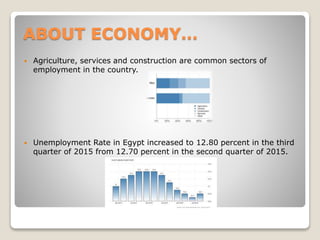
Egypt is located in North Africa, bordering the Mediterranean Sea, Libya, Gaza Strip, Israel, and Sudan. The official name is the Arab Republic of Egypt and it joined the UN in 1945. Arabic is the most widely spoken language, along with English and French. Islam is the dominant religion practiced by about 87% of residents. The current president is Abdel Fattah el-Sisi and Egypt has a presidential republic system of government. The population is over 86 million and growing, with a high birth rate attributed to poverty. Unemployment is around 12.8% with agriculture, services, and construction common jobs. The climate is hot desert apart from the northern coast.