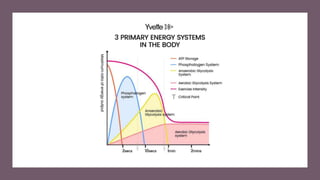
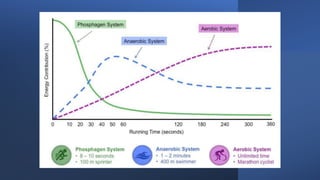
The document discusses three energy systems - anaerobic A-lactic, anaerobic lactic, and aerobic.
1) Anaerobic A-lactic provides high bursts of energy for up to 10 seconds during activities like sprinting or weightlifting.
2) Anaerobic lactic supplies energy for medium to high intensity activities from 10 seconds to a few minutes and produces lactic acid.
3) Aerobic provides energy for low intensity activities lasting 2 minutes or more and continually produces ATP as long as oxygen is available, without lactic acid production.