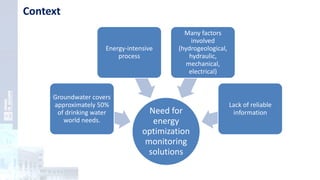
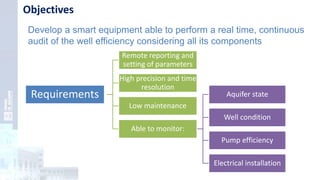
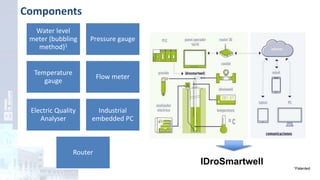
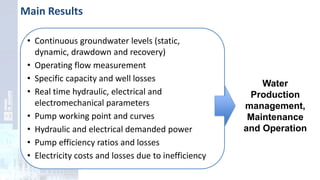
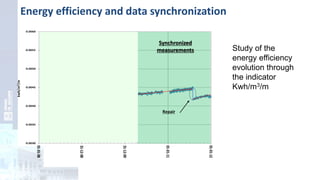
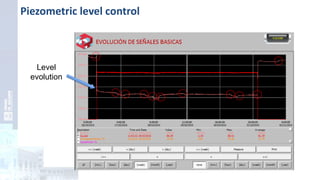
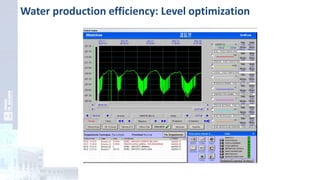
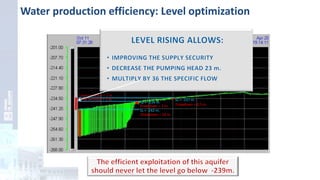
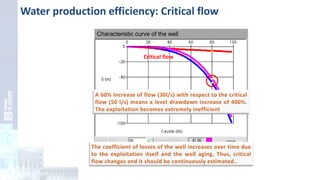
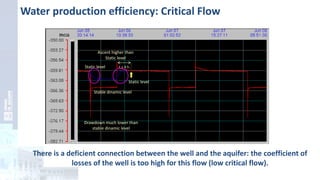
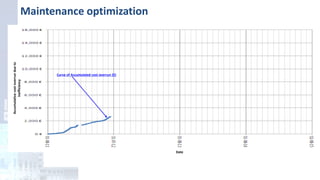
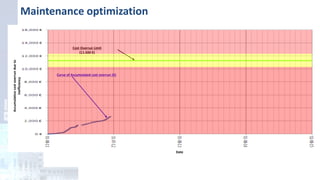
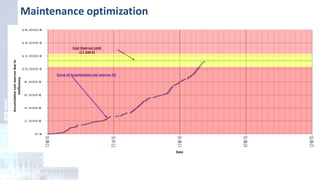
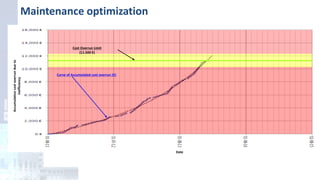
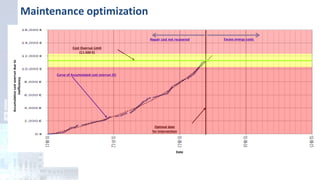
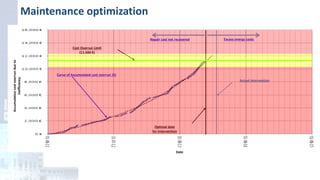
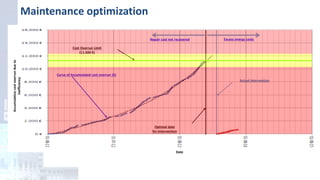
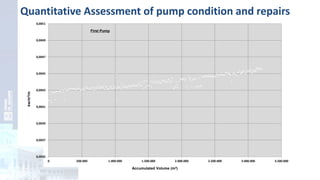
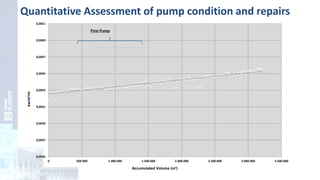
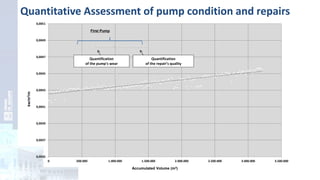
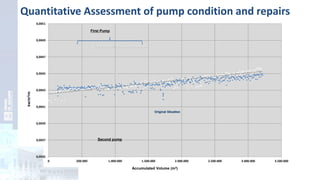
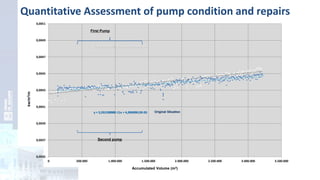
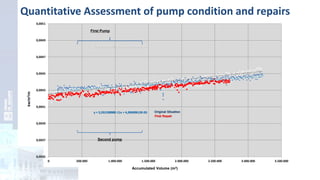
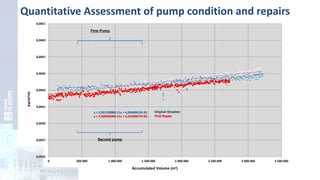
The project focuses on optimizing energy efficiency in groundwater abstraction for Aguas de Alicante, adapting real-time monitoring technology to audit well efficiency and reduce energy costs. Implemented in ten wells, the initiative aims to save approximately 1,934,405 kWh per year, translating to about 260,000 euros in savings. The approach includes assessing pump conditions, efficiencies, and provides comprehensive data reporting for better management and maintenance.