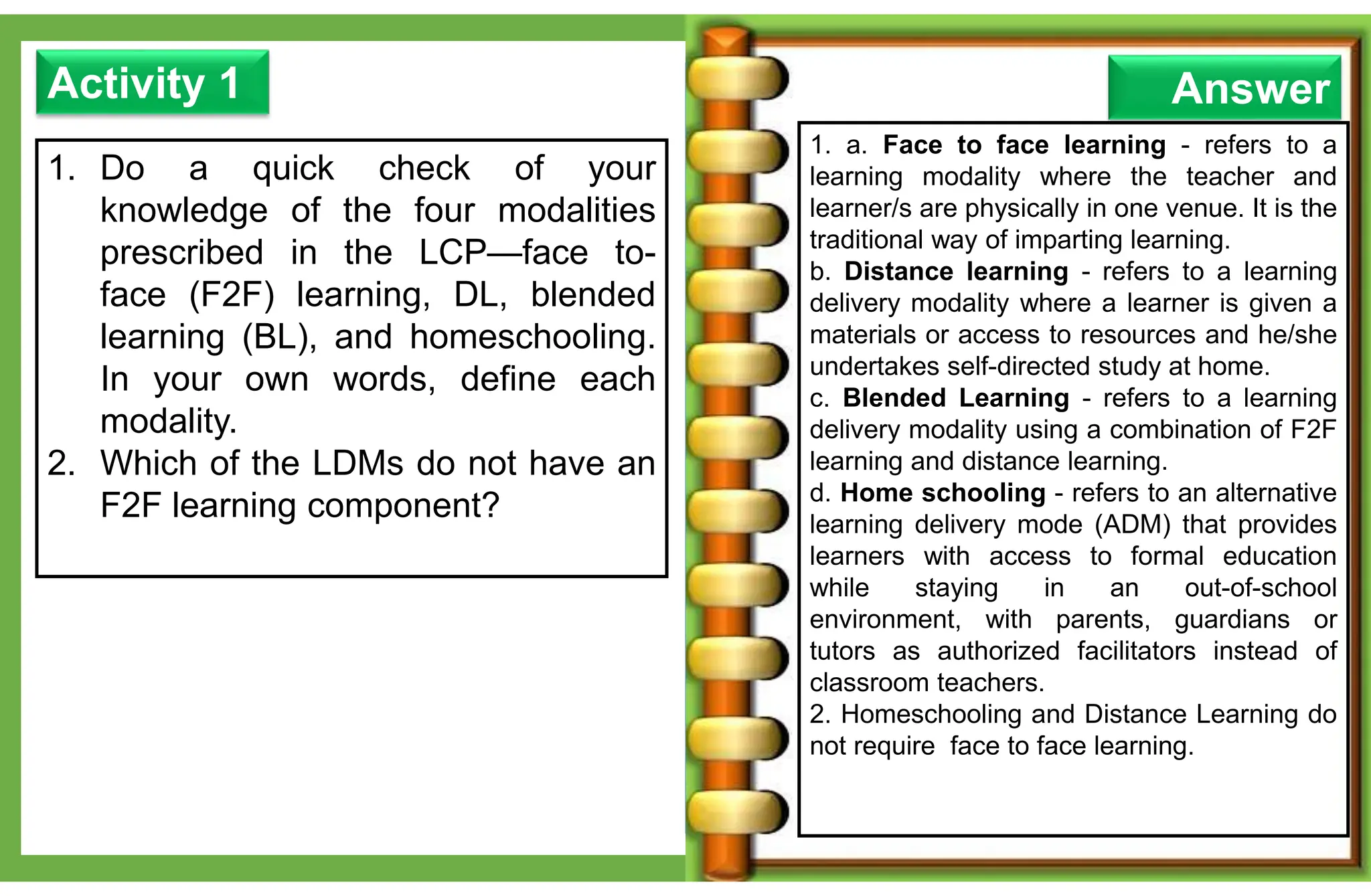
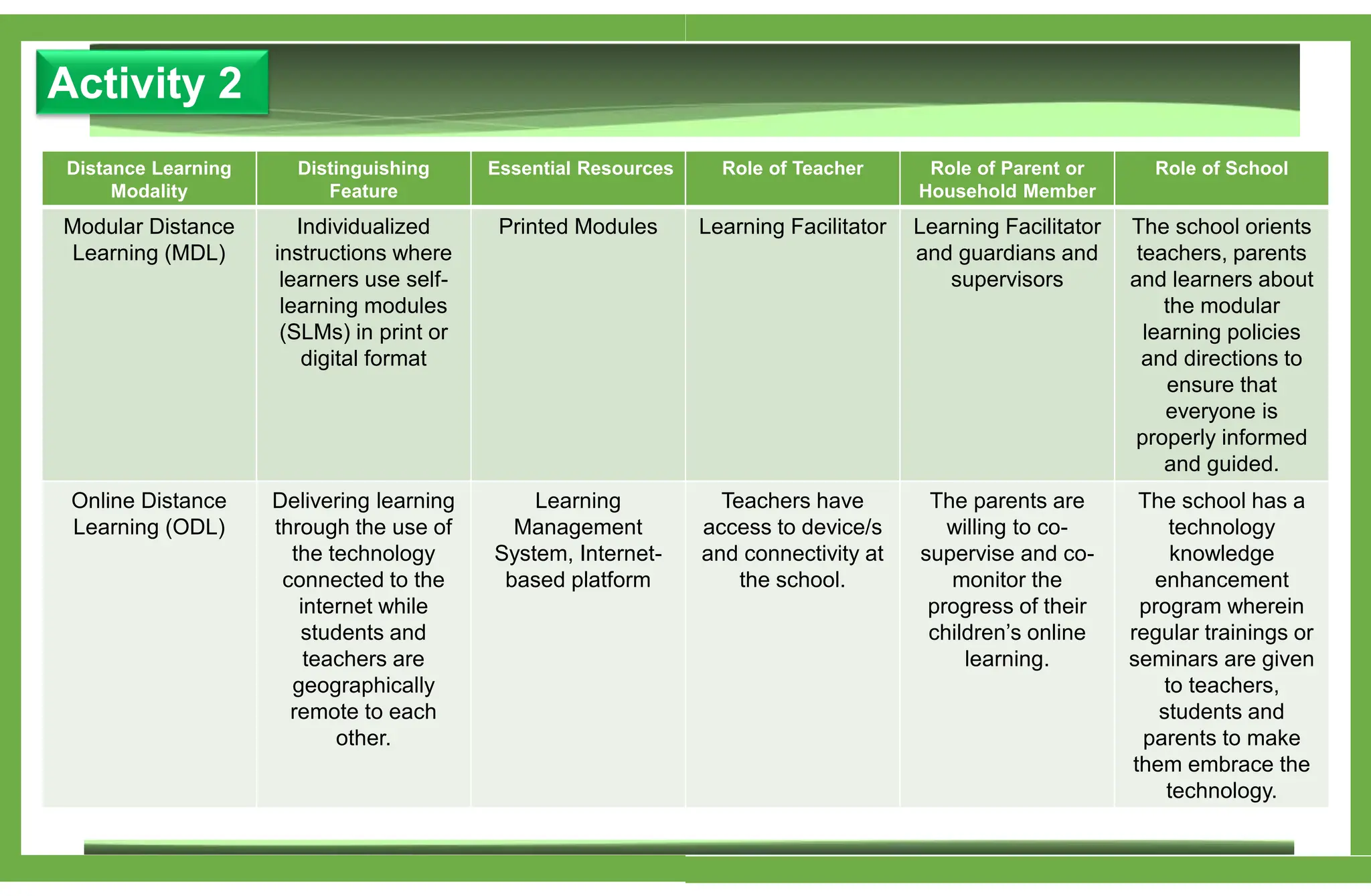
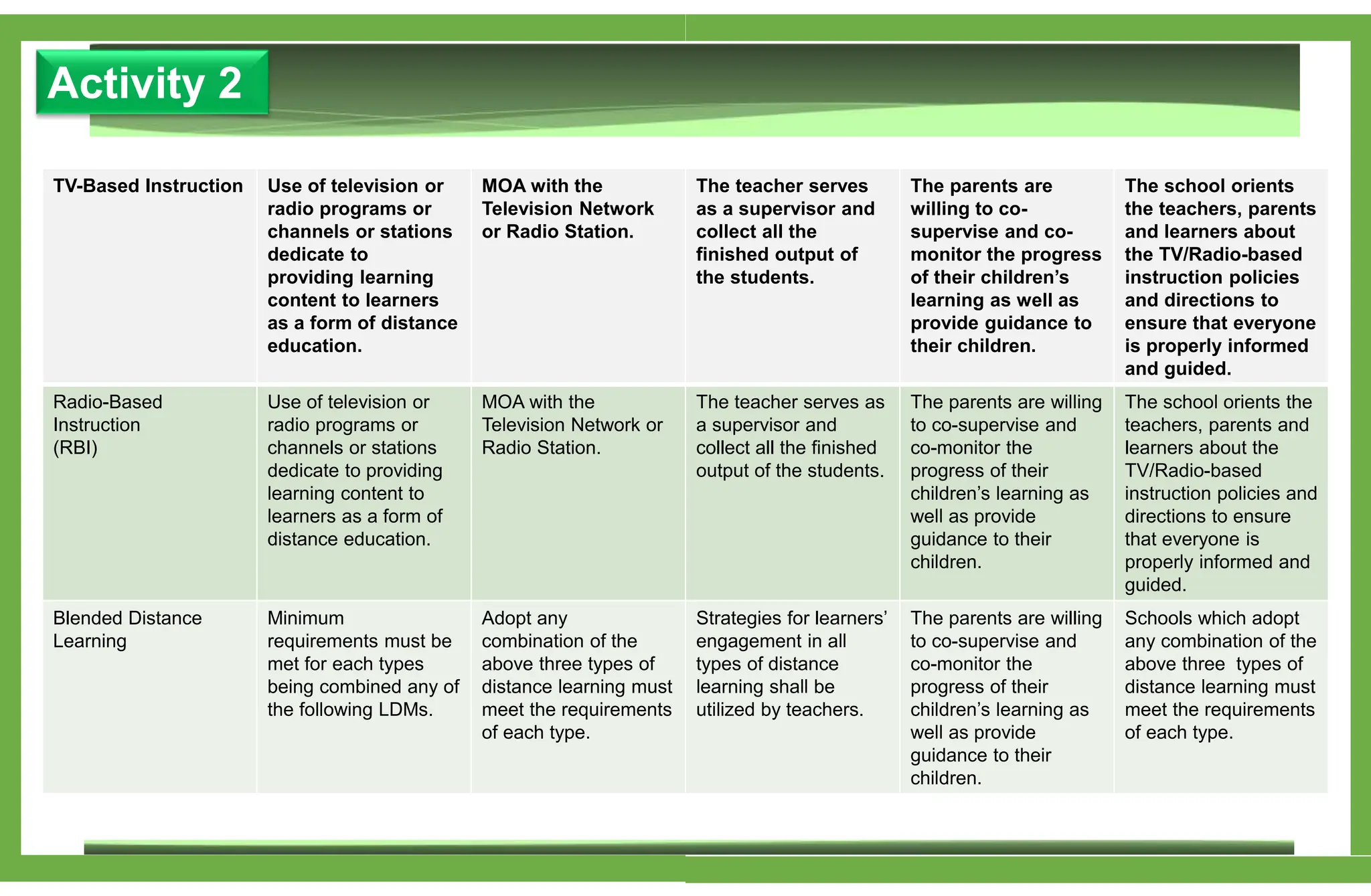
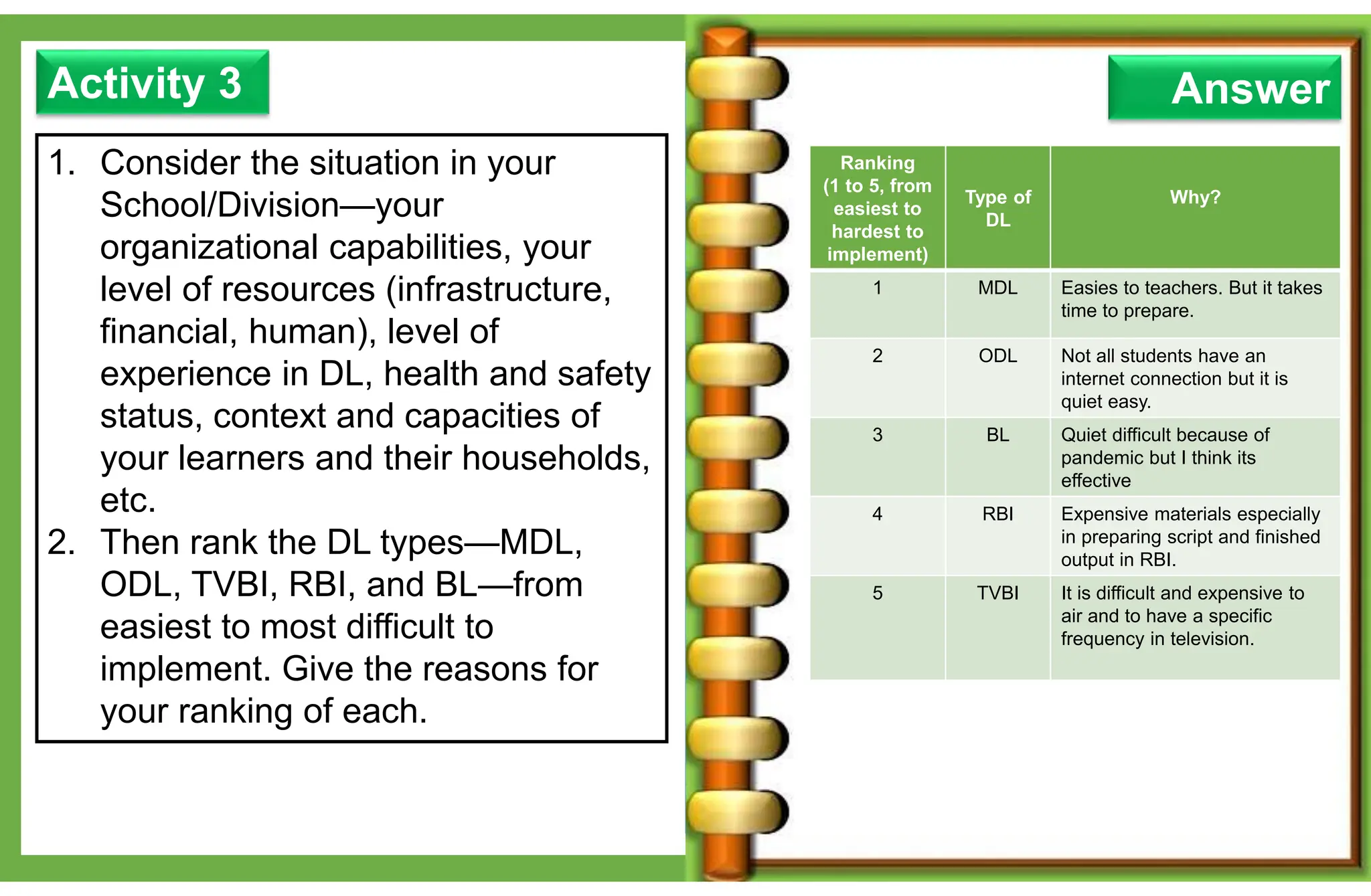
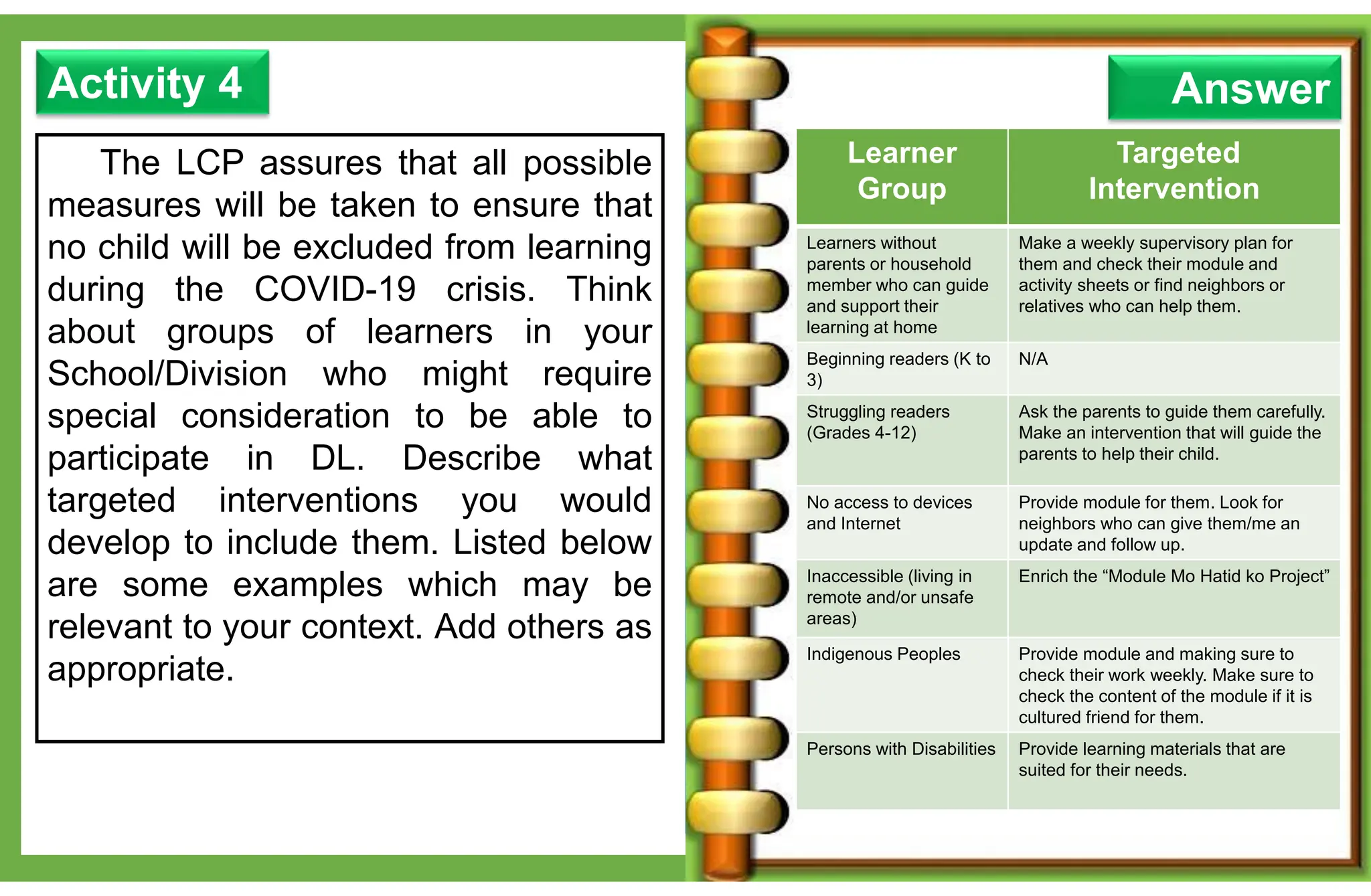
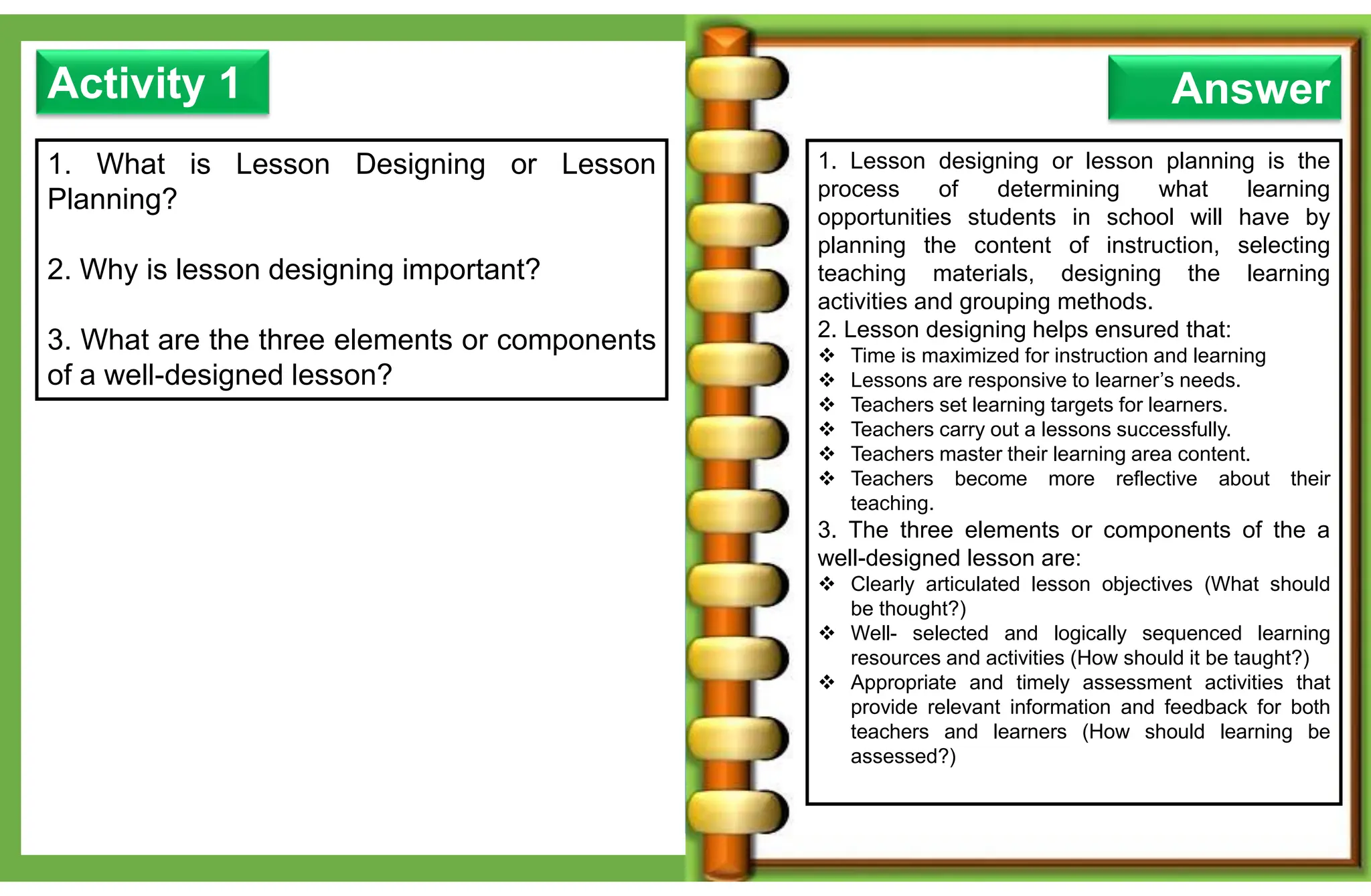
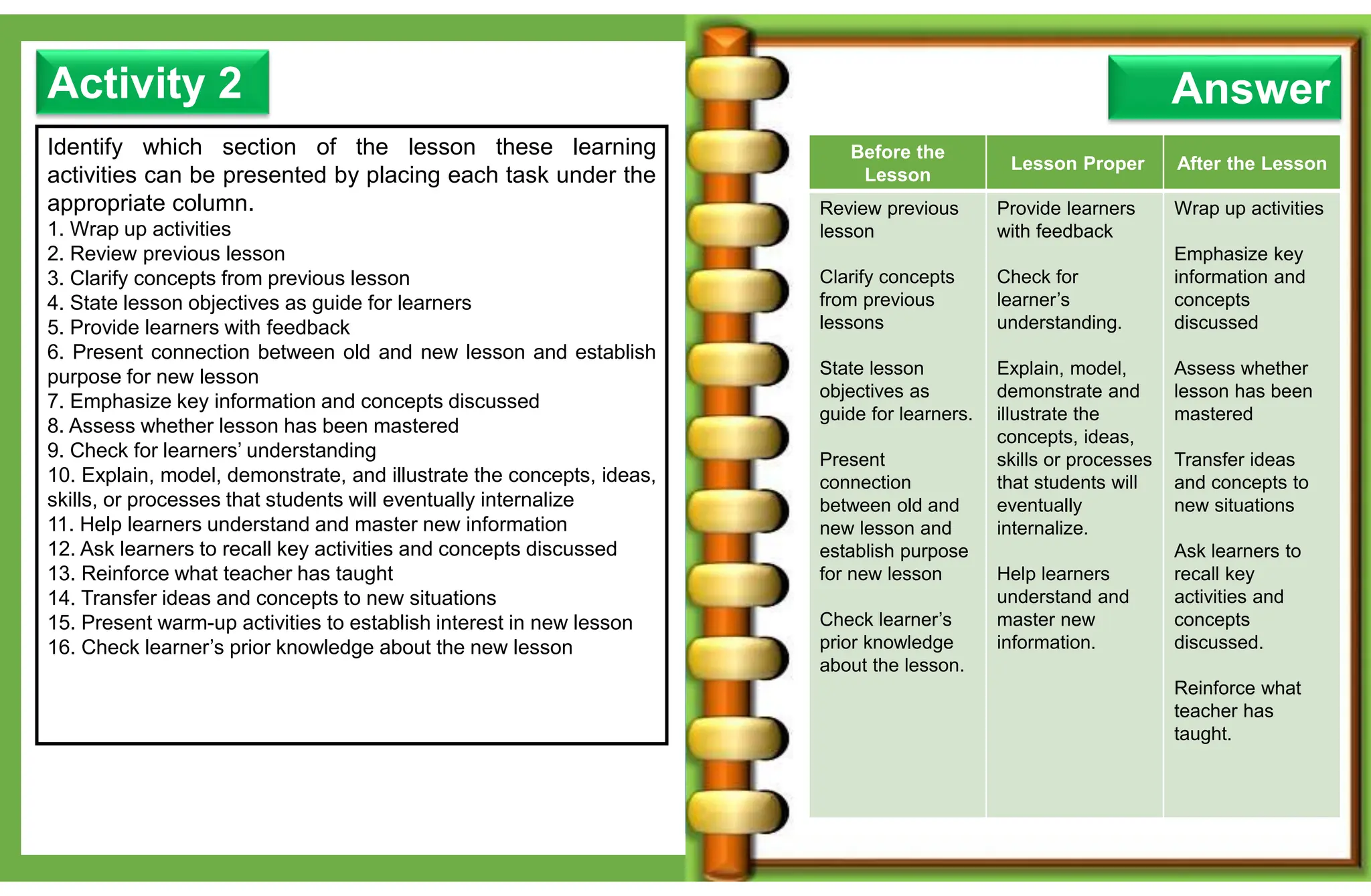
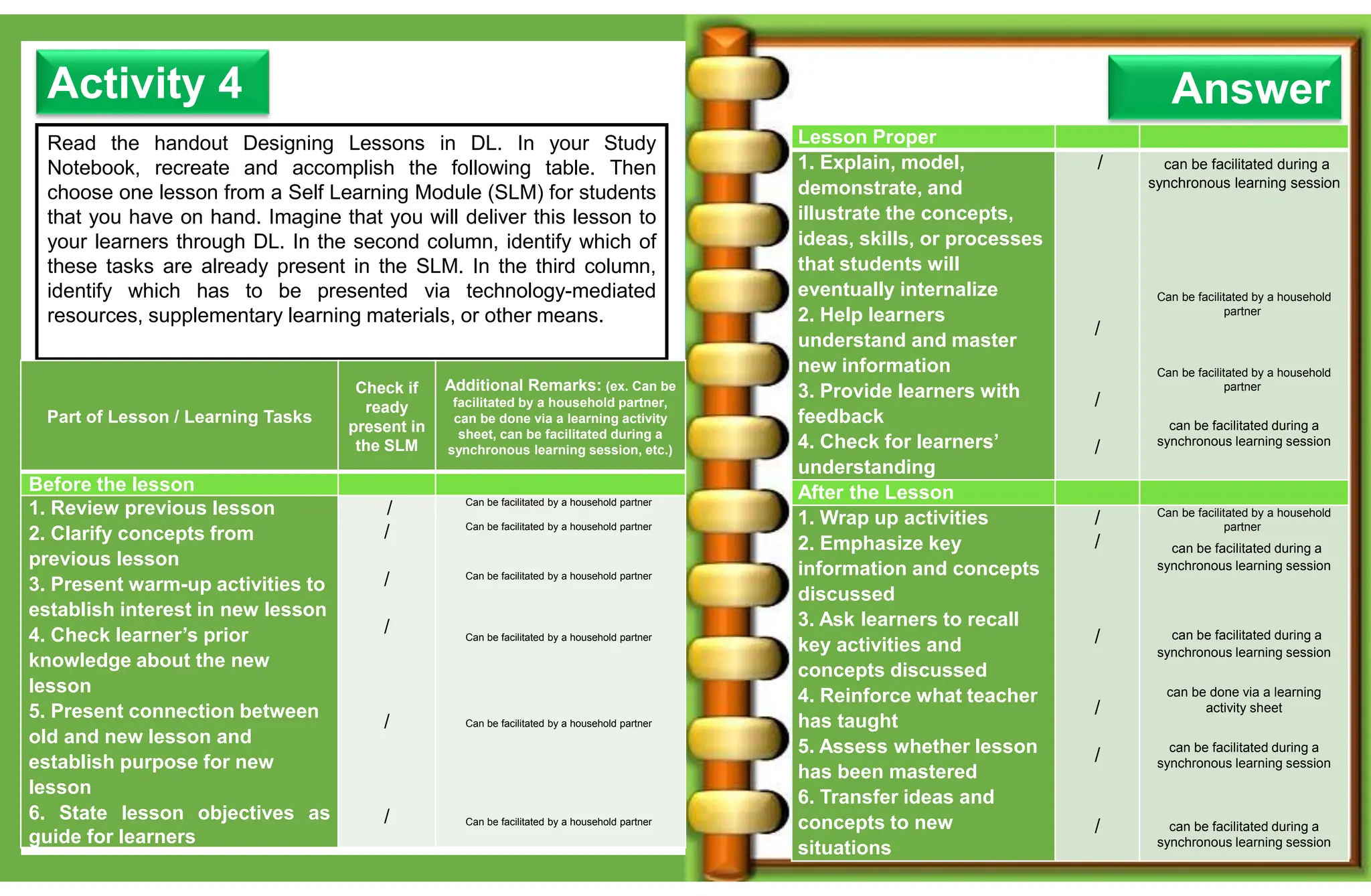
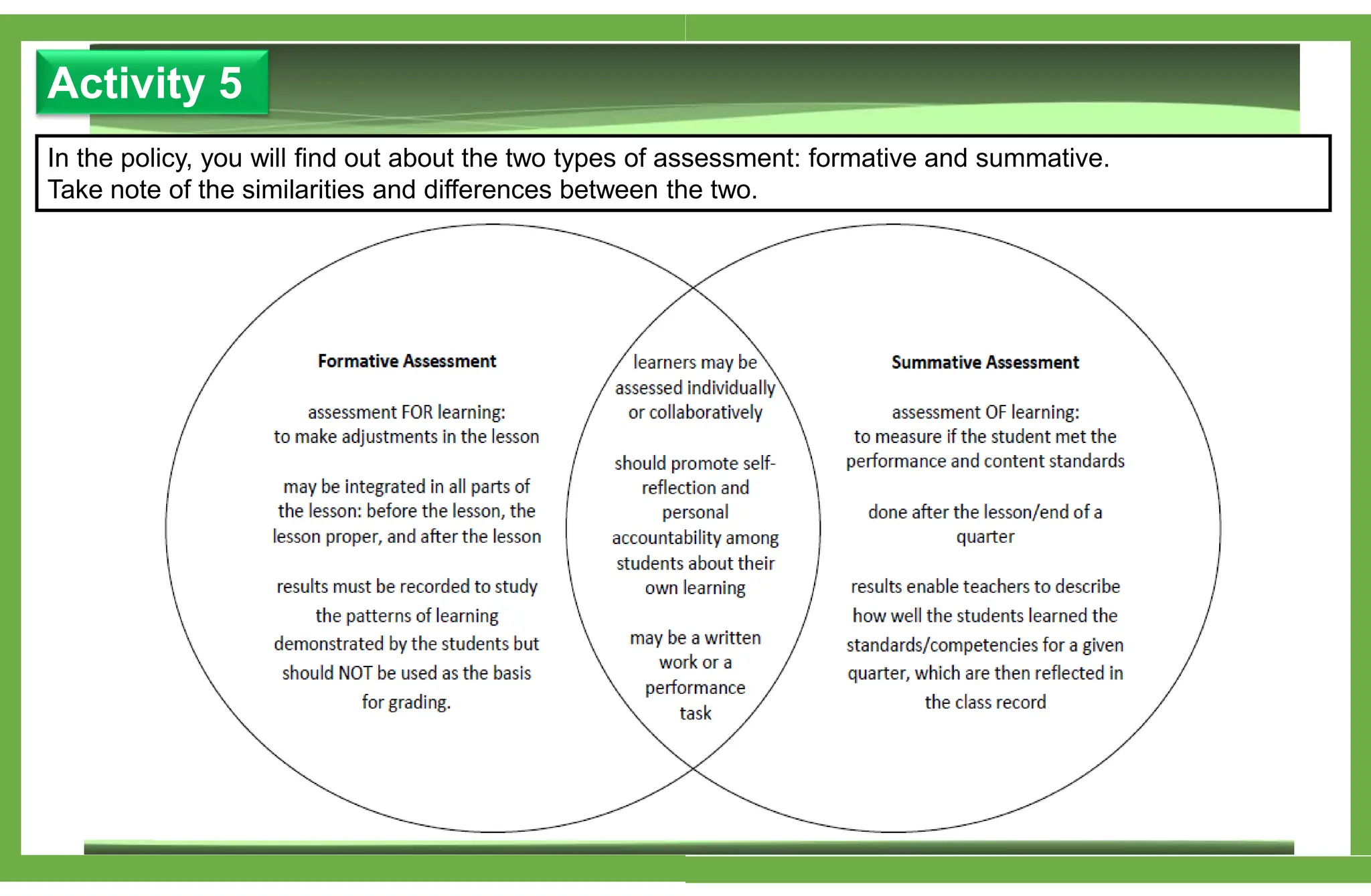
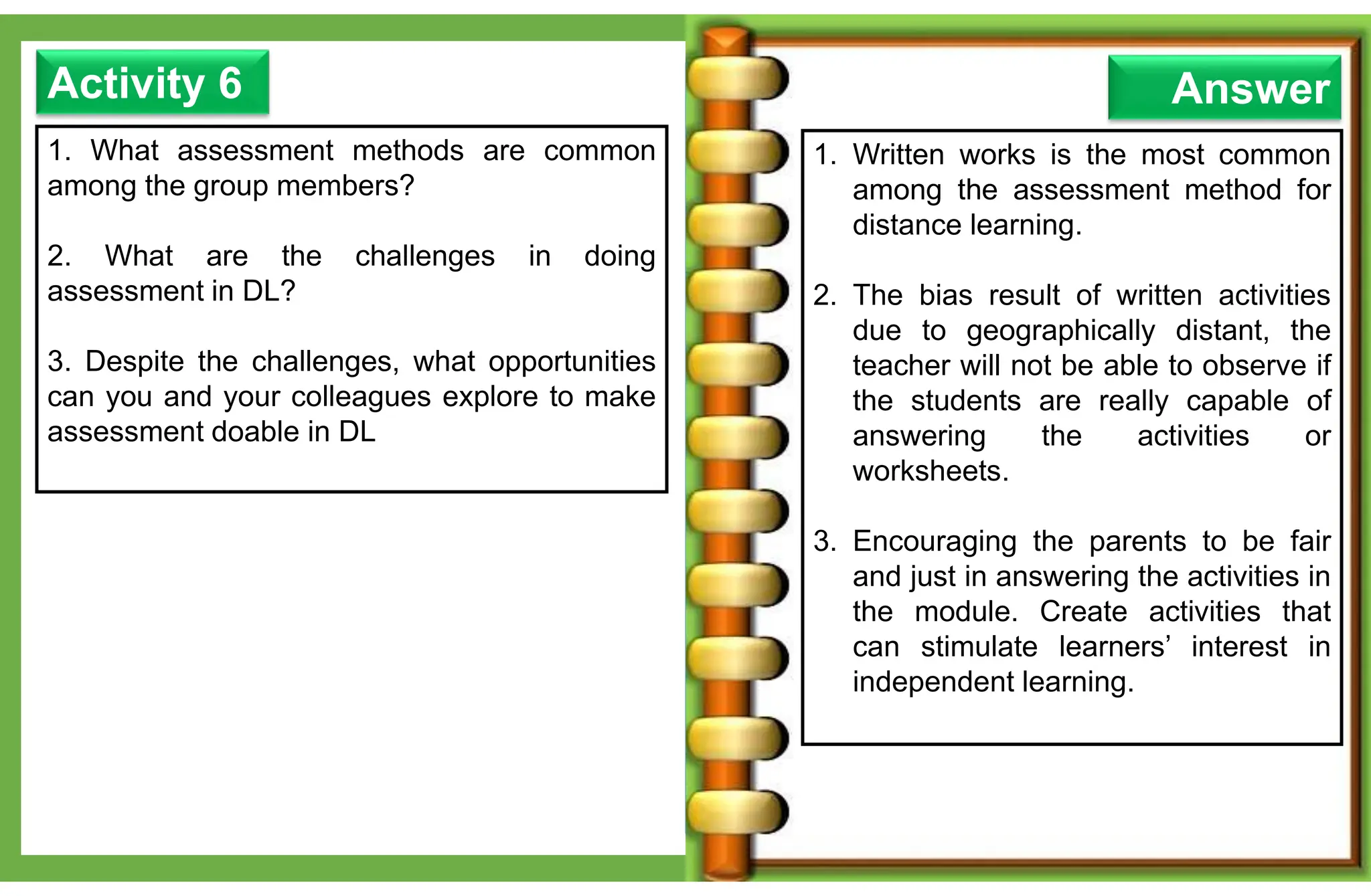
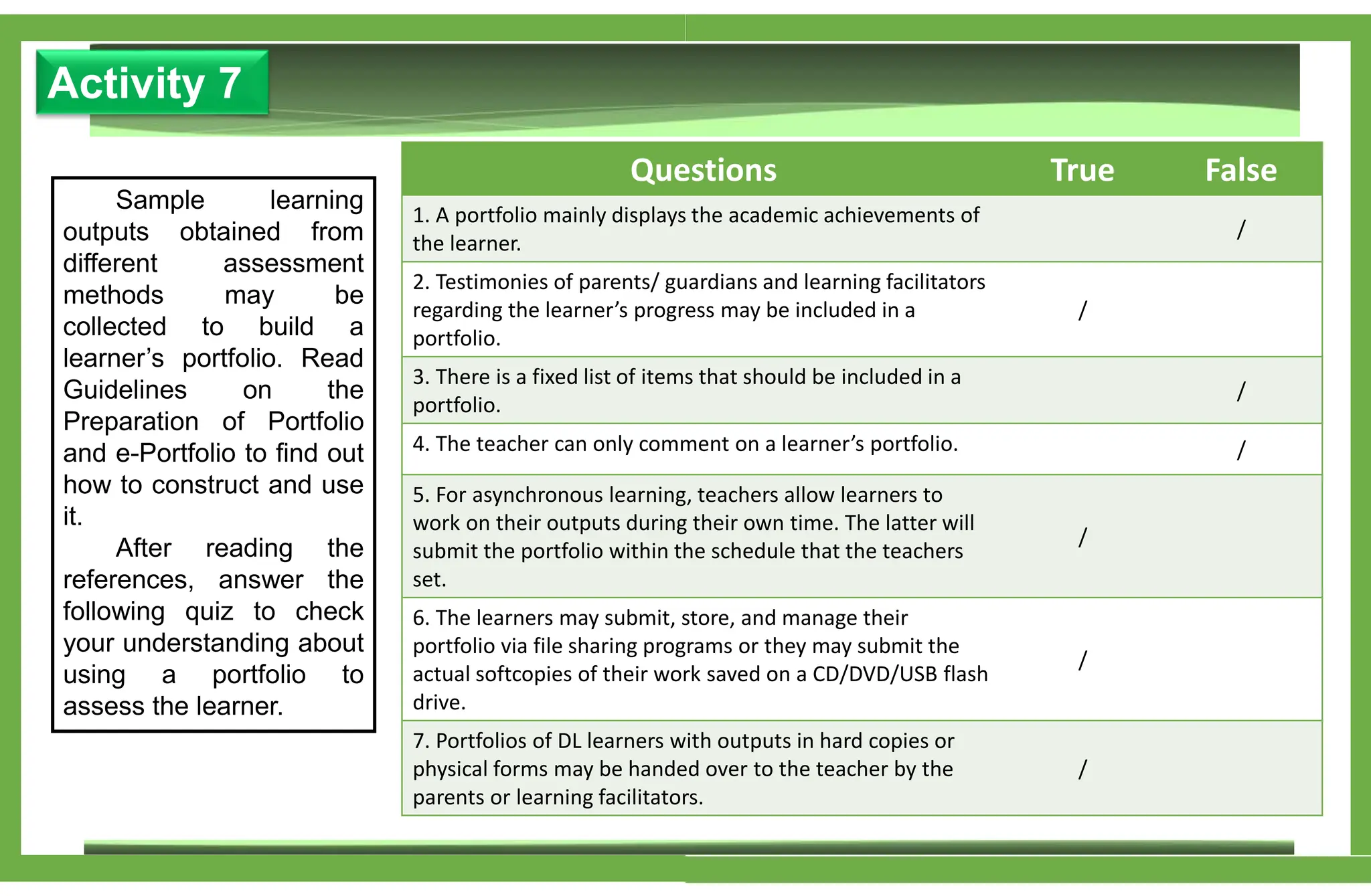
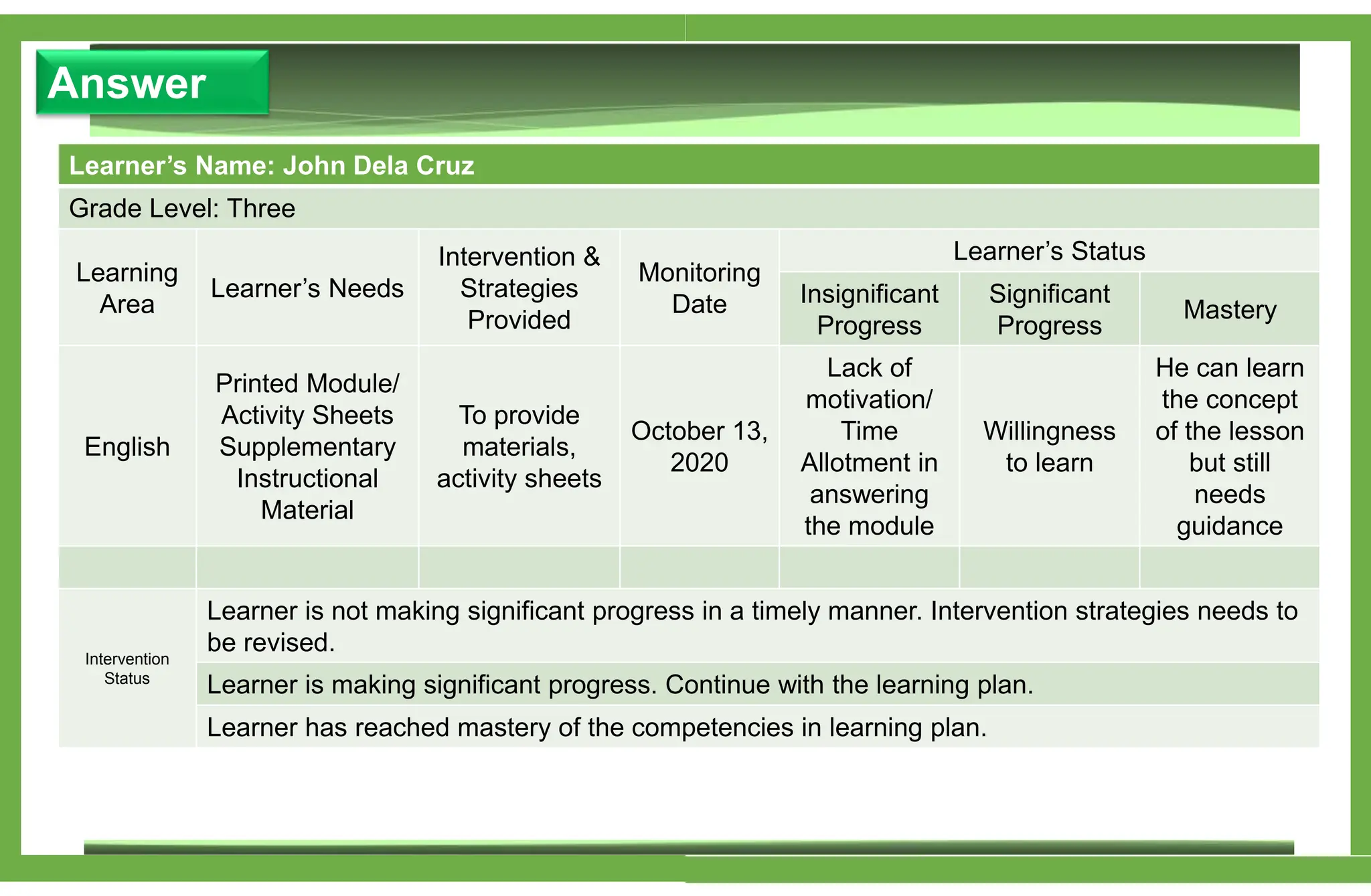
The document outlines various learning modalities and assessment strategies for distance education, particularly during the COVID-19 crisis. It discusses face-to-face learning, distance learning, blended learning, and homeschooling, detailing their definitions, roles of teachers and parents, and necessary resources. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of lesson design and reflection in teaching practices to ensure effective learning outcomes.