This document summarizes a master's thesis on Jatropha as a biofuel feedstock in Zambia. The thesis examines the environmental, economic, and social impacts of the growing Jatropha industry in Zambia. It addresses issues related to Jatropha cultivation, processing, and the use of biodiesel and byproducts. Questionnaires were distributed to small-scale and commercial Jatropha farmers. The results indicate potential benefits like rural development and job creation, but also uncertainties around food security, poverty reduction, and dependence on subsidies. Both positive and negative impacts depend on various social, economic, and environmental factors. Further research is needed to inform policy as the industry expands.



































































![6.1 Internet References
Abdrabbo, A. Atta, N. M.M. Kheira, A., 2008. Response of Jatropha curcas L. to
water deficit: Yield, water use efficiency and oilseed characteristics. Biomass & Bio-
energy xxx, Elsevier [Online] available at
www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=Article [Accessed on 2008-11-14]
Advanced Bio-fuel Solutions [Online] available at
www.advancedbiofuel.net/Introduction.htm [Accessed 2009-01-09]
Baur, H. Meadu, V. van Noordwijk, M. Swallow, B., 2007. Bio-fuel from Jatropha
curcas: opportunities, challenges and development perspectives. World Agroforestry
Centre [Online] available at www.worldbankagroforestry.org_PO07207.pdf,
[Accessed on 2008-12-18].
Benge, M., 2006. Assessment of the potential of Jatropha curcas, (biodiesel tree,) for
energy production and other uses in developing countries. USAID. [Online] available
at:www.echotech.org/mambo/index.php?option=com_docman&task=doc_view&gid
[Accessed on 2009-04-28].
Byrne, B. 1994. Gender Profile of Zambia. Institute of Development Studies
University of Sussex, [Online] available at :www.bridge.ids.ac.uk/reports/re29c.pdf
[Accessed on 2009-04-05].
CJP., 2008. Centre for Jatropha Promotion & Biodiesel. [Online] available at
www.jatrophaworld.org, [Accessed on 2008-11-14]
Demirbas. A., 2007. Importance of bio-diesel as transportation fuel. Sila Science, P.
K. 216, TR-61035 Trabzon, Turkey Received 1 February 2007; accepted 1 A [Online]
available at www.elsevier.com/locate/enpol Energy Policy 35 (2007) 4661–4670)
[Accessed on 2008-12-28].
Energy Information Administration. Official Energy Statistics from the U.S.
Government. [Online] available at (http://www.eia.doe.gov). [Accessed 2009-05-07].
Fact Bio Diesel Limited [Online] available at
http://www.factbiodiesel.com/process_large.jpg) [Accessed 2009-04-29]
FAO., 2008. Breeding and cultivation of sweet sorghum [Online] available at
http://www.fao.org/docrep/t4470e/t4470e05.htm [Accessed 2008-12-25]
Gheewala, S.H. Prueksakorn, K., 2006. Energy and Greenhouse Gas Implications of
Bio-diesel Production from Jatropha curcas L. The Joint Graduate School of Energy
and Environment, King Mongkut’s University of Technology Thonburi, Bangkok,
Thailand [Online] available at http://www.jgsee.kmutt.ac.th/see1/cd/file/E-053.pdf
[Accessed 2009-05-06]
Jatropha Tech [Online] available at (http://www.jatrophatech.com/index.htm).
[Accessed 2009-05-03]
62](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fulltext011-120501141634-phpapp02/75/Jatropha-Zambia-s-First-Bio-diesel-Feedstock-74-2048.jpg)
![July 2008. Final Draft Position Paper on Jatropha Curcas in Zambia. [E-mail]
(Personal communication, 6 February 2009).
Kimble, M. Pasdeloup, M.V. Spencer, C., 2008. Sustainable Bio-energy Development
in UEMOA Member Countries. [Online] available at (http://www.globalproblems-
globalsolutionsfiles.org/gpgs_files/pdf/UNF_Bioenergy/UNF_Bioenergy_full_report.
pdf) [Accessed on 2008-12-28]
Kumar, A. Sharma, S., 2008. A review (Jatropha curcas L.): industrial crops and
products. (2008), www.elsevier.com/locate/indcrop, [Online] available at –
www.sciencedirect.com) [Accessed on 2008-11-28]
Map of Zambia [Online] available at (http://www.geology.com/world/zambia-
map.gif) [Accessed 2009-04-26]
Müller, A. Schmidhuber, J. Hoogeveen, J. Steduto, P., 2007. Some insights in the
effect of growing bio-energy demand on global food security and natural resources,
[Online] available at www.globalbioenergy.org/uploads/media/0701_FAO_Mueller)
[Accessed on 2009-01-10]
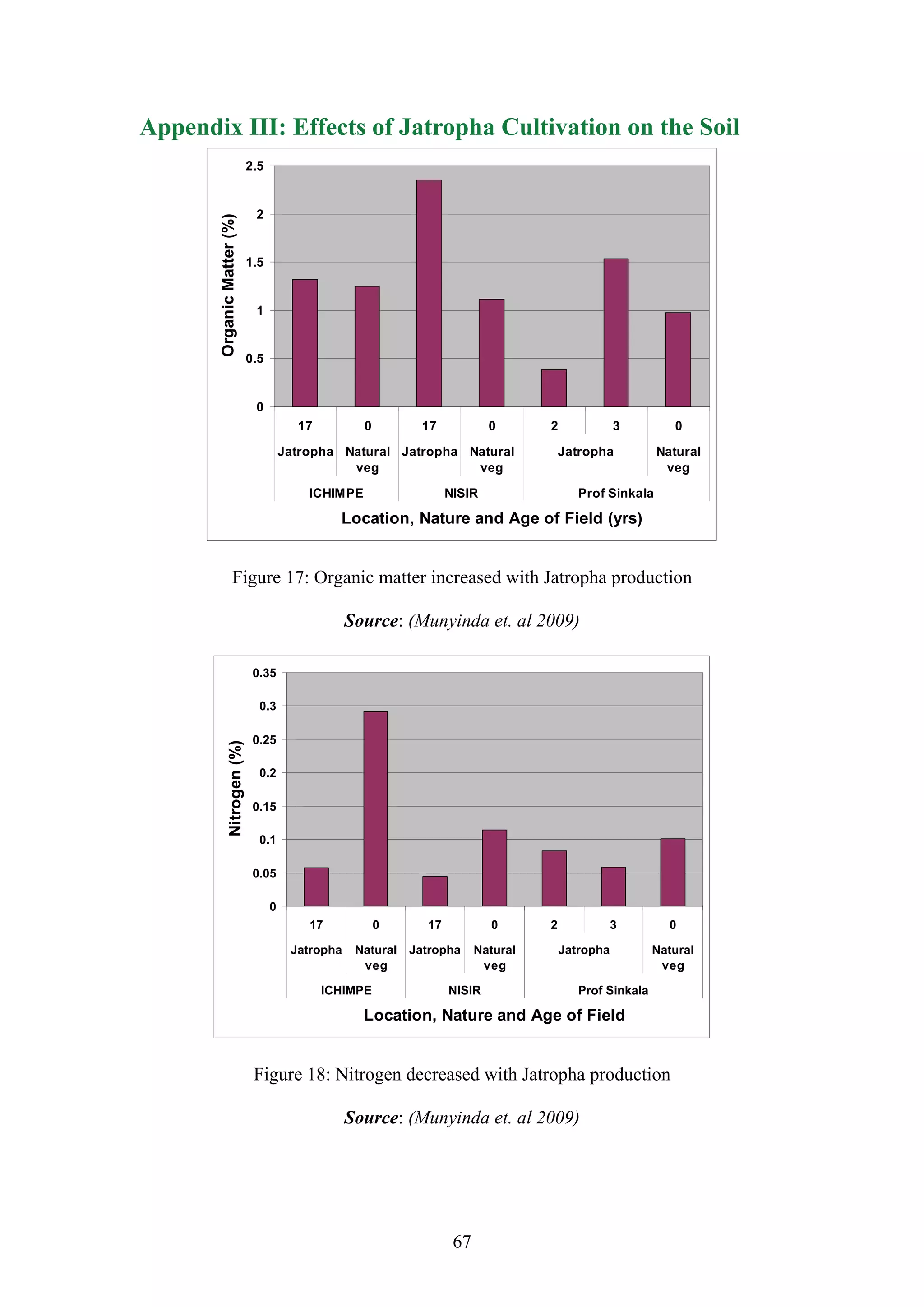
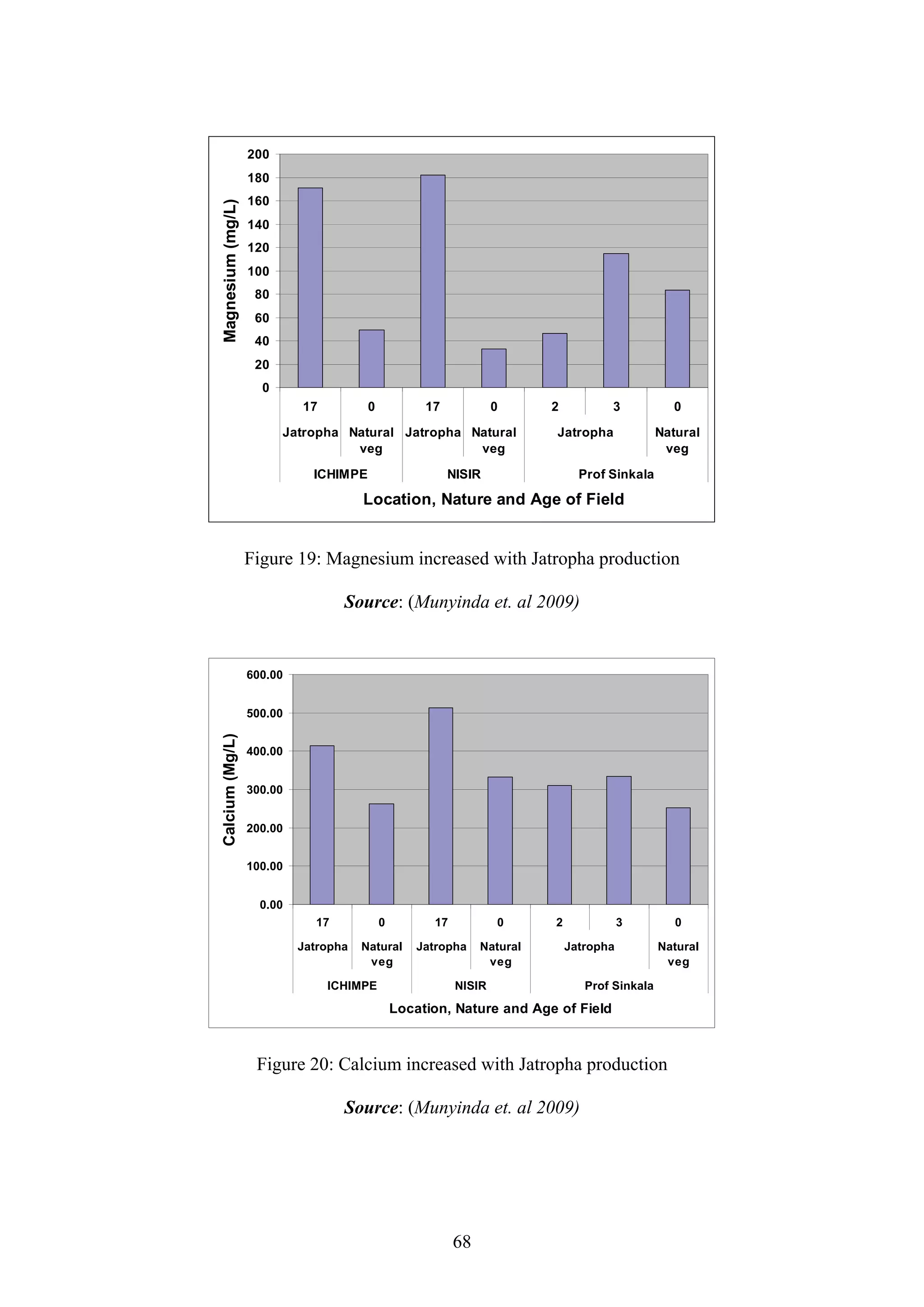
Munyinda, K. Yerokun, O. Mataa, M. Mutambo, M. Mooba, C. Effect of Jatropha on
Soil Quality and Crop Improvement of Jatropha. School of Agricultural Sciences,
Crop Science Department, University of Zambia. (Accepted for publication January
2009).
National Bio-fuels Study., 2006. An Investigation into the Feasibility of Establishing
a Bio-fuels Industry in the Republic of South Africa. Final Report. [Online] available
at http://www.africanbiofuels.co.za/Biofuels_Feasibility_SA.pdf [Accessed on 2009-
04-06]
Openshaw, K., 2000. A review of Jatropha curcas: an oil plant of unfilled promise.
[Online] available at www.elsevier.com/locate/biombioe, Biomass and Bio-energy 19
(2000) [Accessed on 2008-10-28]
Oval Biofuels Limited [Online] available at www.ovalbiofuels.com [Accessed on
2009-04-06]
Rajagopal, D. Zilberman, D., 2007. Review of Environmental, Economic and Policy
Aspects of Bio-fuels. Policy Research Working Paper – 4341. Sustainable Rural and
Urban Development. University of California. [Online] available at
http://are.berkeley.edu/~dwrh/CERES_Web/Docs/wps4341.pdf [Accessed on 2009-
04-06]
Renewable Energy UK [Online] available at www.reuk.co.uk/Pressing-Jatropha.html
[Accessed on 2009-05-05]
Schuppers, J., 2006. Biofuels in the European Union. – A Vision for 2030 and Beyond.
Final draft report of the Biofuels Research Advisory Council [Online] available at
http://ec.europa.eu/research/energy/pdf/draft_vision_report_en.pdf [Accessed on
2009-04-11].
63](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fulltext011-120501141634-phpapp02/75/Jatropha-Zambia-s-First-Bio-diesel-Feedstock-75-2048.jpg)
![Sun Ecofuels Private Limited. [Online] available at http://www.sunecofuels.com
[Accessed on 2009-04-06]
Tigere, T.A. Gatsi, T.C. Mudita, I.I. Chikuvire, T.J. Thamangani, S. Mavunganidze,
Z., 2006. Potential of Jatropha Curcas in Improving Smallholder Farmers’
Livelihoods in Zimbabwe: An Exploratory Study of Makosa Ward, Mutoko District .
[Online] Available at http://www.jsd-africa.com/Jsda/Fall2006/PDF [Accessed on
2009-01-10]
64](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fulltext011-120501141634-phpapp02/75/Jatropha-Zambia-s-First-Bio-diesel-Feedstock-76-2048.jpg)