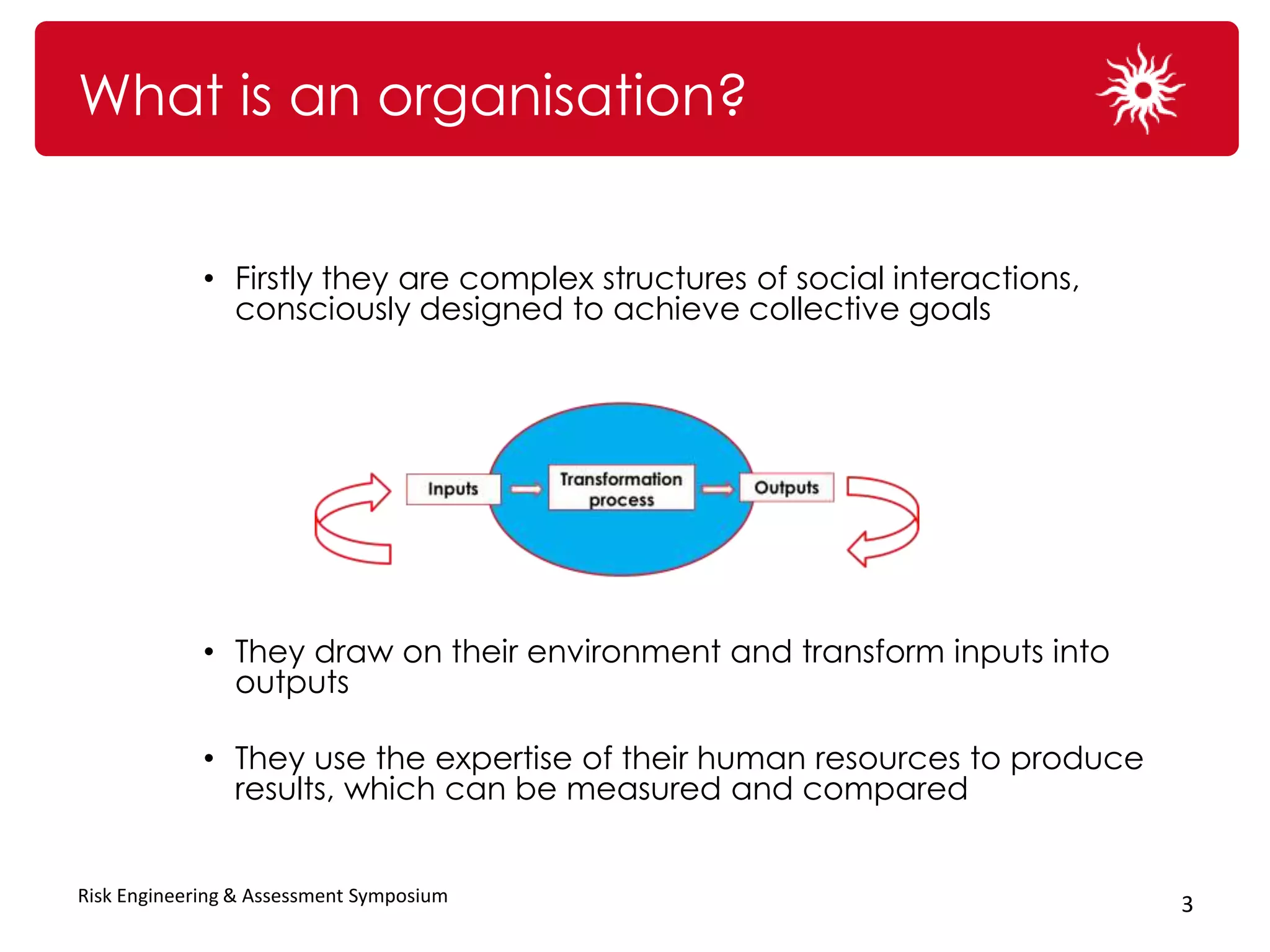
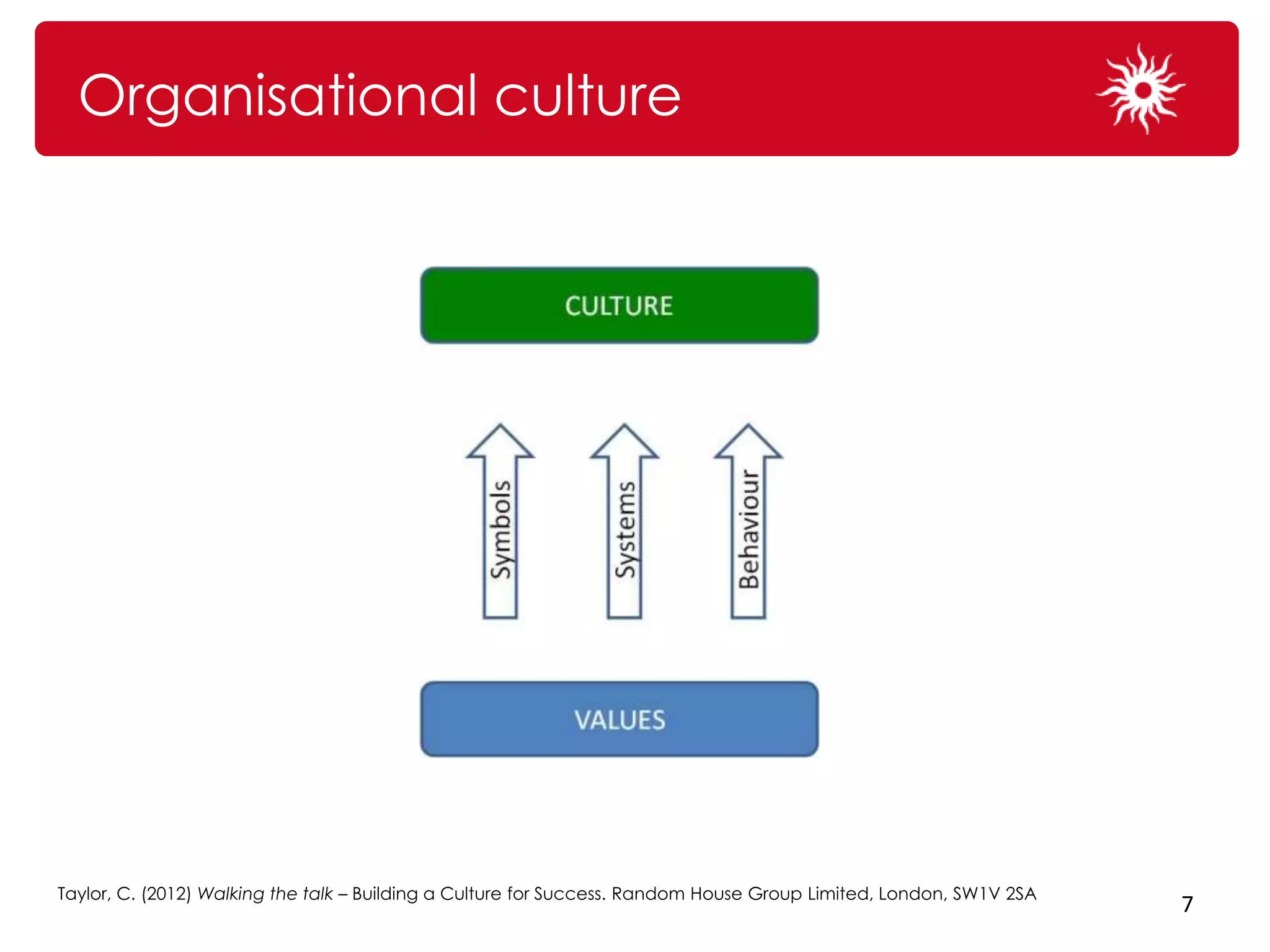
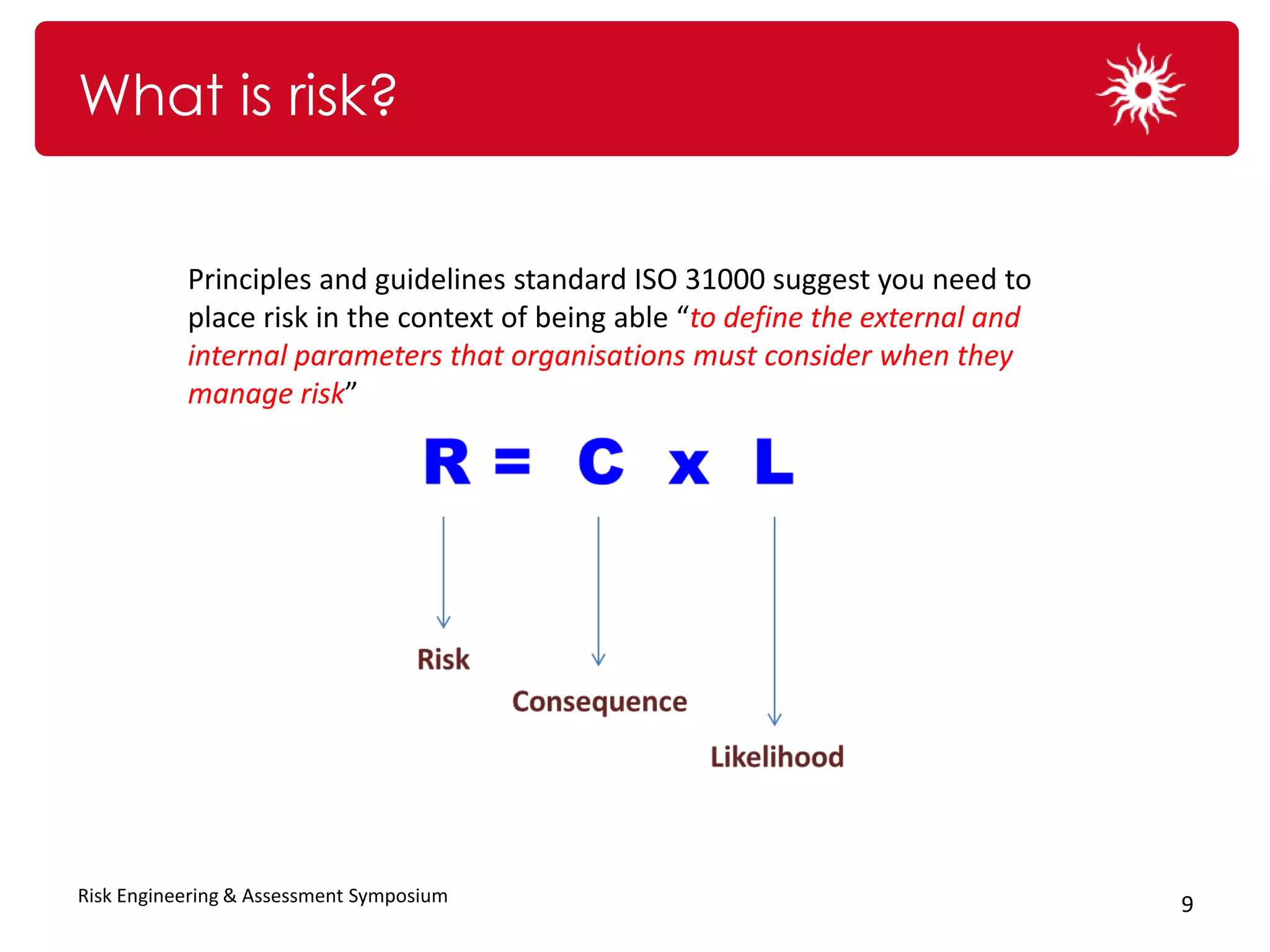
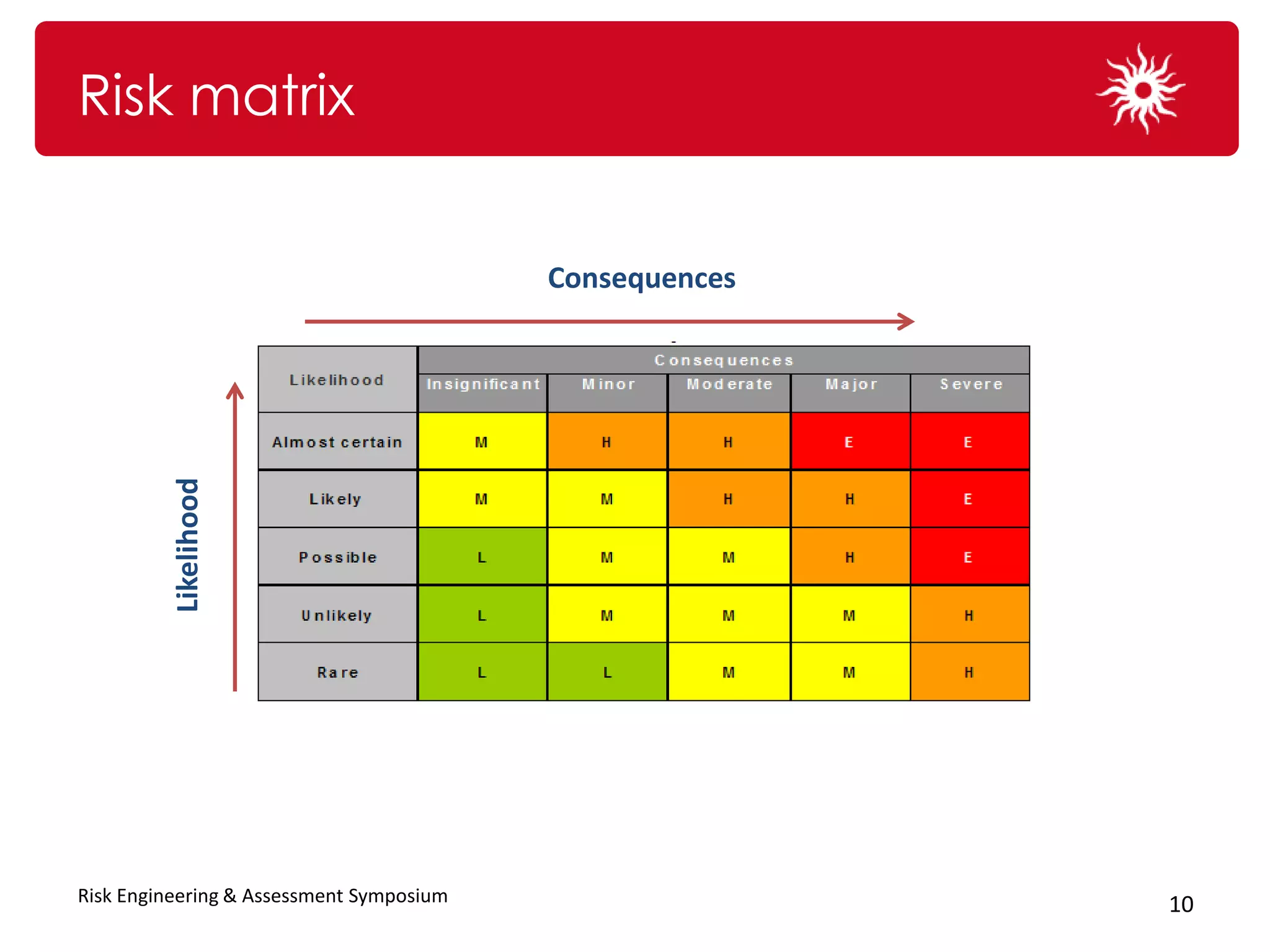
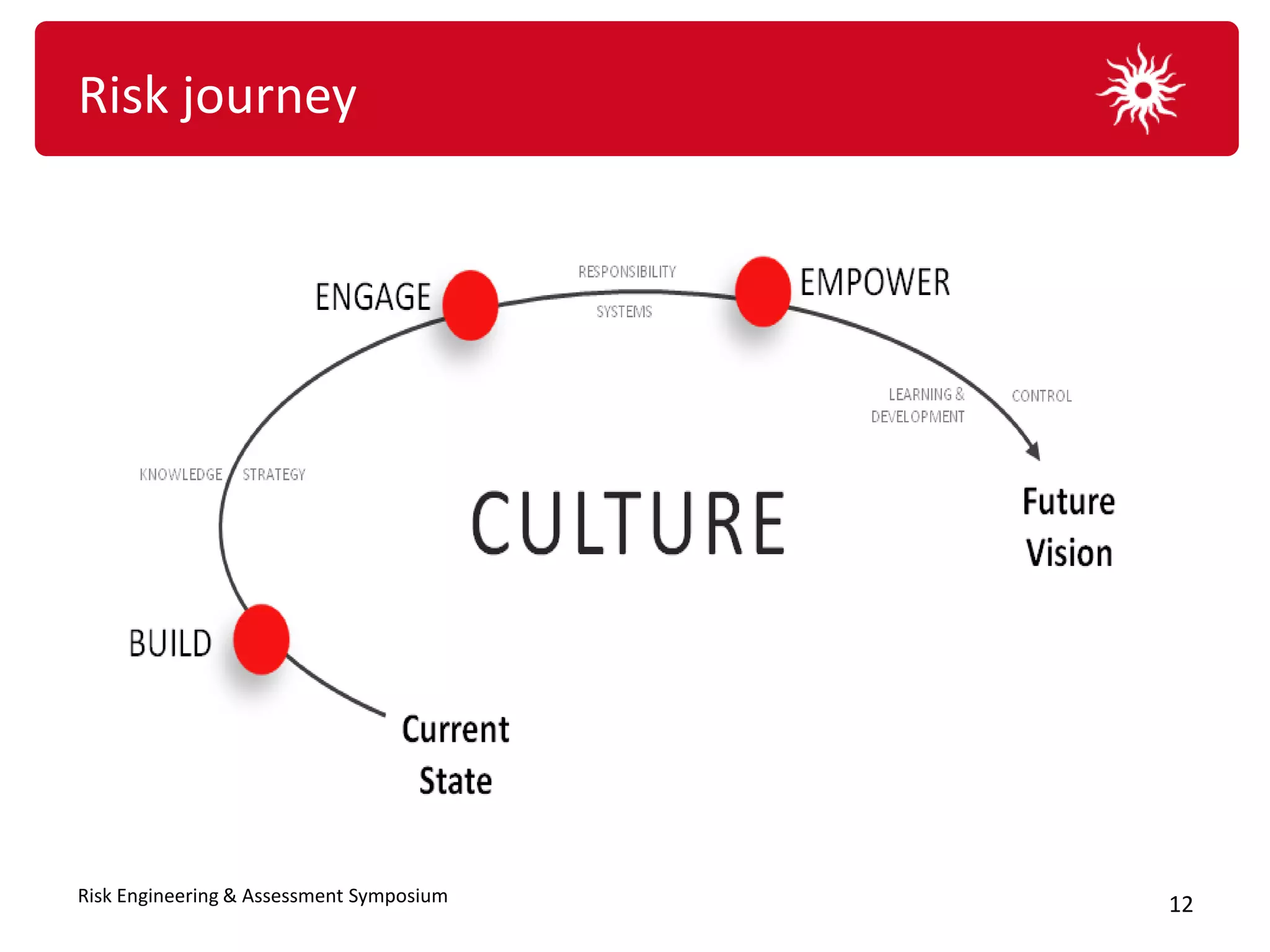
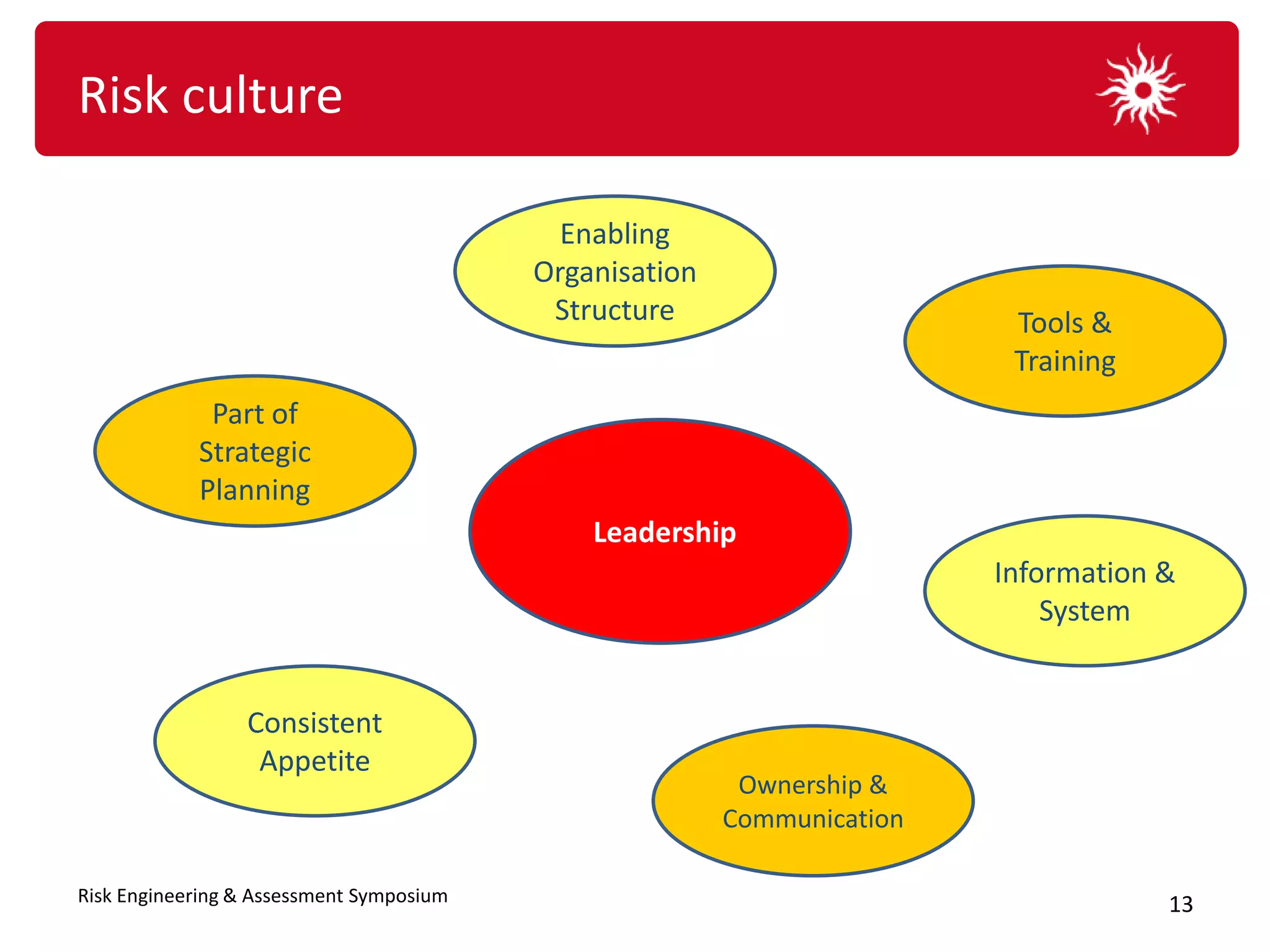
The document discusses the significance of organizational culture and risk awareness in achieving business success, emphasizing that effective culture influences leadership, employee behavior, and overall performance. It highlights the financial costs associated with poor cultural fit and risk awareness, using case studies such as BHP Billiton and Krispy Kreme to illustrate successful and unsuccessful practices. The document concludes with strategies for fostering a robust risk culture and the importance of persistence and engagement in this process.











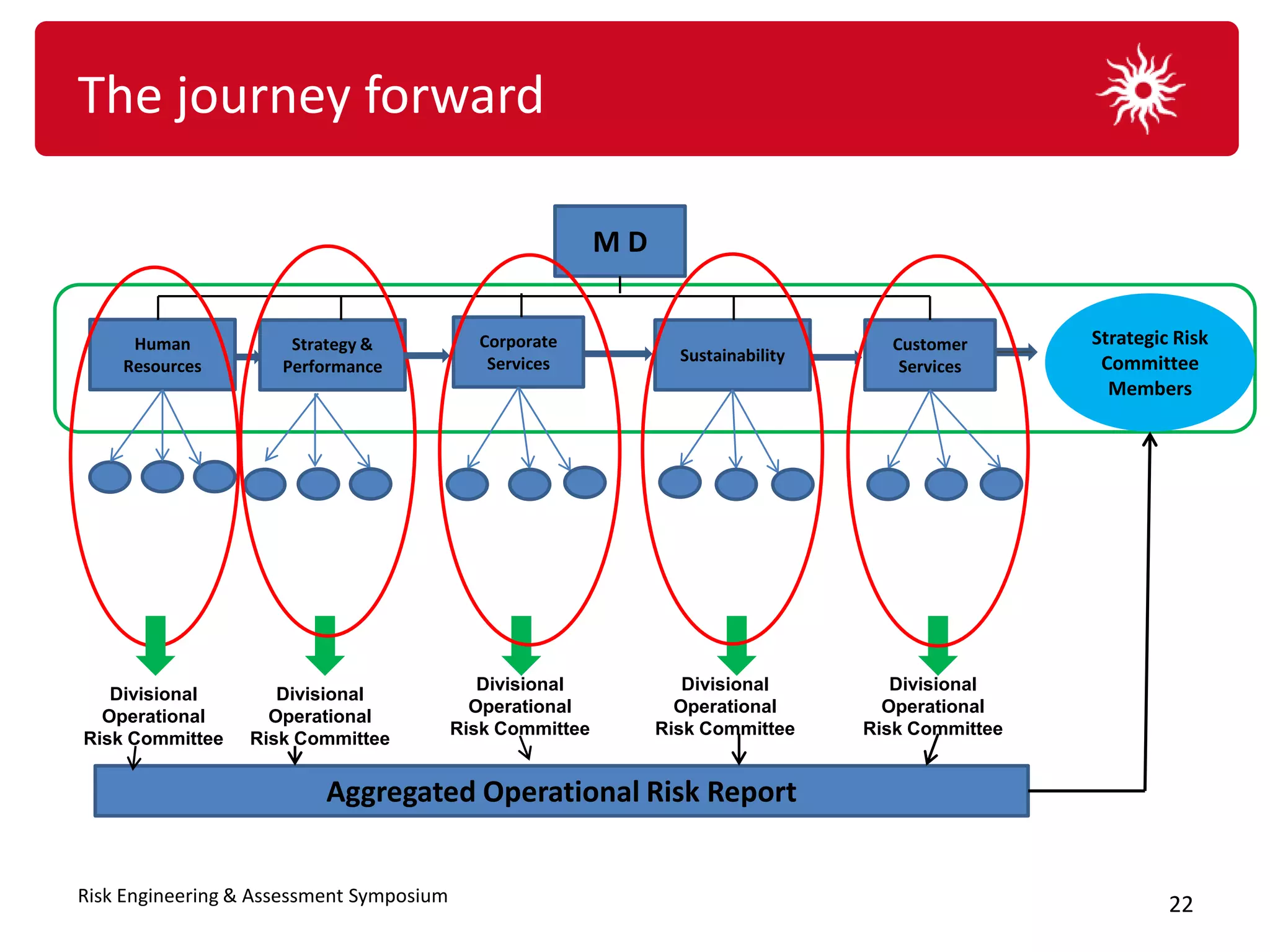
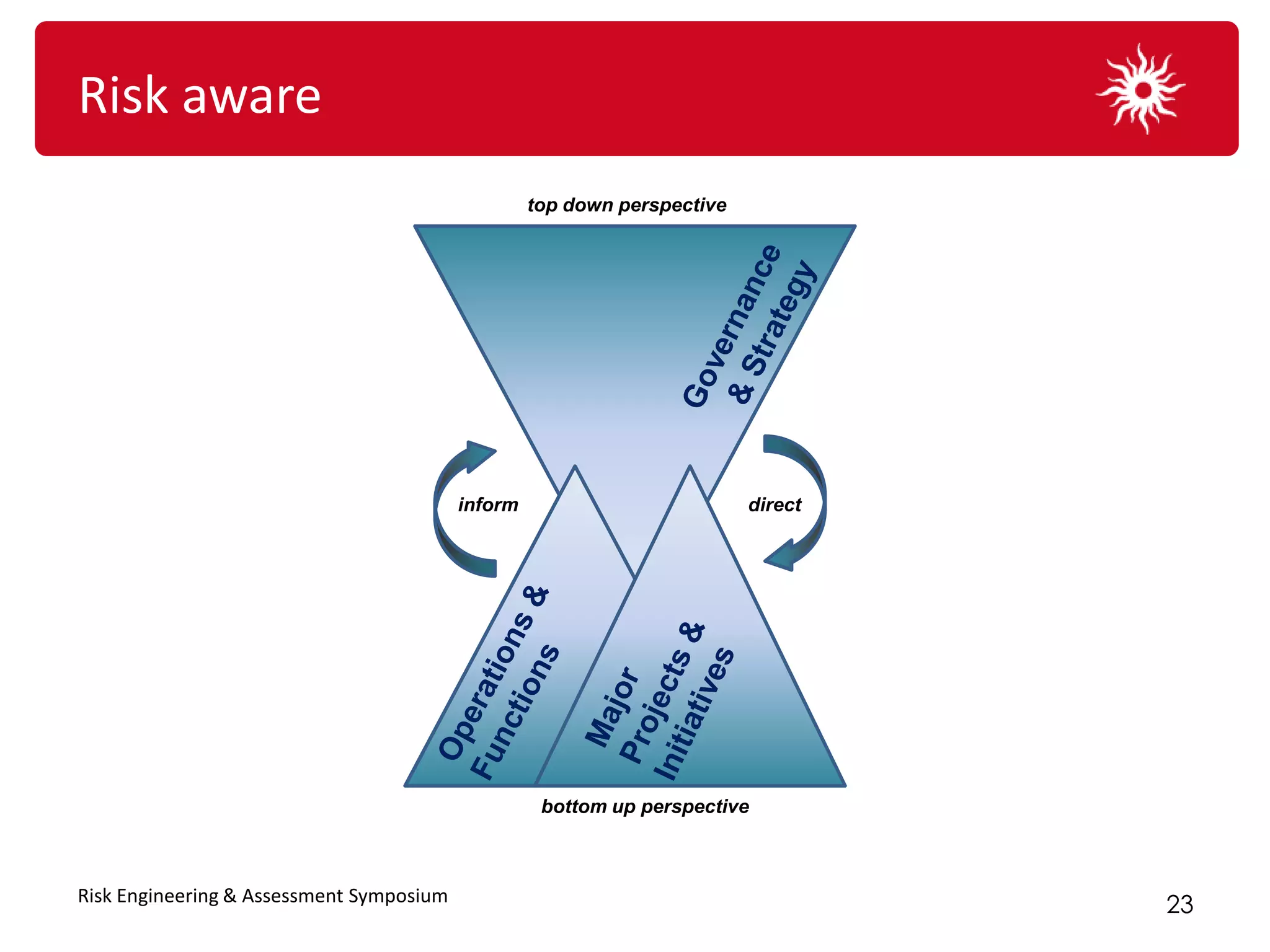
![The journey forward
Set the stage
- Create a sense or urgency
- Put together a guiding team
Decide what to do SafetyC’s Journey C’s
5 Journey – 5
- Develop the change vision and
strategy
High
Management
Activity
Make it happen
Supervisory
- Communicate the Activity
understanding and buy-in Management
Team Activity
- Empower others to act Low
Leadership
- Produce short term wins
Cr
Co
Co
Co
Cu
isi
nt
m
m
ltu
- Do not let up
s
pl
m
ro
re
ia
itm
l
nc
en
e
t
Make it stick
- Create a new culture
MindTools (2012) Implementing Change Powerfully & Successfully [online] MindTools
http://www.mindtools.com/pages/article/newPPM_82.htm (accessed) 5 July 2012.
21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engineeringsymposium-120724200522-phpapp02/75/Engineering-Symposium-21-2048.jpg)