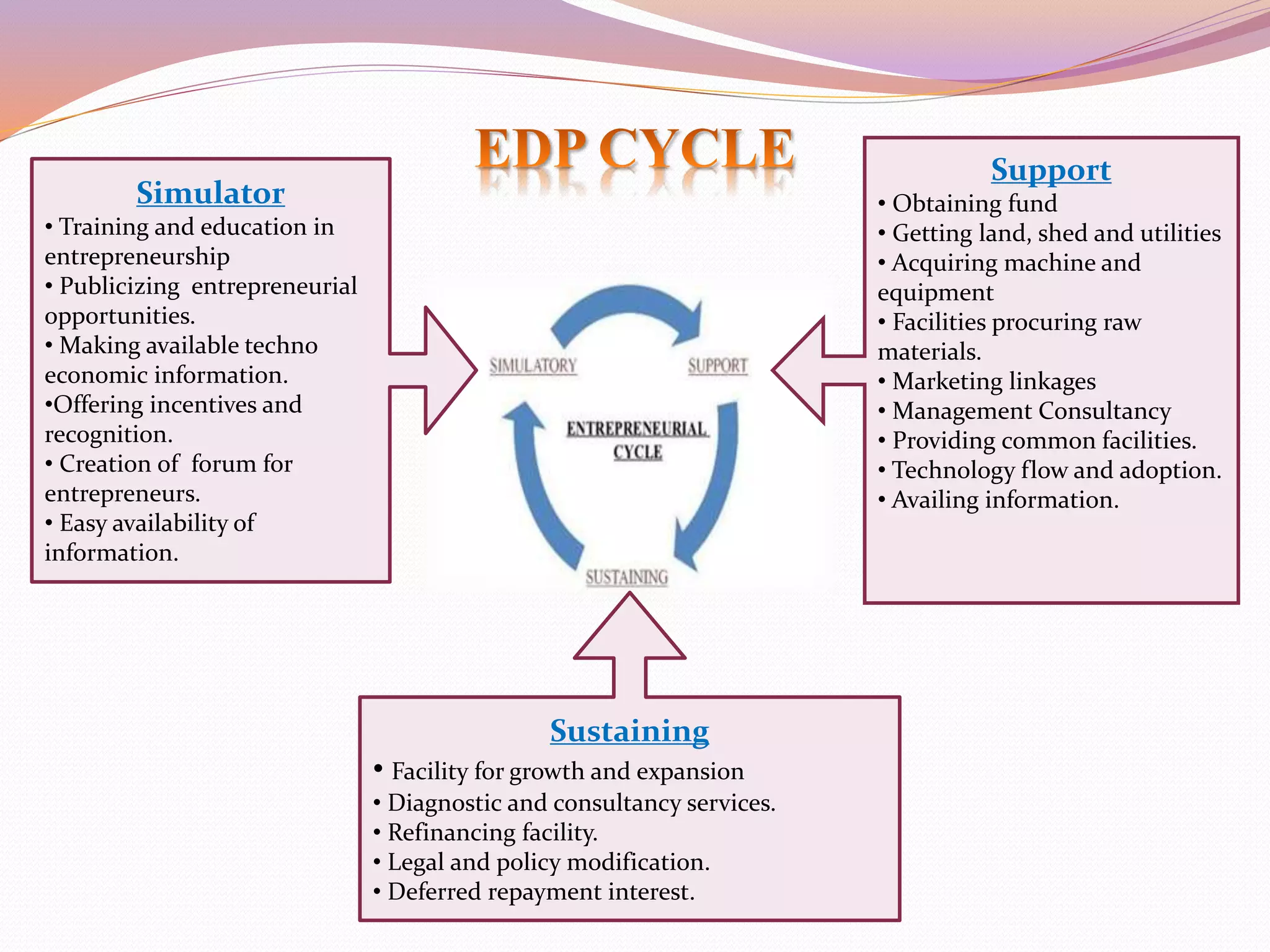
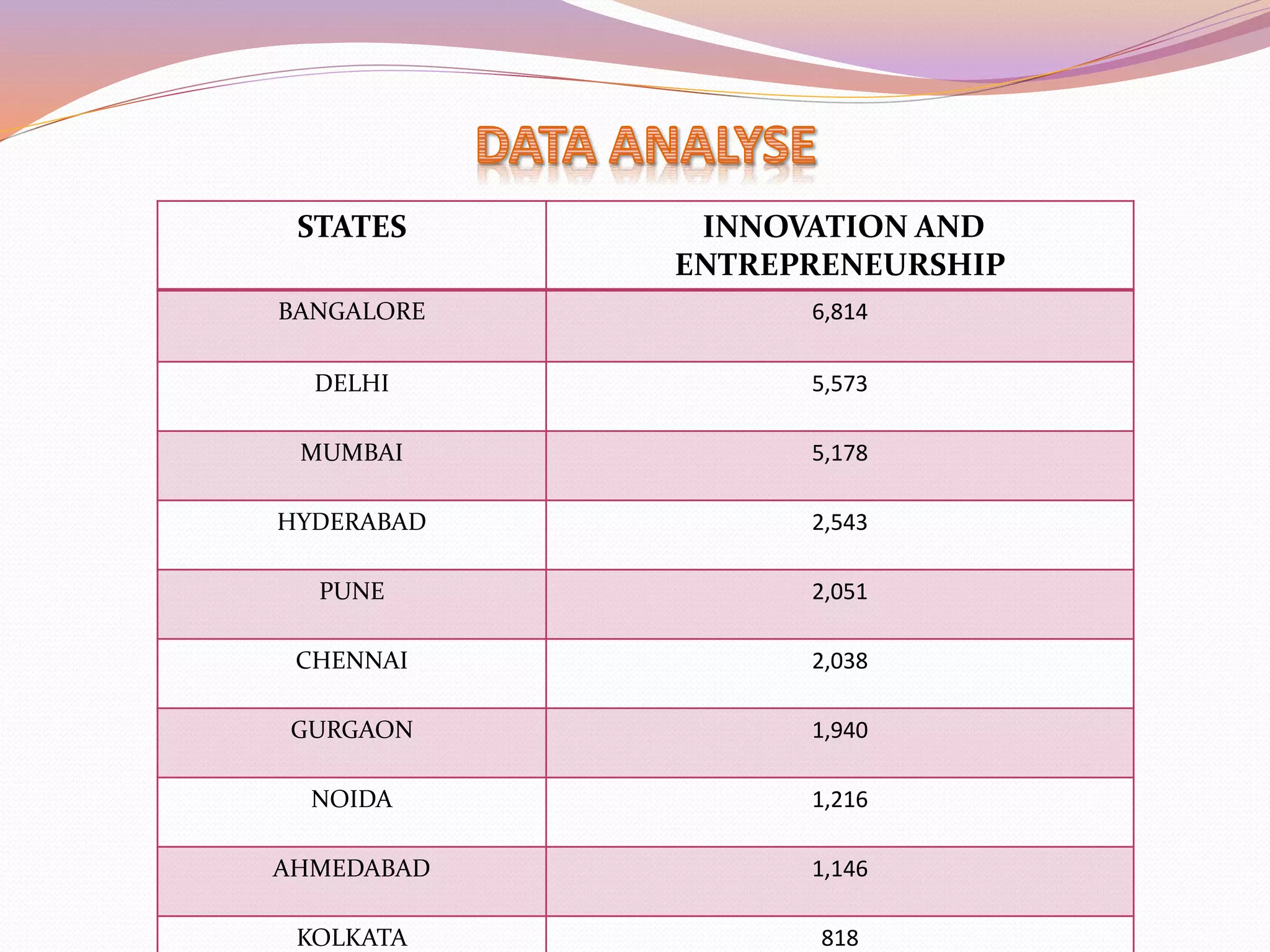
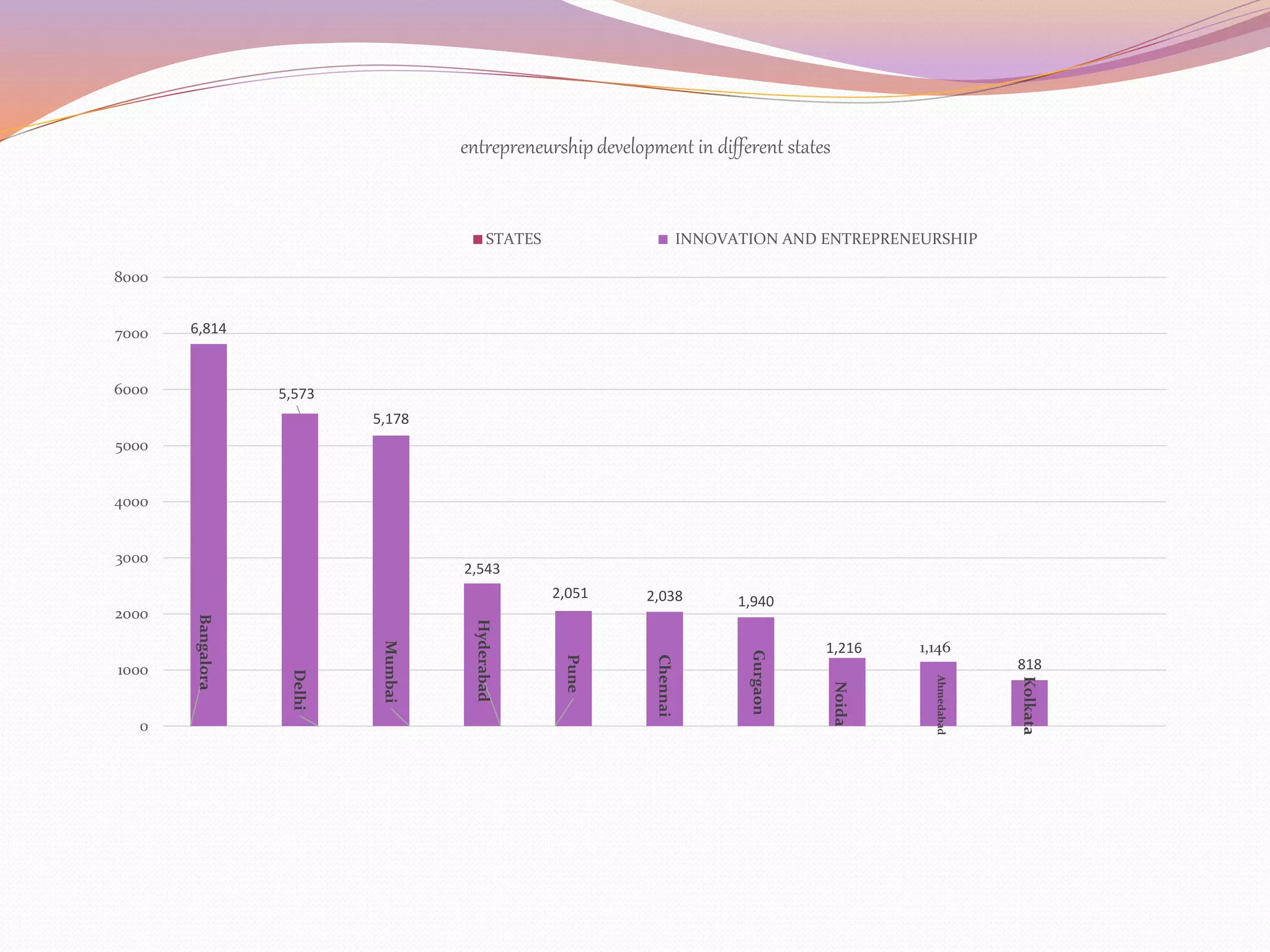
The document discusses entrepreneurship development programs (EDP) in India. It explains that EDP aims to encourage self-employment through training and motivating potential entrepreneurs. The phases of an EDP include an initial training phase, development phase, and follow-up phase. It also outlines different types of entrepreneurship like social entrepreneurship and innovative entrepreneurship. It lists some government schemes to support startups like SAMRIDH, NEWGEN IEDC, and DEDS. Finally, it provides data on the top Indian startups and states with the most innovation and entrepreneurship activity, with Bangalore having the highest number.