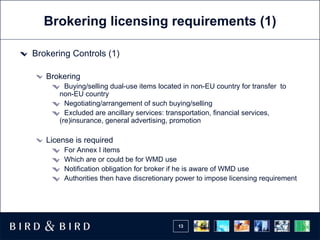
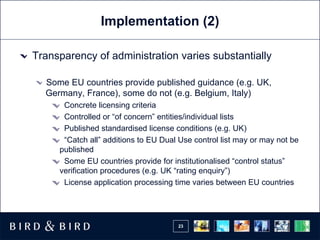
The document summarizes updates to EU dual-use export controls regulations, including requiring licenses for intra-EU transfers of sensitive items, new transit controls, and expanded brokering and recordkeeping requirements. Key changes include national authorities having discretion over imposing licenses on non-Annex I items, licensing potentially required for items in transit through the EU, and brokers now needing licenses if aware items could enable weapons of mass destruction.