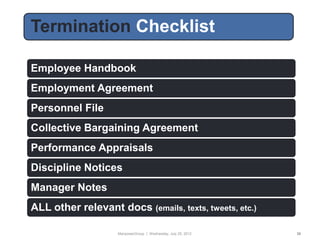
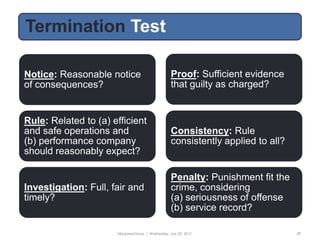
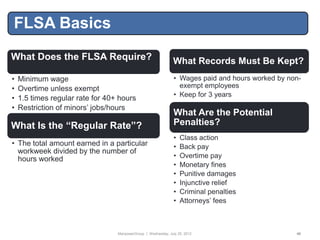
This document provides an employment law toolbox with various cheat sheets and guides on important employment law topics. It includes 3-sentence summaries of key employment laws such as the ADA, ADEA, EPA, ERISA, COBRA and FCRA. The toolbox is intended to serve as a quick reference for understanding essential elements of major employment statutes and avoiding common legal pitfalls.












































![Law Firm Guidelines
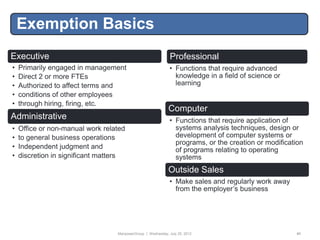
Initial Information
Please contact [NAME] promptly at the outset of each matter to discuss: (1) your proposed strategy; (2) the Company‟s potential
liability, if any; and (3) an estimate of fees and expenses, including the billing rates of each attorney or paralegal expected to
work on the matter.
If you are handling a litigation matter; please provide the following additional information: (1) all key dates, including trial; (2)
anticipated discovery; (3) whether mediation or arbitration may be appropriate; and (4) settlement potential, including estimated
settlement value.
Staffing
We expect your firm to work jointly with the Company to determine how the matter will be staffed. No changes in staffing or
billing rates may be made without the Company‟s prior approval.
Budgets
A written budget is required on all matters. Please use the attached form. Budgets may not be changed or exceeded without the
Company‟s approval.
Unauthorized Expenses
The Company will not pay for any of the following without prior approval: (1) legal memoranda; (2) deposition summaries; (3)
computer legal research exceeding $500; (4) travel expenses exceeding $500 or first-class travel; (5) attendance by more than
one person at any meeting, deposition or hearing; (6) expert witnesses, consultants or local counsel; (7) work done by local
counsel other than routine filings; (8) legal research to educate your staff in a substantive area; (9) time for attorneys or
paralegals to get up-to-speed on a matter due to staffing changes; (10) filing, word processing, proofreading, librarian or other
clerical costs; (11) photocopy expenses exceeding ten cents per page or $250 for a single job; (12) fax charges exceeding actual
phone charges; (13) local phone charges; (14) special/rush messengers; (15) office supplies; (16) entertainment expenses; (17)
work caused by your firm‟s error; (18) time spent preparing, reviewing or discussing budgets or invoices; and (19) any other
disbursements other than at cost.
ManpowerGroup | Wednesday, July 25, 2012 51](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webinareltoolbox-120725083928-phpapp02/85/Employment-Law-Toolbox-51-320.jpg)
![Law Firm Guidelines (continued)
Litigation
The Company‟s approval is required prior to: (1) filing any claim or lawsuit; (2) taking any significant legal position; (3) requesting
or responding to discovery; (4) making any substantive motion; (5) settling any matter; or (6) appealing any ruling or judgment.
No significant communication or court document should be sent without the Company‟s prior approval. We expect you to keep
the Company informed of all significant developments and key dates.
The Company seeks to balance the need to resolve matters expeditiously with the need to protect the Company‟s policies,
practices and positions on significant legal issues. We expect you to work with the Company to identify matters that are
appropriate for early resolution or for alternative dispute resolution through mediation, arbitration or other means.
Do not engage experts, consultants or local counsel without the Company‟s prior approval. We expect you to supervise and
monitor the expenses related to such persons and to notify the Company if any such services are expected to exceed $1,000.
Confidentiality
Do not discuss any matter or any aspect of your representation of the Company with any media or any other person outside your
firm without the Company‟s prior approval. Forward all media inquires to [NAME] immediately. We expect your firm to take all
necessary steps to protect the attorney-client privilege, including protecting these guidelines and all related documents from
disclosure.
Conflicts of Interest
Notify the Company immediately of any potential conflicts of interest or ethical concerns. Your firm may not continue in its
representation of the Company until the conflict or concern has been resolved or waived in writing by the Company.
Immediately notify the Company of any of the following: (1) your firm‟s representation of any parties or related entities that are
potentially adverse to the Company in any matter; (2) any litigation in which your firm is asserting any issue opposed to the
Company‟s interests; (3) any representation by your firm of any competitor of the Company; and (4) any other issue that could
potentially result in a conflict of interest or ethical concern..
ManpowerGroup | Wednesday, July 25, 2012 52](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webinareltoolbox-120725083928-phpapp02/85/Employment-Law-Toolbox-52-320.jpg)
![Law Firm Guidelines (continued)
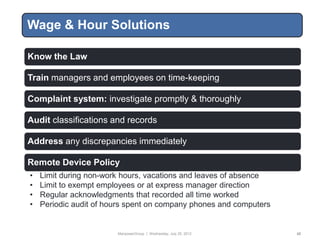
Invoices
Please submit invoices on a monthly basis to [NAME]. Each invoice must include: (1) the date and name of the person who
performed each task; (2) the hourly rate; (3) a detailed description of each task; (4) the amount of time expended on each task;
and (5) total cost per day. For example:
Date Name Rate Description Time Cost
01/01/08 J Law $145 Telephone conference with D. Miller to prepare for 0.7 $101.50
deposition (0.3); draft J. Wilson affidavit (0.2); review
settlement demand from opposing counsel (0.2)
For each matter, also include: (1) total hours and fees billed that month by each person; total fees, costs and disbursements for
the month; and (3) total fees, costs and disbursements to date. In addition, provide copies of all vendor invoices (e.g.,
transcripts, expert witnesses, outside copying, etc.).
Report Card
To help improve the working relationship, the Company will periodically provide feedback to your firm using the attached report
card. Areas rated include cost, results, responsiveness, practicality, expertise, knowledge of the Company and its industry and
adherence to these guidelines.
Thank you for your service on behalf of the Company and attention to these guidelines.
Agreed to by:
__________________________________
Date: _____________________________
ManpowerGroup | Wednesday, July 25, 2012 53](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webinareltoolbox-120725083928-phpapp02/85/Employment-Law-Toolbox-53-320.jpg)
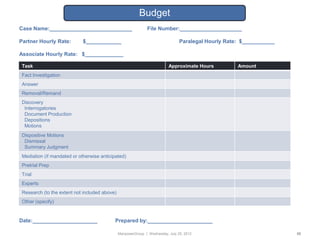
![Law Firm Report Card
Firm Name:
Subject Area(s) (e.g., litigation)
Criteria Grade Comments
Cost
Results
Responsiveness
Subject matter expertise
Practicality of advice
Knowledge of [COMPANY
NAME] & industry
Adherence to Outside Counsel
Guidelines
Overall Grade:
Additional Comments:
ManpowerGroup | Wednesday, July 25, 2012 54](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webinareltoolbox-120725083928-phpapp02/85/Employment-Law-Toolbox-54-320.jpg)
![Law Firm Request for Proposal (RFP) Guidelines
Introduction
To maintain the integrity of its law firm selection and retention process, [COMPANY NAME] adheres to the
following request for proposal (RFP) policy.
Circumstances Where An RFP May Be Appropriate
• The Company is faced with a new or unique legal issue.
• The Company is faced with a legal issue that may have an unusually large spend or cost.
• The Company does not have a current relationship with legal counsel that has the expertise or skills to
handle a particular issue or believes that current legal counsel should reduce fees for this particular
project.
• Every three years for all law firms with more than $10,000 in annual fees.
RFP Process
• RFPs are overseen by a Selection Review Team (SRT) consisting of [IDENTIFY TEAM, e.g., reps from
HR, Legal, Procurement, etc.].
• The SRT will coordinate the RFP and communicate with each competing firm regarding the steps in the
process.
• Participating law firms may be required to submit budget estimates, provide references and/or visit the
Company‟s headquarters for an interview.
ManpowerGroup | Wednesday, July 25, 2012 56](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webinareltoolbox-120725083928-phpapp02/85/Employment-Law-Toolbox-56-320.jpg)