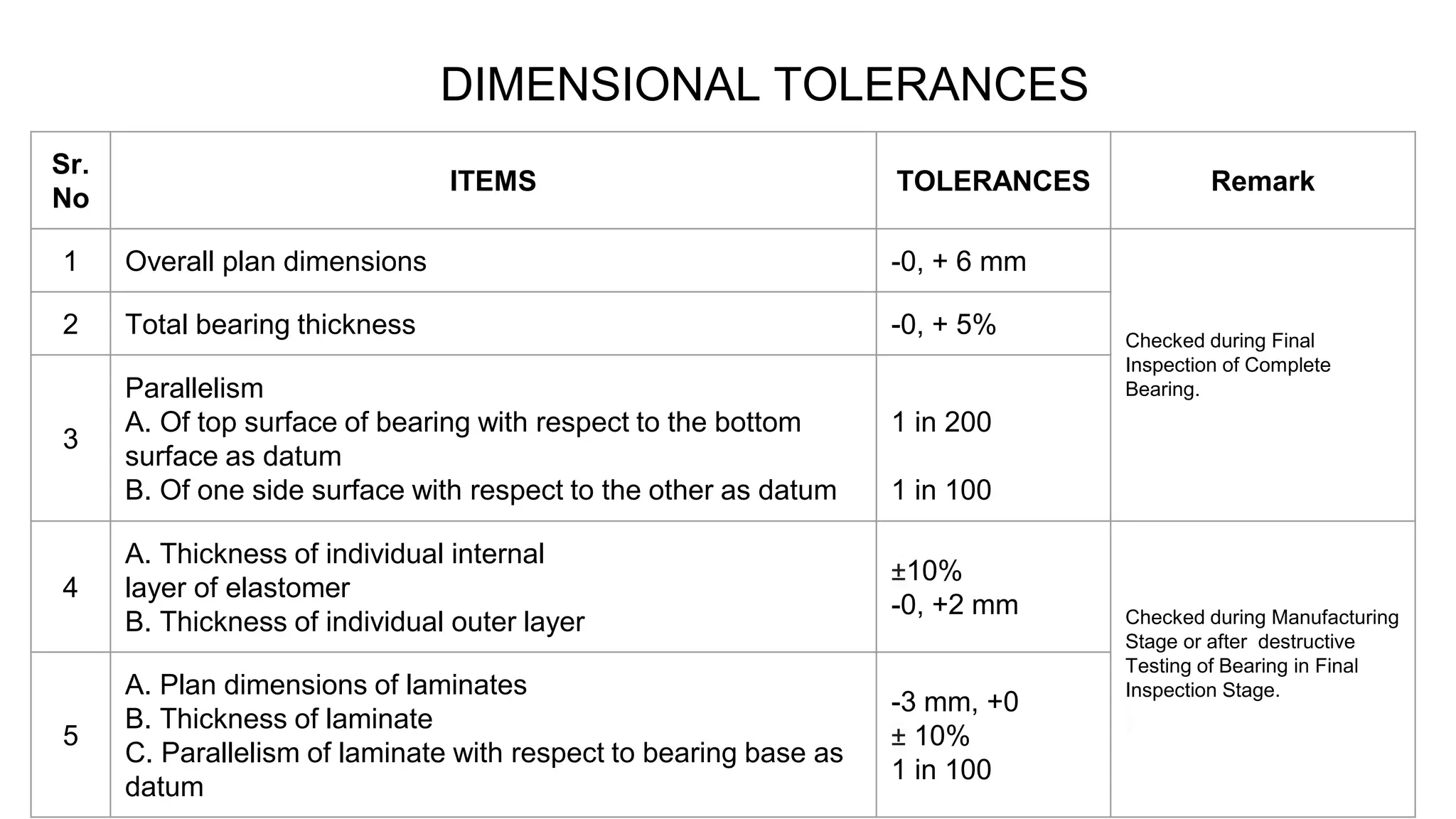
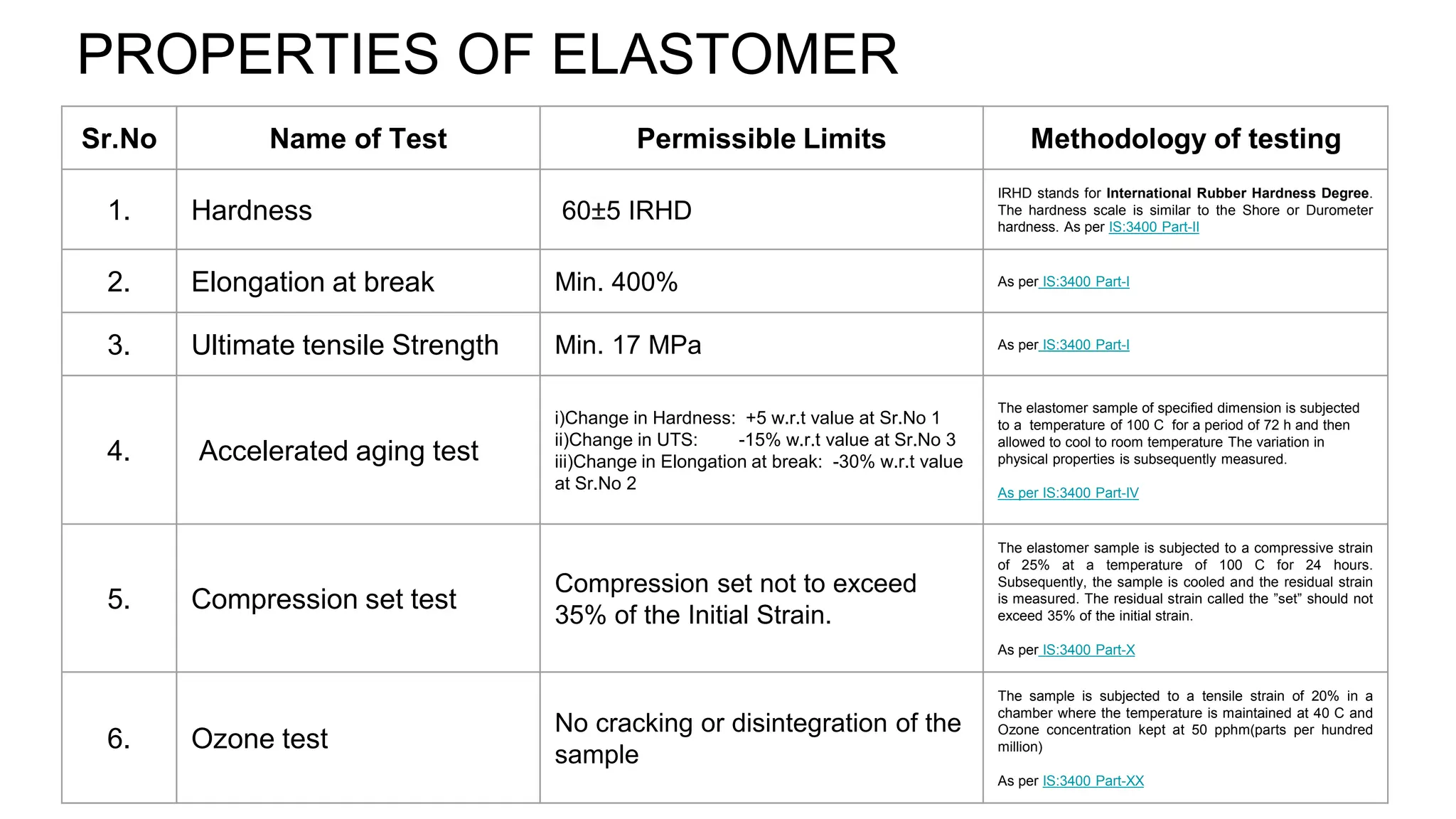
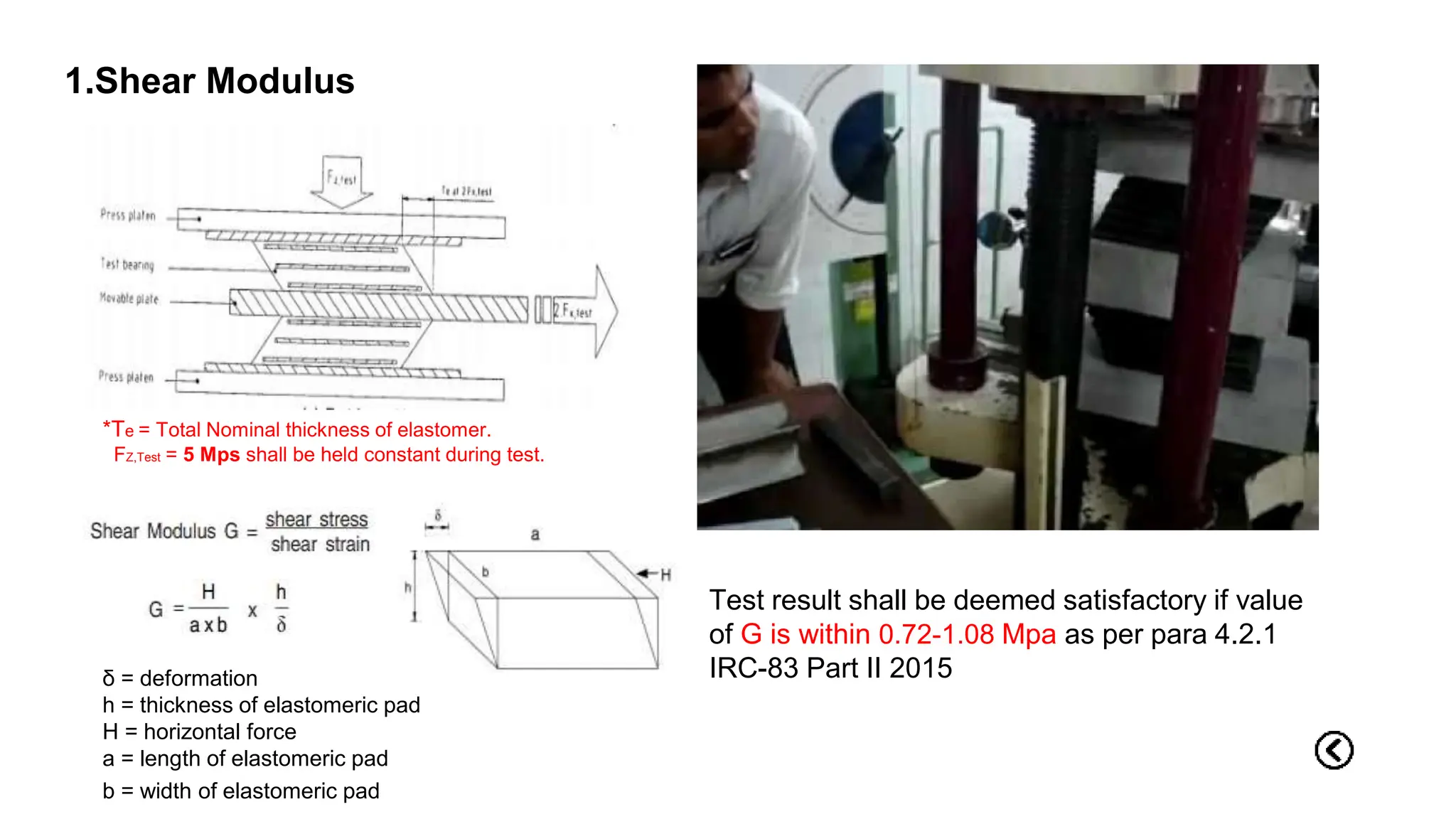
The document outlines the testing procedures and standards for elastomeric bearings as per IRC:83 Part-II-2015, highlighting the importance of pre-manufacture checks to prevent early deterioration and costly replacements. It details specific tests for both the elastomer and steel components, acceptance criteria for different lot sizes, and certification requirements for quality assurance. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of inspection post-installation to ensure proper functioning of the bearings.