-focus-groups-and-Nominal-Group-Technique-33-2048.jpg)

![REFERENCES
• Delbecq, A., Van de Ven, Andrew, & Gustafson, D.
(1975). Group techniques for program planning a :
guide to nominal group and Delphi processes.
Glenview Ill.: Scott Foresman.
• Further references in:
• Varga-Atkins, McIsaac et al (2011) Using the nominal
group technique with clickers to research student
experiences of e-learning: a project report
[http://slidesha.re/xQlBCg ]
• Varga-Atkins, McIsaac et al (2011) The Nominal Group
Technique – a practical guide for facilitators
[http://slidesha.re/AmYOgv]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/evaluationtechniquesofteachingsedaworkshop2012-11-15slideshare-121116032430-phpapp01/75/Evaluation-techniques-of-teaching-focus-groups-and-Nominal-Group-Technique-35-2048.jpg)