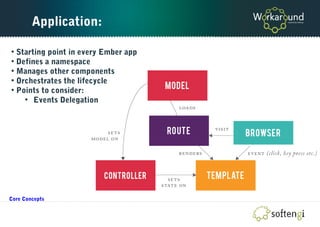
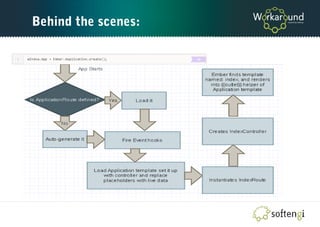
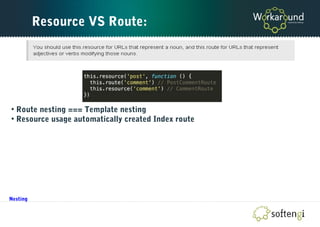
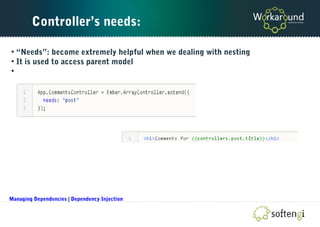
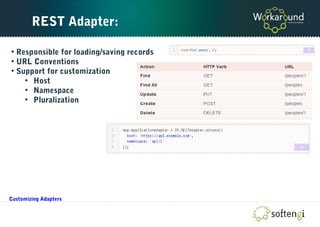
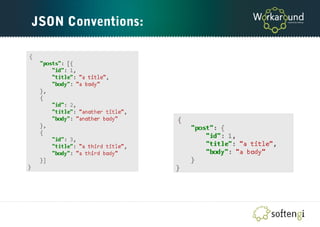
The document is a comprehensive guide on Ember.js, a JavaScript MVC framework for building ambitious web applications, detailing its core concepts, tools, and testing methods. It covers the framework's favoring of convention over configuration, the structure of applications, and the importance of the router, models, and components. Additionally, it provides insights into Ember CLI for productivity and testing strategies for applications built on Ember.js.