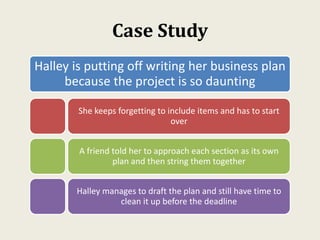
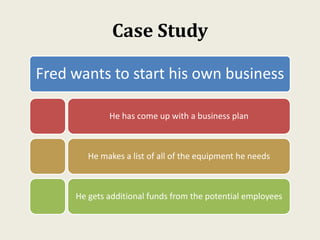
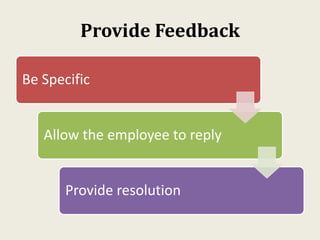
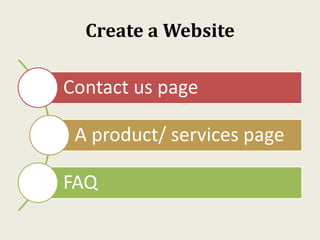
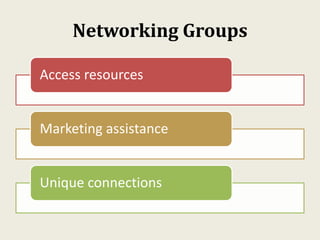
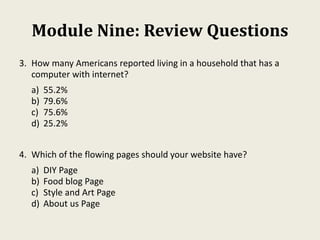
This document provides an overview of creating a business plan. It emphasizes that a business plan is essential for guiding an entrepreneurial venture, despite seeming boring to create. The business plan lays out the objectives, strategies, and financial forecasts for a business. It is used to attract investors, set goals, and measure performance. Creating a good business plan requires thorough market research, a clear company overview, and realistic financial projections.