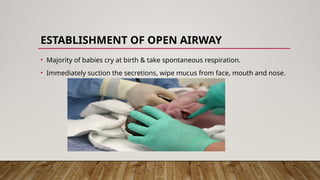
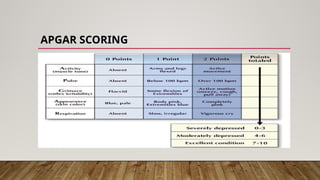
Essential newborn care involves strategies aimed at improving the health of newborns through early interventions after birth and up to 28 days. Key components include immediate care, breastfeeding initiation within the first hour, temperature maintenance, and daily routine care to monitor for danger signs. Proper education for mothers and family members is crucial for promoting the health and well-being of newborns.