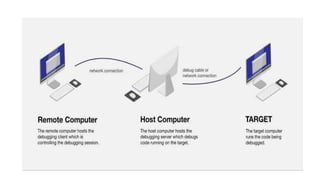
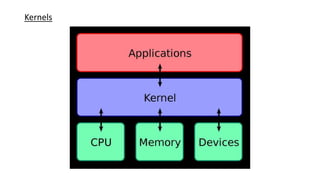
The document discusses host-based debugging, emphasizing the challenges posed by architectural differences such as word size and byte order when debugging C/C++ and assembly applications. It elaborates on remote debugging, kernels, ROM emulators, logic analyzers, and 'bulletproof run control' to ensure consistent and reliable testing results. Each tool and technique is essential for identifying and resolving issues in embedded systems and enhances overall software quality.