This document discusses various topics related to decision making, including:
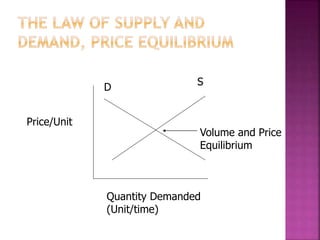
1) It describes decision making as encompassing many small decisions made throughout the day, as well as more complex problems that require organized thought and have economic components.
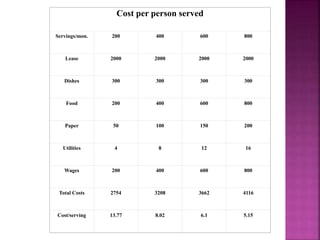
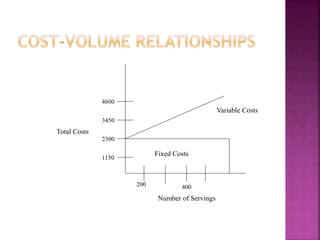
2) It discusses different types of costs like fixed, variable, and semi-variable costs that are considered in economic analysis and how they relate to volume. Capital expenditures and new product design are provided as examples of problems requiring decision making.
3) An example is given showing how total costs change with volume based on the cost-volume relationship, with fixed costs remaining constant and variable costs and average unit costs decreasing as volume increases.