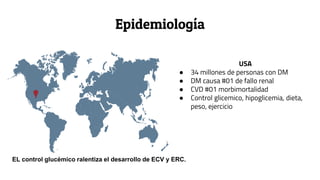
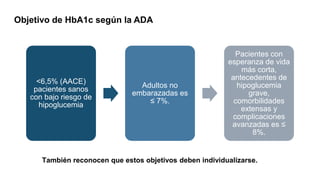
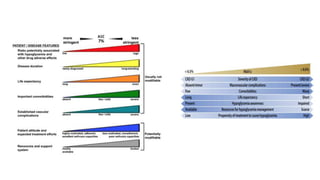
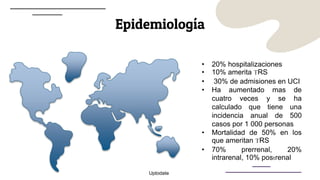
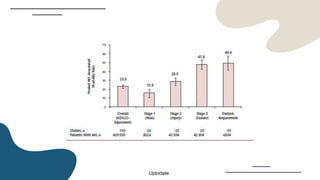
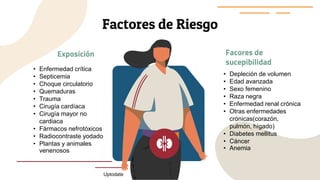
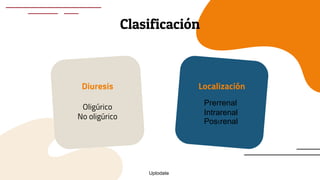
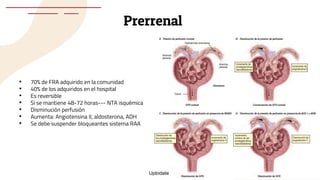
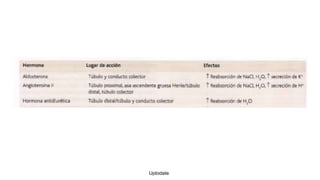
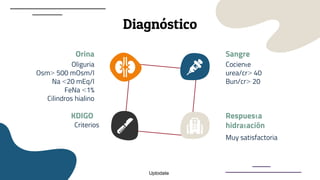
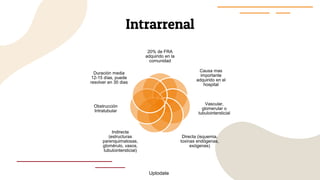
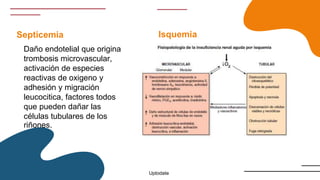
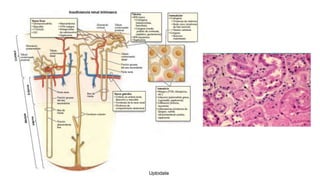
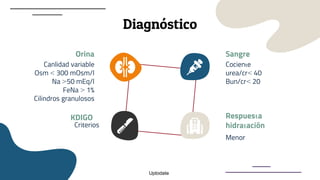
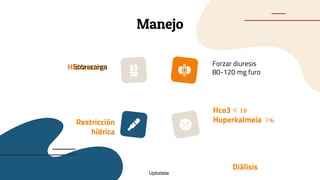
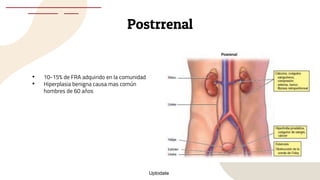
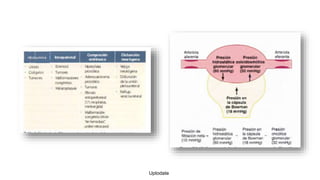
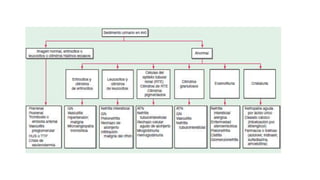
This document provides guidance on managing diabetes in patients with chronic kidney disease. It discusses epidemiology and the importance of glycemic control in slowing kidney disease progression. A case study is presented of a 65-year-old man with type 2 diabetes and stage 3 CKD, and appropriate HbA1c goals and measurement considerations are reviewed. Options for antihyperglycemic agents in CKD, including risks and benefits, are covered. Acute kidney injury is defined as a sudden reduction in renal function.