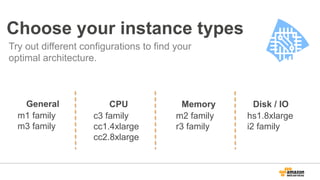
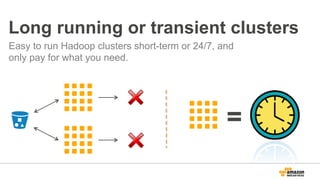
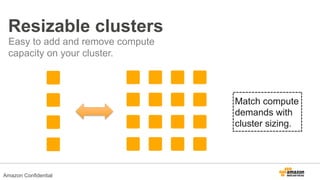
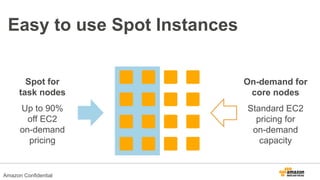
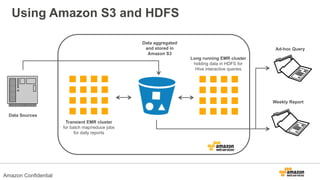
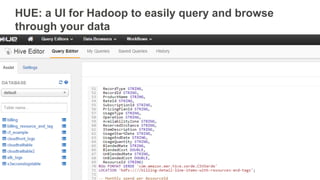
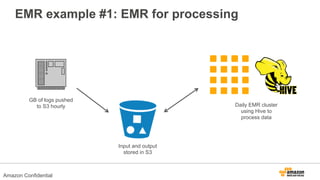
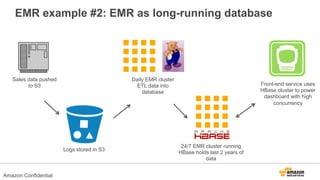
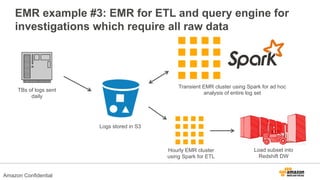
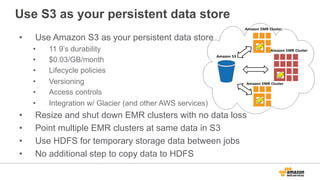
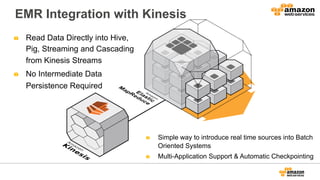
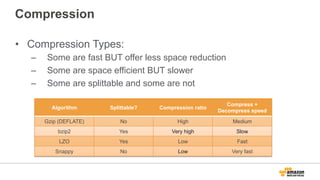
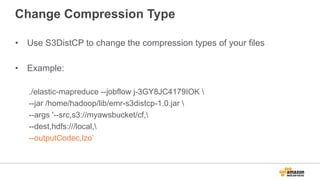
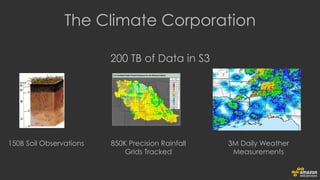
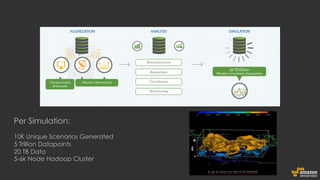
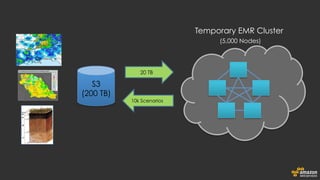
The document discusses using Amazon EMR to scale analytics workloads on AWS. It provides an overview of EMR and how it allows users to easily run Hadoop clusters on AWS. It discusses how EMR allows tuning clusters and reducing costs by using Spot instances. It also discusses using various AWS services like S3, HDFS and integrating various Hadoop ecosystem tools on EMR. It provides examples of using EMR for batch processing logs, as a long-running database and for ad-hoc analysis of large datasets. It emphasizes using S3 for persistent storage and provides best practices around file sizes, compression and bootstrap actions.