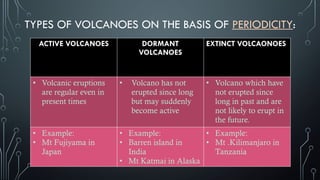
The document discusses endogenetic movements, focusing on volcanoes, which are openings in the Earth's crust that release lava, ash, and gases during eruptions. It categorizes volcanoes based on their structure into central-type and fissure-type, and also by periodicity into active, dormant, and extinct volcanoes. The effects of volcanic eruptions are presented, highlighting both negative impacts, such as loss of life and environmental imbalance, and positive outcomes, like increased soil fertility and mineral deposits.