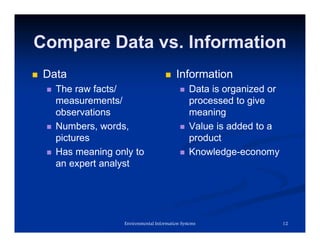
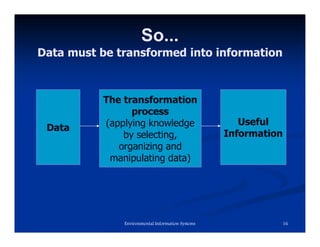
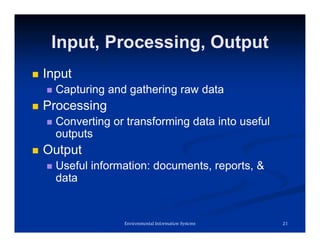
The document explains information systems, focusing on the transformation of raw data into meaningful information through organized processing. It details the components and functions of environmental information systems, highlighting the importance of accurate, reliable, and timely information for decision-making. Additionally, it discusses the role of feedback mechanisms in improving input and processing activities to meet organizational objectives.