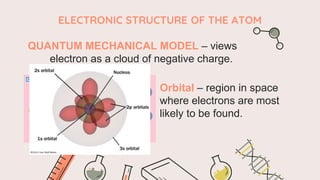
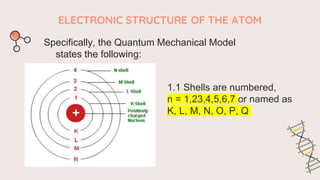
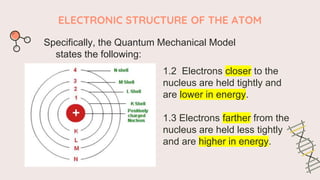
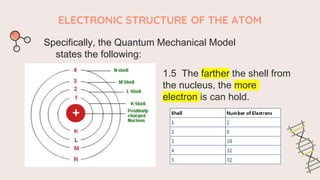
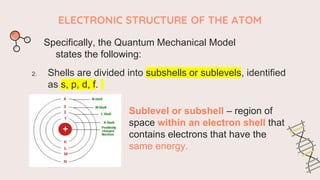
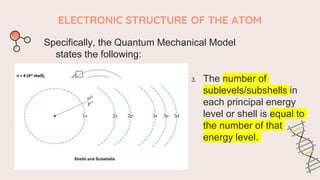
The document describes the quantum mechanical model of the atom. It states that the model views electrons as existing in clouds or orbitals around the nucleus, with higher probability of finding electrons in regions called principal energy levels or shells. Electrons in inner shells are held more tightly and have lower energy than those in outer shells. Shells are divided into subshells which are further divided into orbitals that can each hold two electrons. Electrons fill the lowest energy orbitals first according to the Aufbau principle.