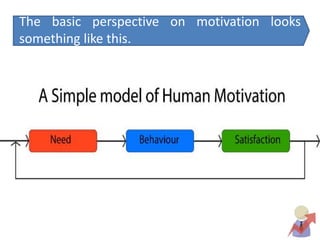
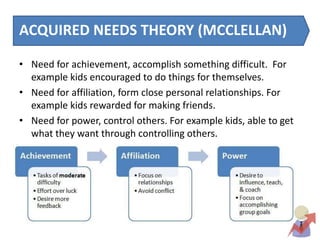
This document discusses employee motivation and provides an overview of relevant theories. It outlines factors that encourage motivation, including management actions, communication, respect, and benefits. Theories covered include Maslow's hierarchy of needs, McClelland's acquired needs theory, and Herzberg's two-factor theory. The importance of motivation for performance, retention, and productivity is also discussed. Recommendations for motivating employees include recognition, feedback, involvement in decision-making, and celebrating successes.