The document provides instructions for creating a screencast to justify design choices made for a PSA poster or billboard. It discusses:
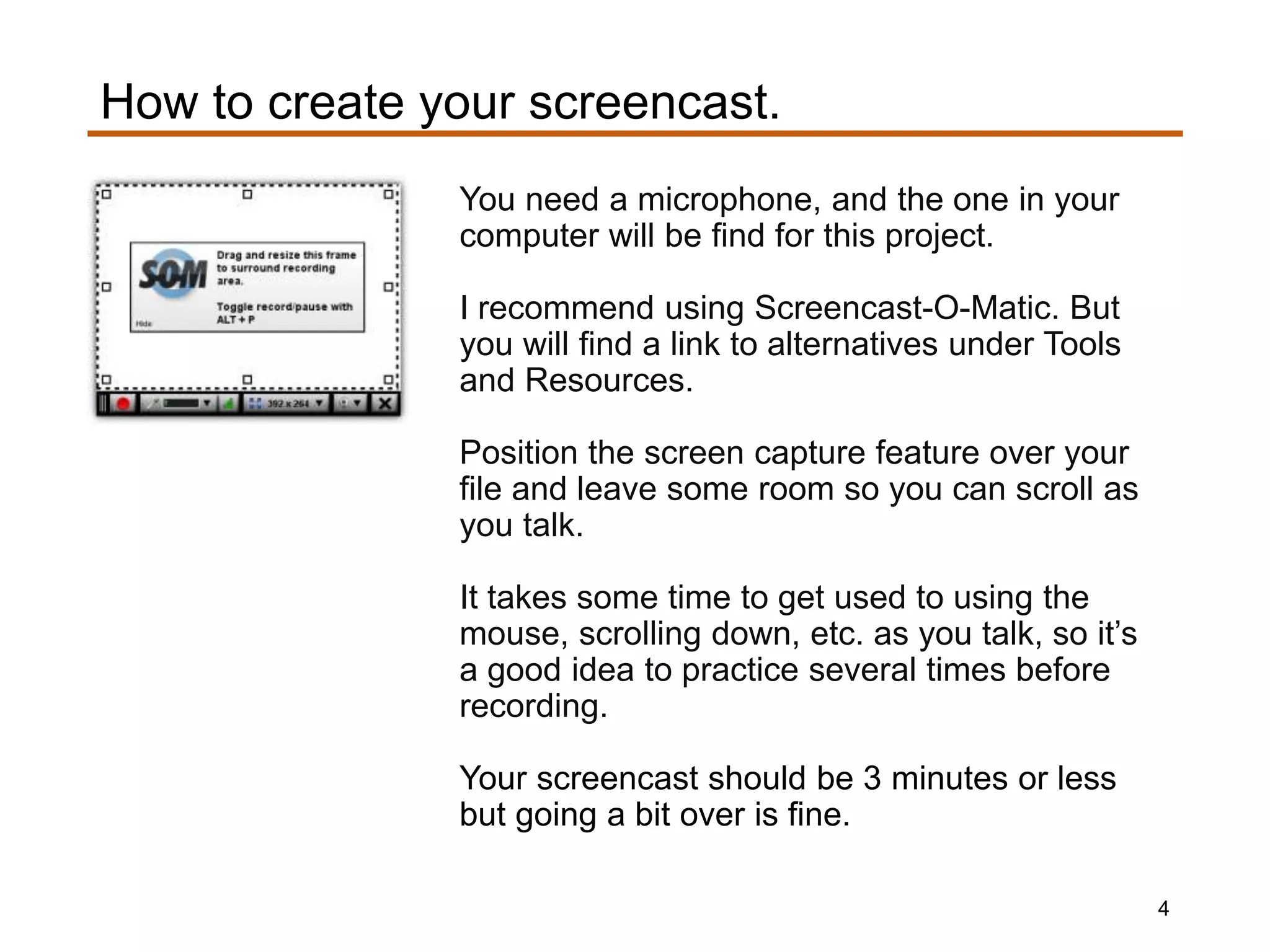
1) Using a screen capture tool like Screencast-O-Matic to record a narrated demonstration of the design file.
2) Writing a script that introduces the subject/audience, defines design principles applied to the poster, and justifies each design choice using principles rather than personal tastes.
3) Practicing several times before recording the 3-minute screencast and testing the screen capture setup.