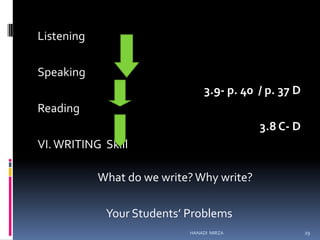
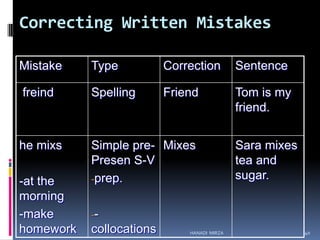
This document outlines Hanadi Mirza's presentation on improving English language skills at L.I.U. The presentation covers teaching English in the classroom, how students learn and retain new information, and developing key language skills like listening, speaking, reading, and writing. It provides teaching strategies and activities for each skill, addressing common student problems. The schedule includes sessions on teaching methods, memory and learning, developing individual skills, and concluding with a group work activity.
















![Correcting Pronunciation
Simplified Phonetics
[ə] = (euh) sound
Answer
[an sər]
Respond
job
[djob ]
Schedule
[sked jouwəl] Time table
People
[py pəl]
persons
Suggest
[sag djèst]
Jounralist
[djər nalist]
Work in pairs [wərk in pèrz]
Question
[kwest shən]
HANADI MIRZA
20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/englishws-liu-131211071619-phpapp02/85/English-Language-Workshop-Dec-2013-20-320.jpg)






![Reading Aloud
Simplified Phonetics
Past Tense of Regular Verbs
(-ed) [- id] , [-t] , or [-d] ? WANTED -DECIDED
[-t] & [-d] + [-id] / Vd + [-d] / vl + [-t]
ASKED - PLAYED
Created , Needed / Proved / Fixed
Plural Form of Nouns
(-s) [-z] or [-s] or [-əz] ? MAPS- BOTTLES - CHURCHES
vd + [-z] / vl + [-s] / -ch, -sh, -ss, -x + [-əz]
Boys, girls / cats, lin ks / classes, foxes
HANADI MIRZA
27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/englishws-liu-131211071619-phpapp02/85/English-Language-Workshop-Dec-2013-27-320.jpg)