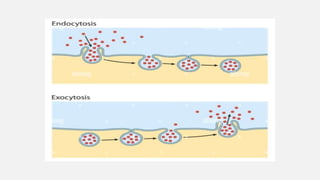
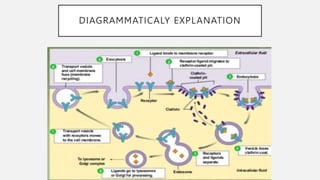
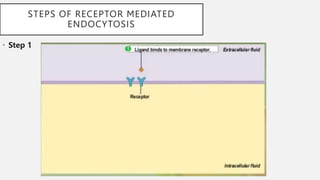
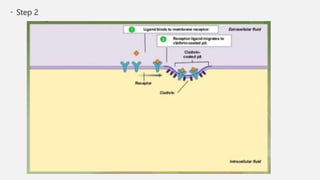
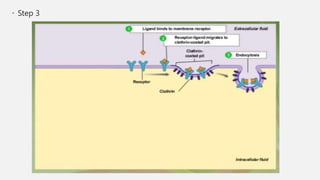
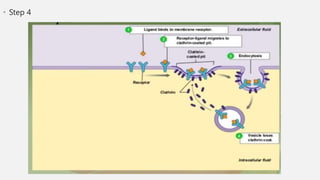
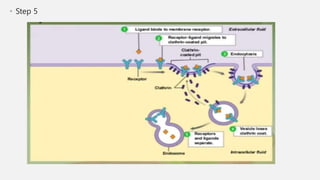
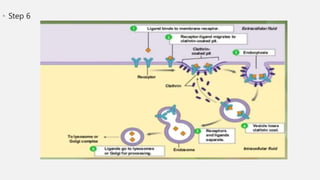
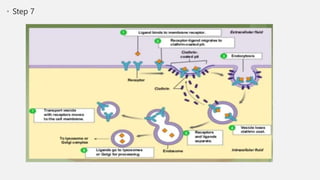
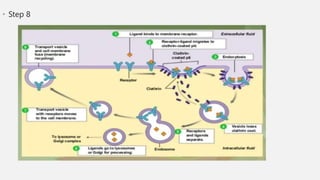
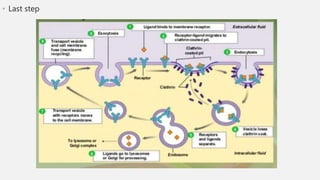
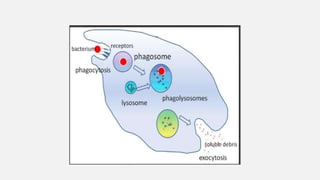
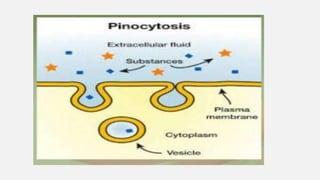
The document explains two processes by which cells move materials across their membranes: endocytosis and exocytosis. Endocytosis involves three types—receptor mediated endocytosis, phagocytosis, and pinocytosis—where cells either ingest large particles or dissolved substances. Phagocytosis, discovered by Ilya Metchnikoff, involves the engulfing of solid particles, while pinocytosis focuses on the intake of liquid or dissolved nutrients.