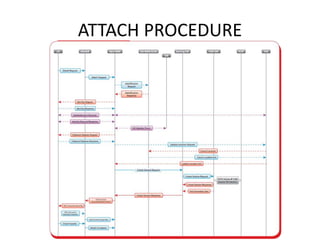
The Evolved Packet System (EPS) architecture consists of the E-UTRAN radio network and Evolved Packet Core network. The EPS architecture includes the User Equipment (UE), e-nodeB base stations, Mobility Management Entity (MME), Home Subscriber Server (HSS), Serving Gateway (S-GW), and Packet Data Network Gateway (P-GW). When a UE wants to attach to the network, it sends an attach request to the e-nodeB, which determines the appropriate MME. The MME then authenticates the UE with the HSS and sets up bearers between the e-nodeB, S-GW, and P-GW to complete the attach procedure and allow the UE