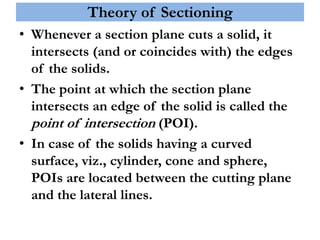
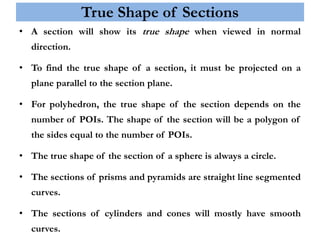
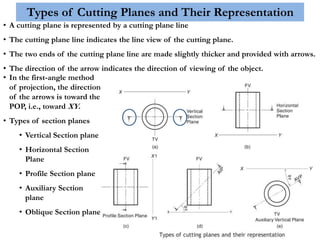
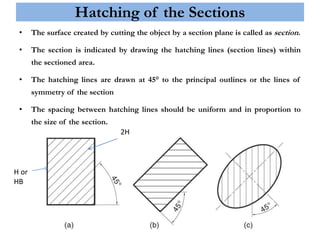
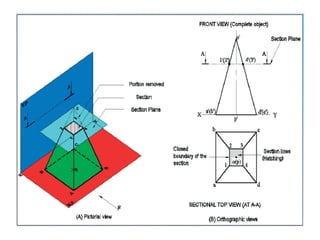
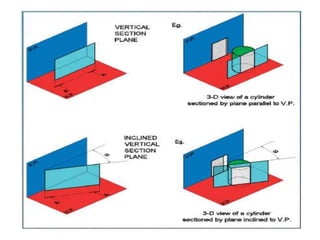
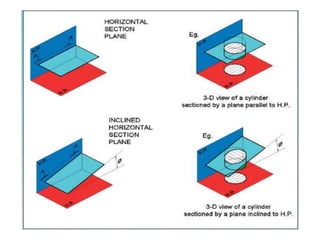
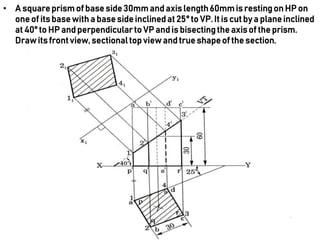
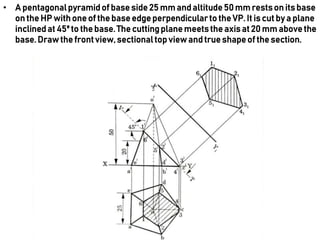
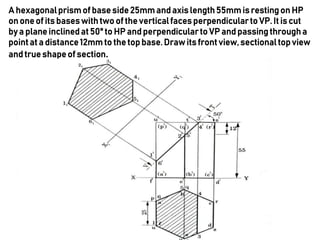
This document provides information on sectioning of solids in engineering graphics. It discusses key concepts like section planes, points of intersection, and true shapes of sections. Different types of section planes are described along with their representations. Guidelines are provided for hatching sections and examples given to illustrate obtaining front views, sectional top views, and true shapes of sections for various solids cut by different planes.