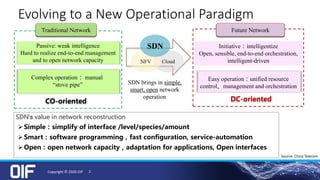
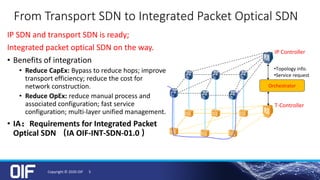
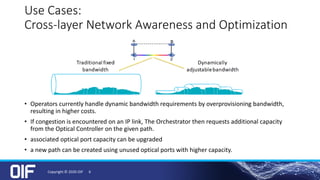
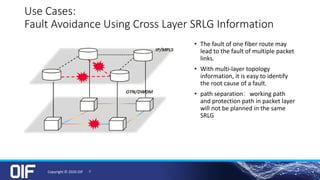
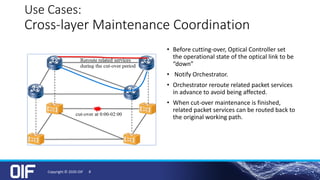
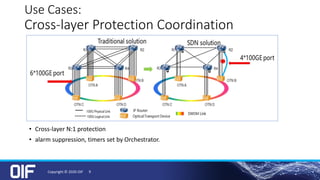
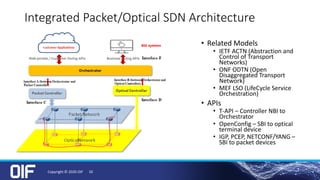
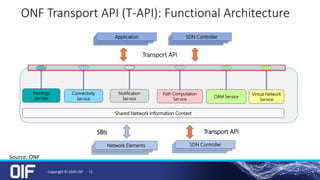
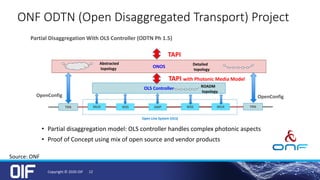
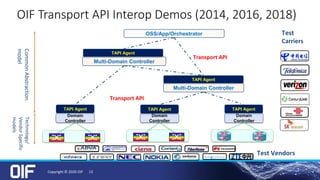
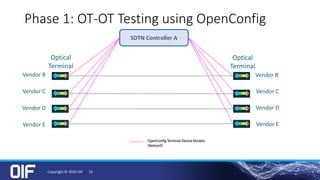
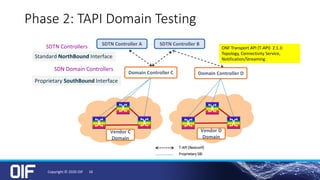
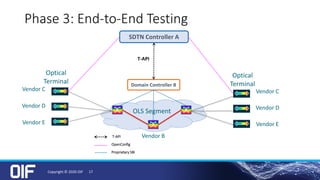
The document discusses the development and implementation of integrated packet/optical SDN (Software-Defined Networking) to enhance transport network operations, aiming for simpler, smarter, and more open network management. It outlines the OIF's mission to foster interoperability among over 100 members across the industry while detailing specific use cases, architecture requirements, and testing phases for the orchestration of these networks. The OIF has provided substantial input to accelerate standardization and ensure efficient delivery of dynamic connectivity services.