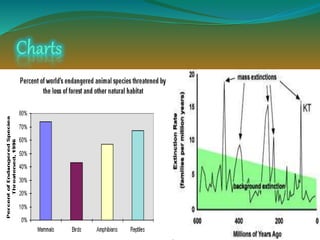
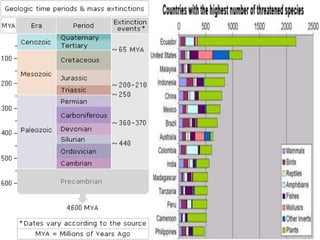
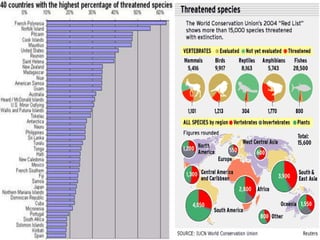
The document discusses various classifications of species based on population levels and threats, ranging from normal species to extinct species. It also explains some of the main threats facing species, including habitat destruction, illegal poaching and wildlife trade, pollution, climate change, and overexploitation from activities like overfishing. Conservation efforts are needed to help protect endangered species and their habitats.