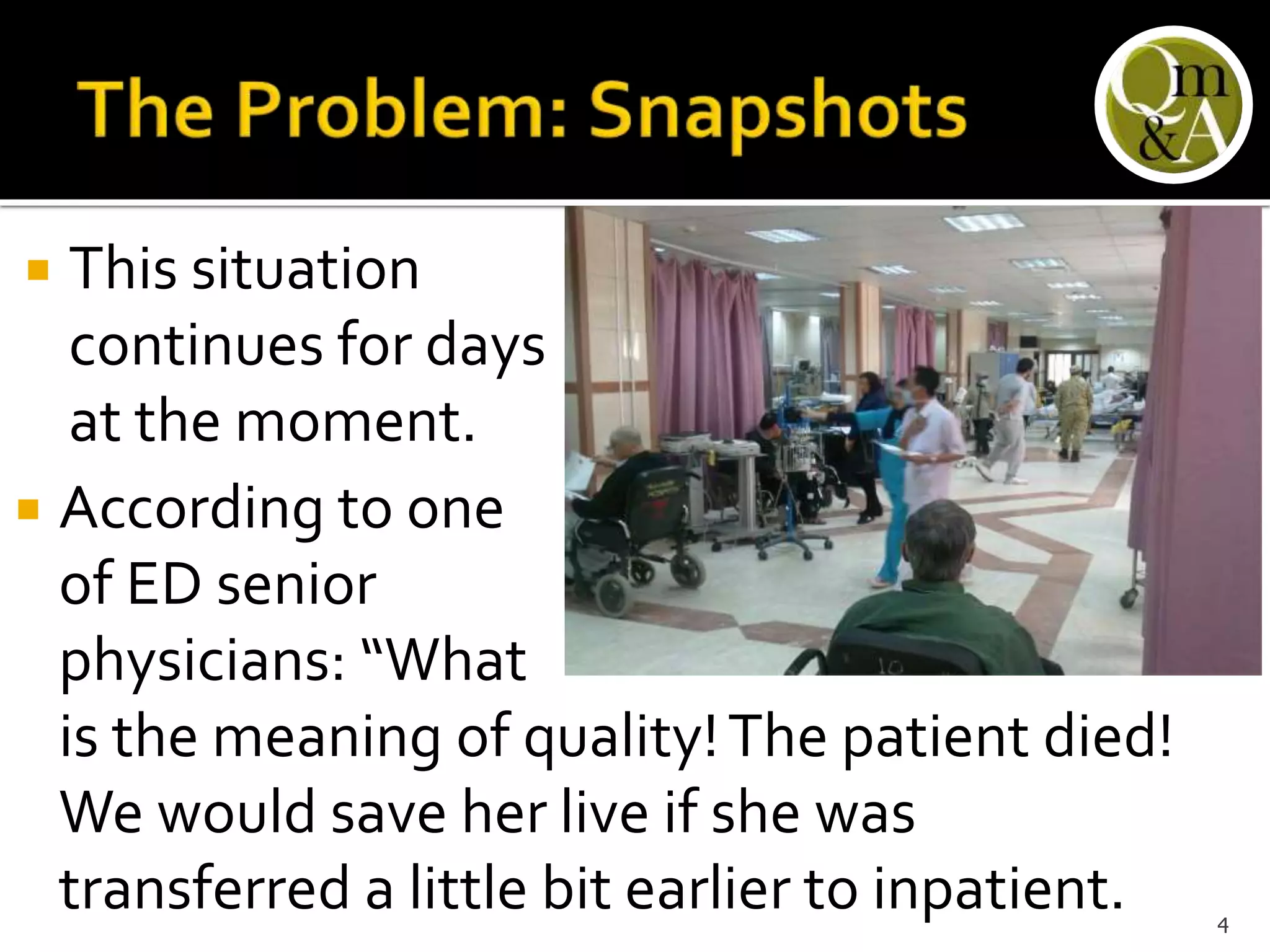
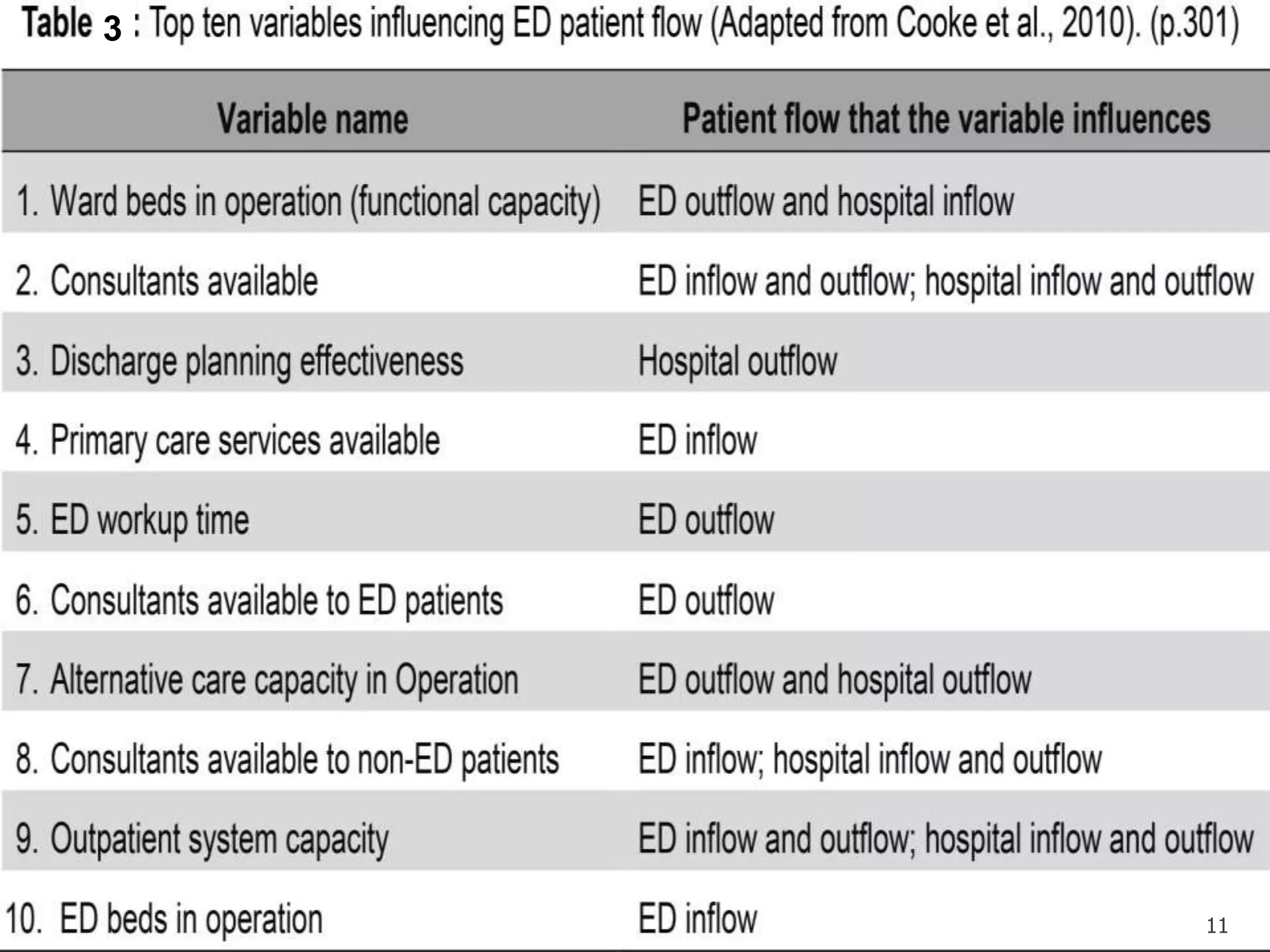
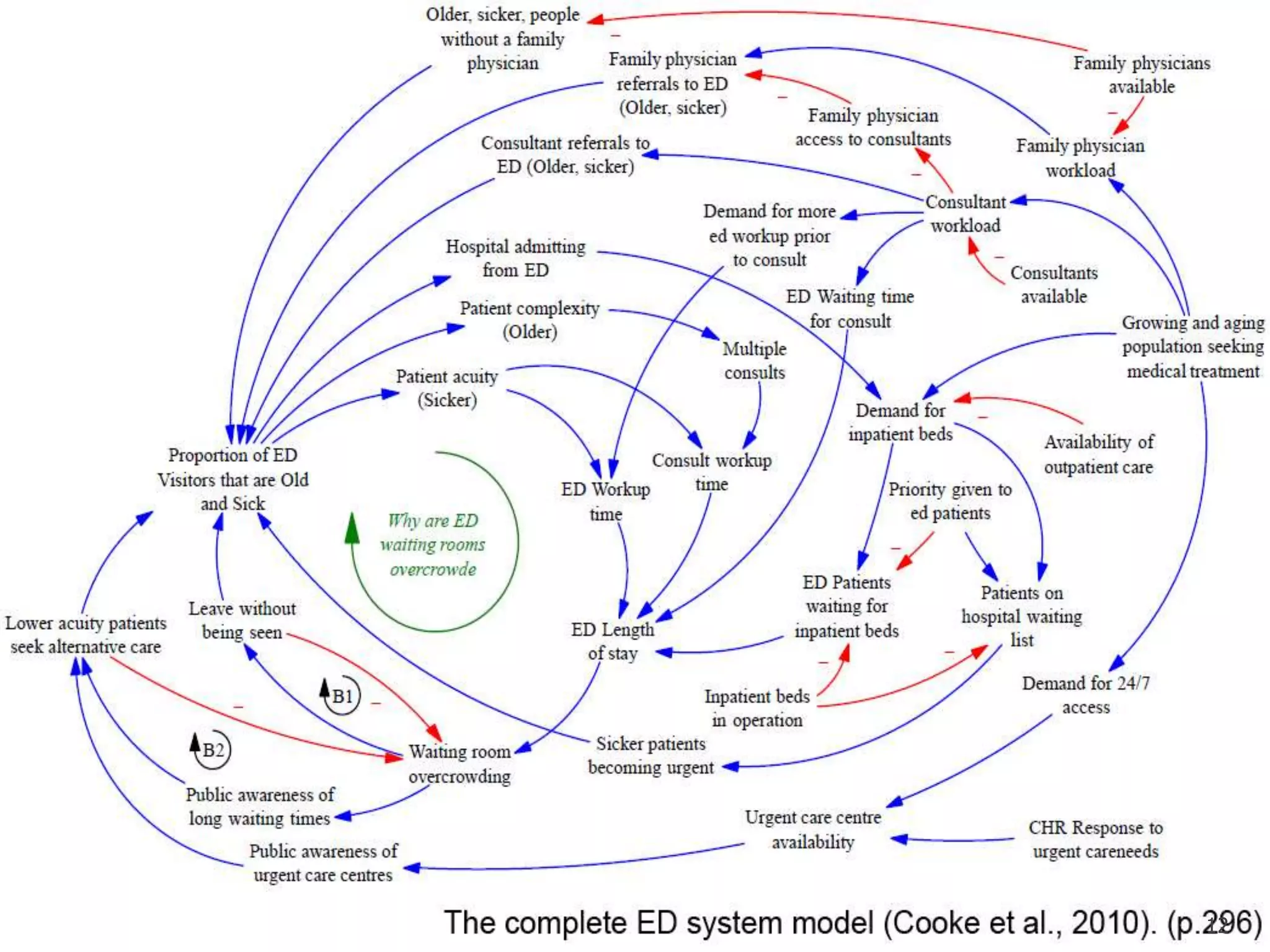
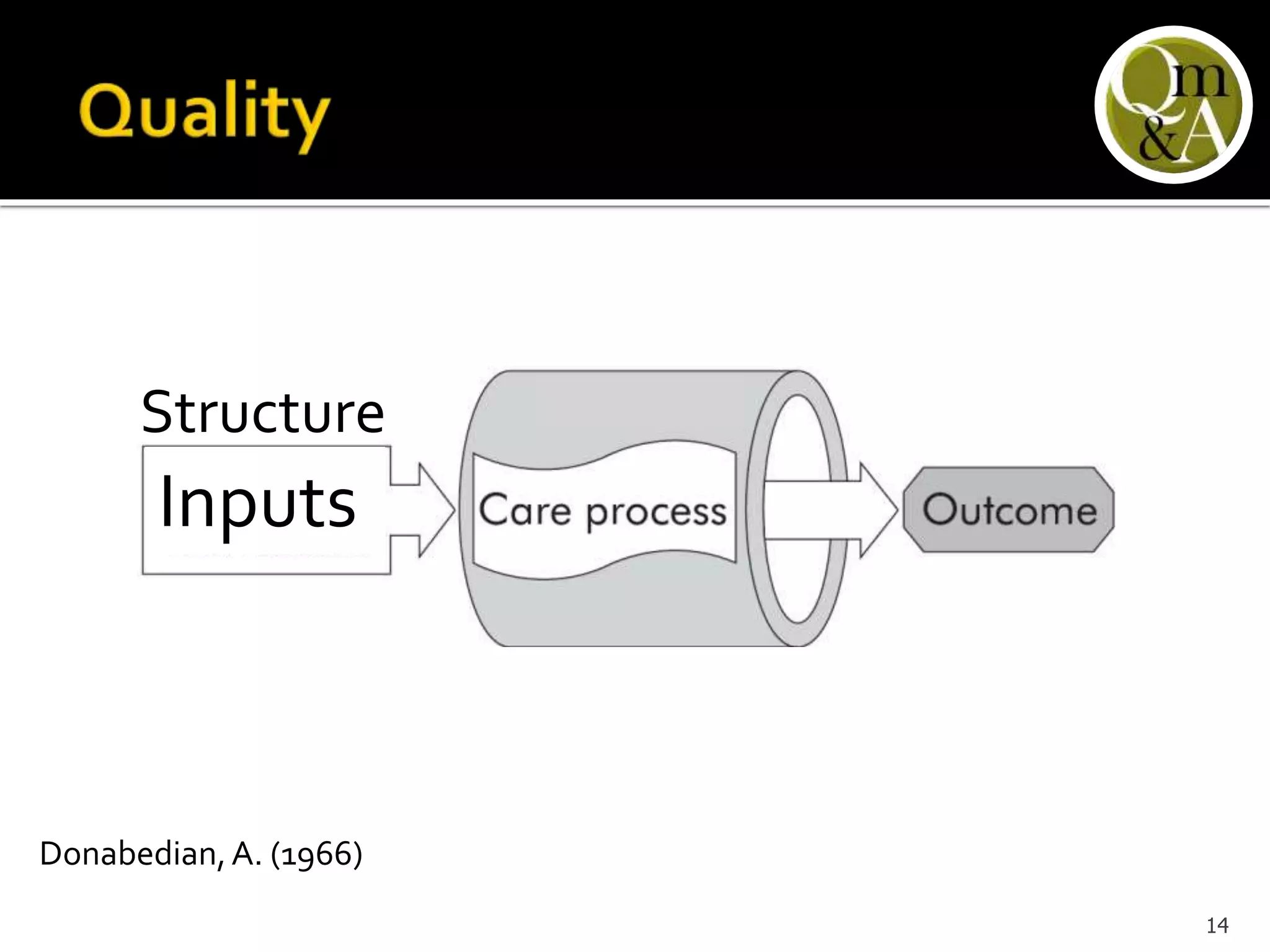
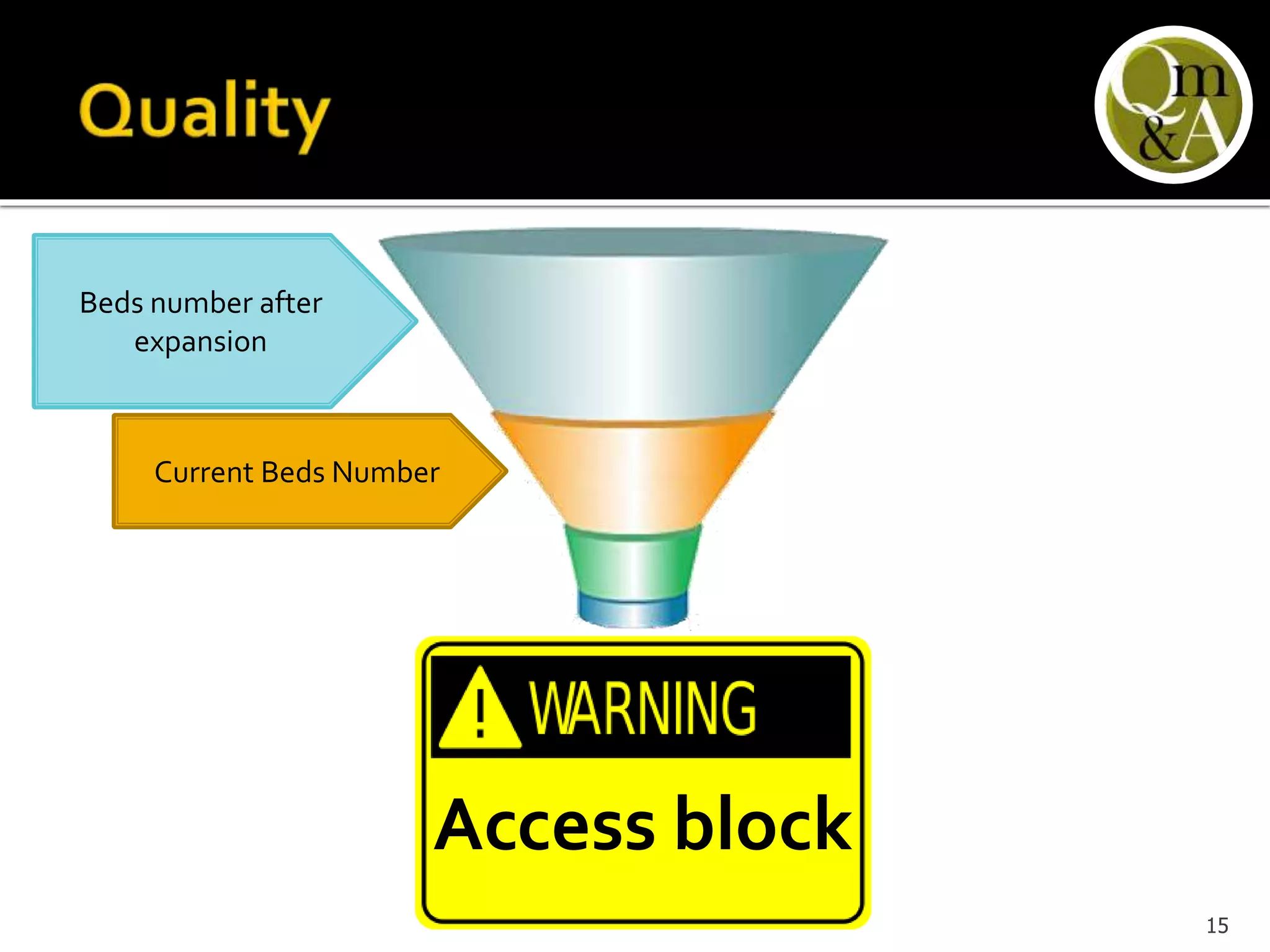
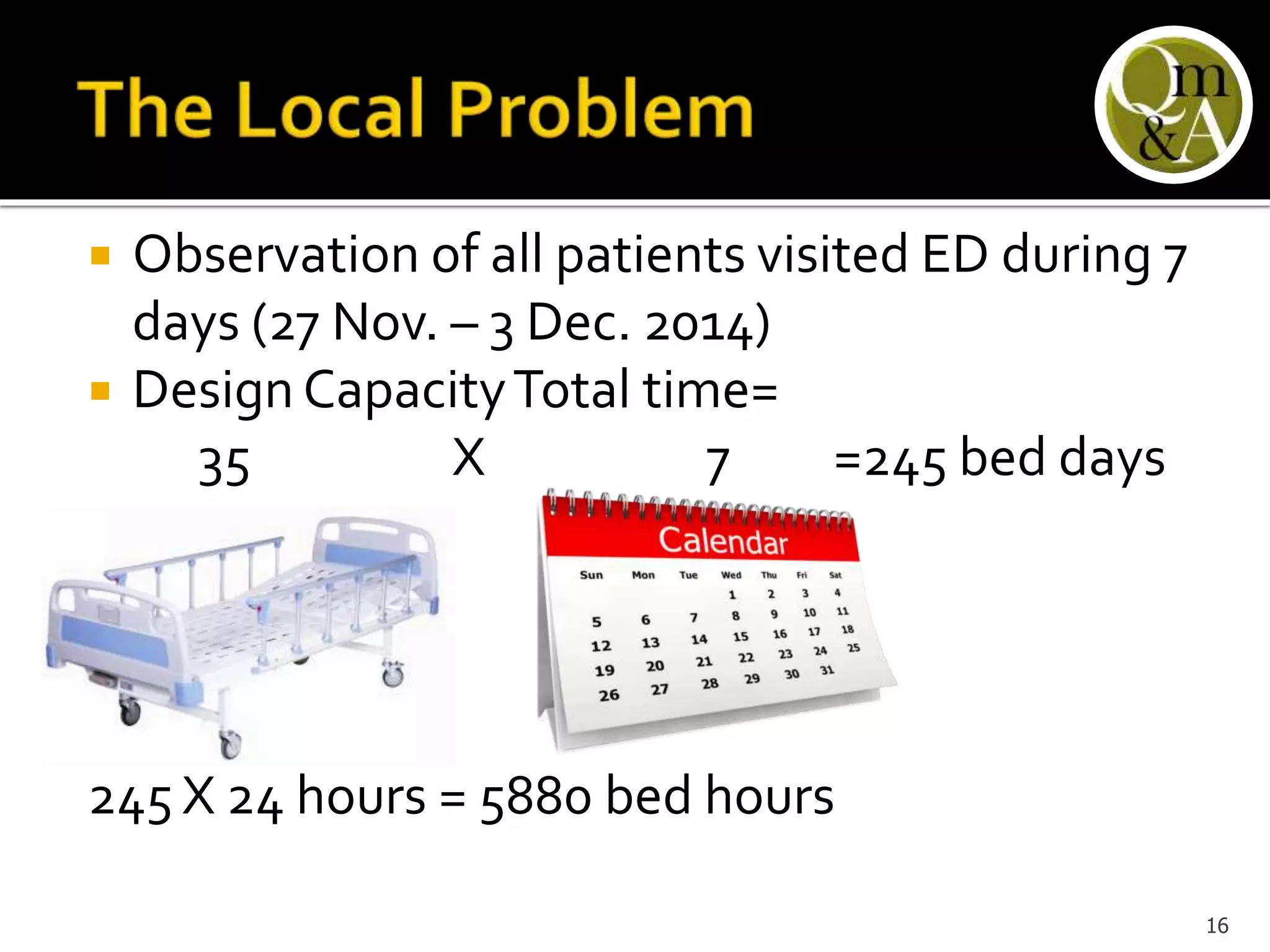
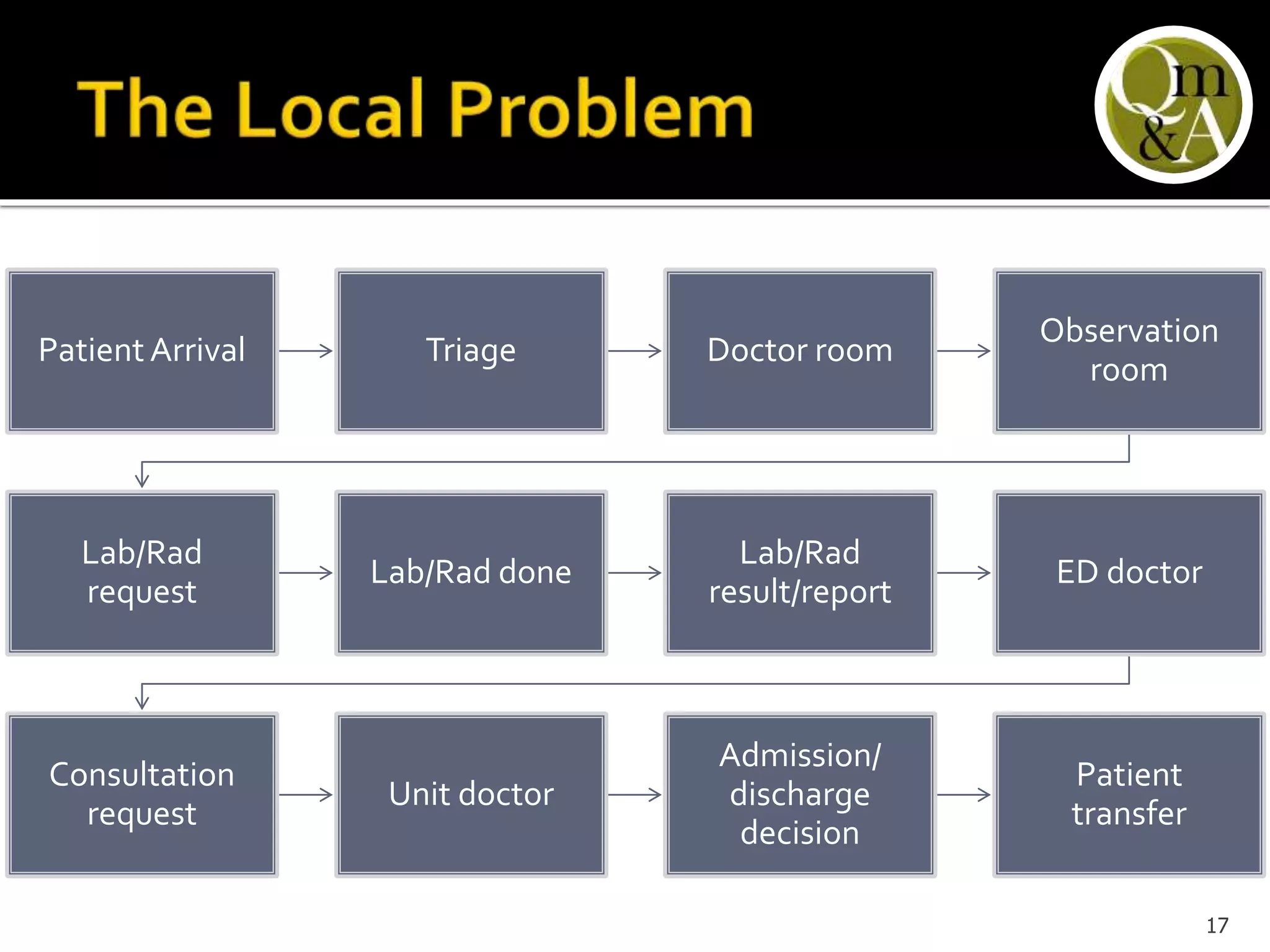
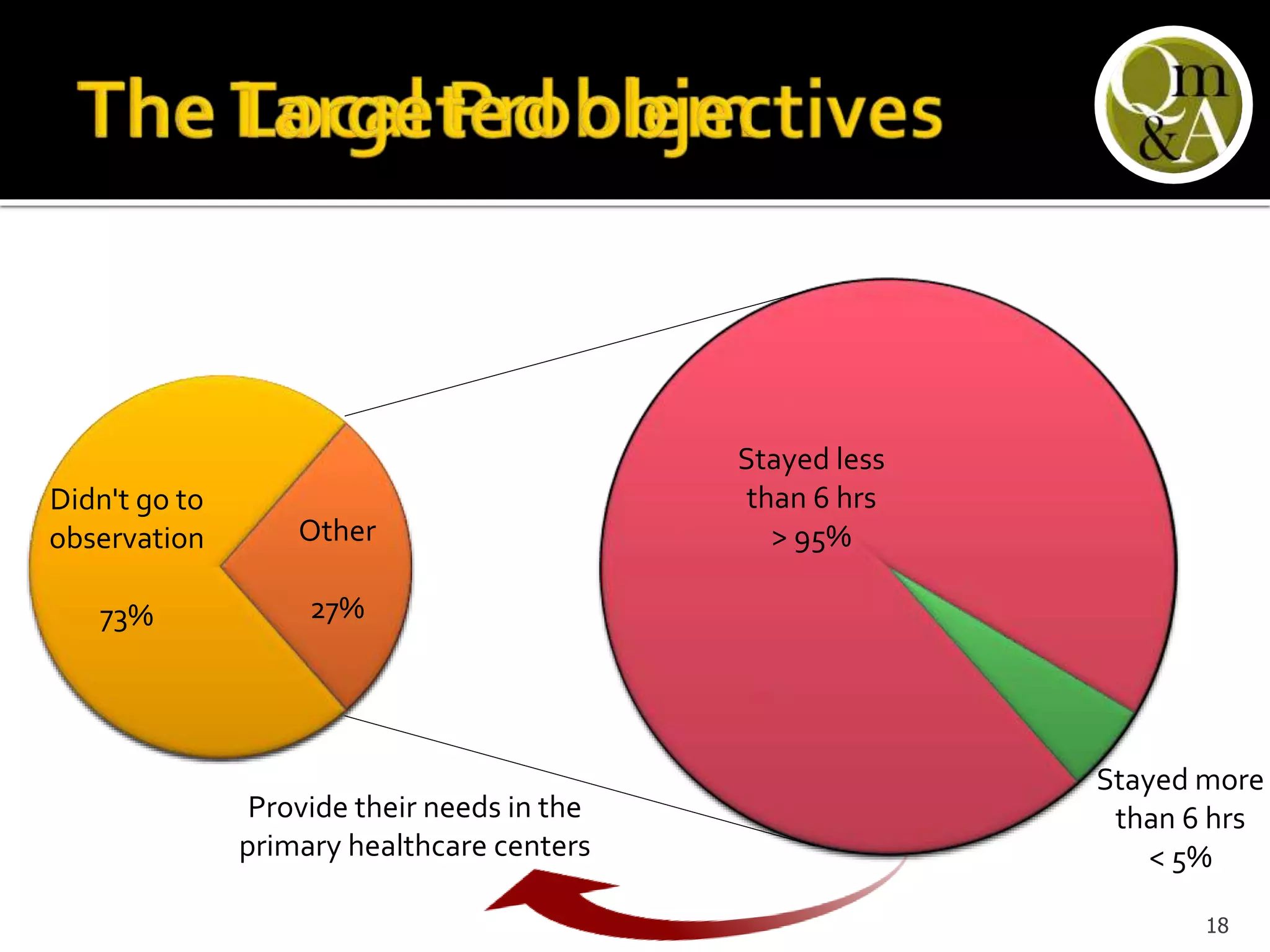
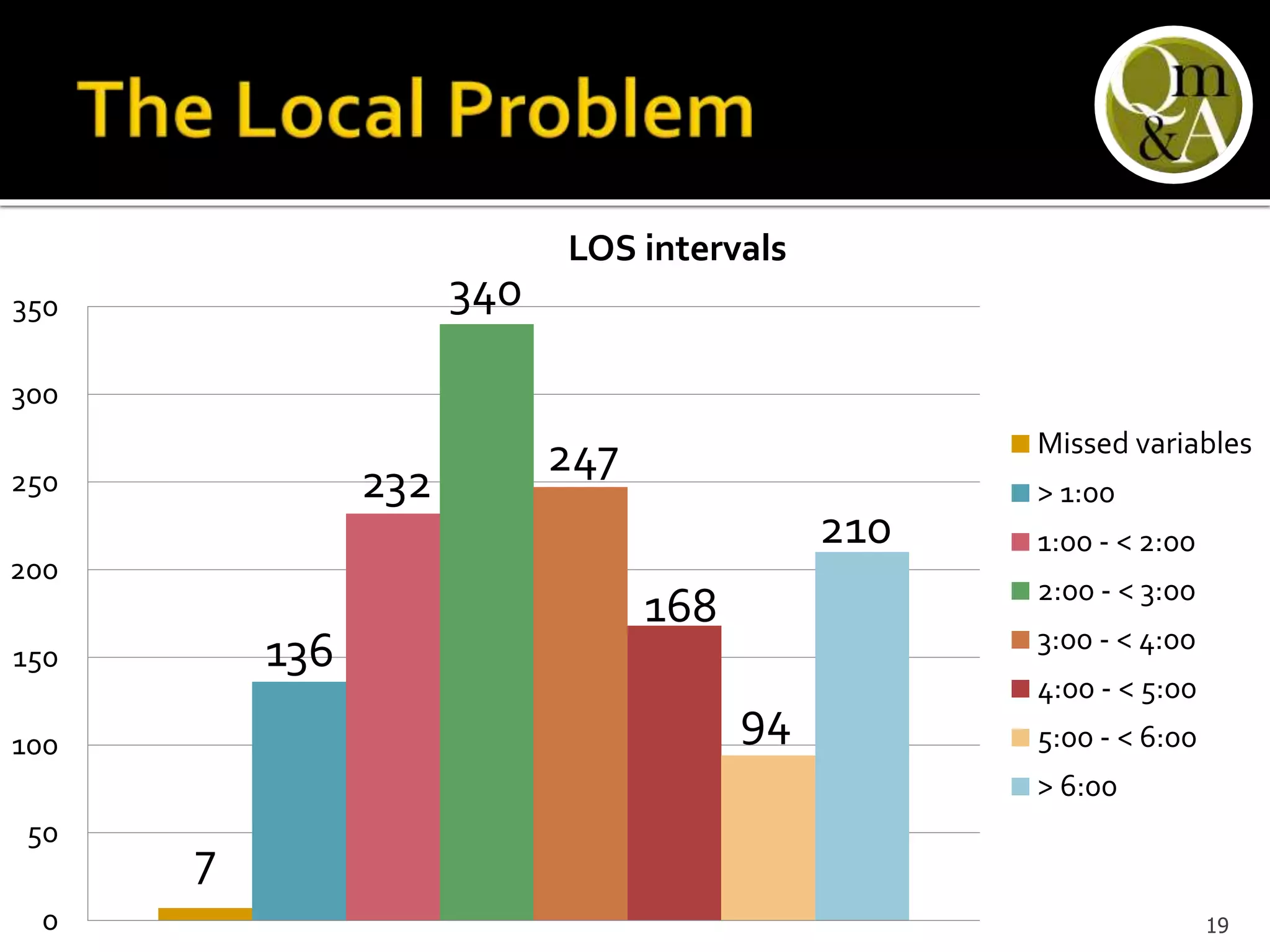
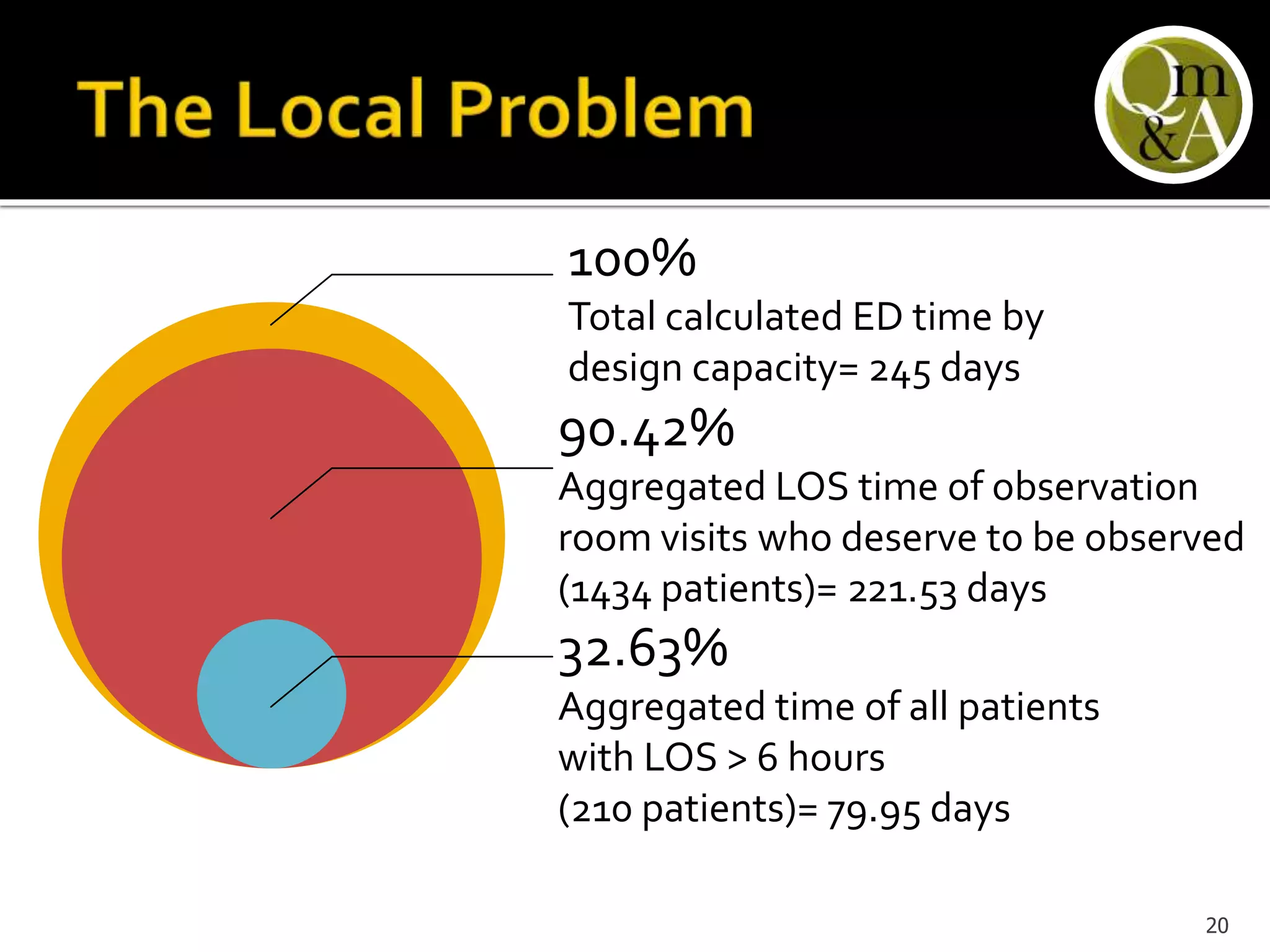
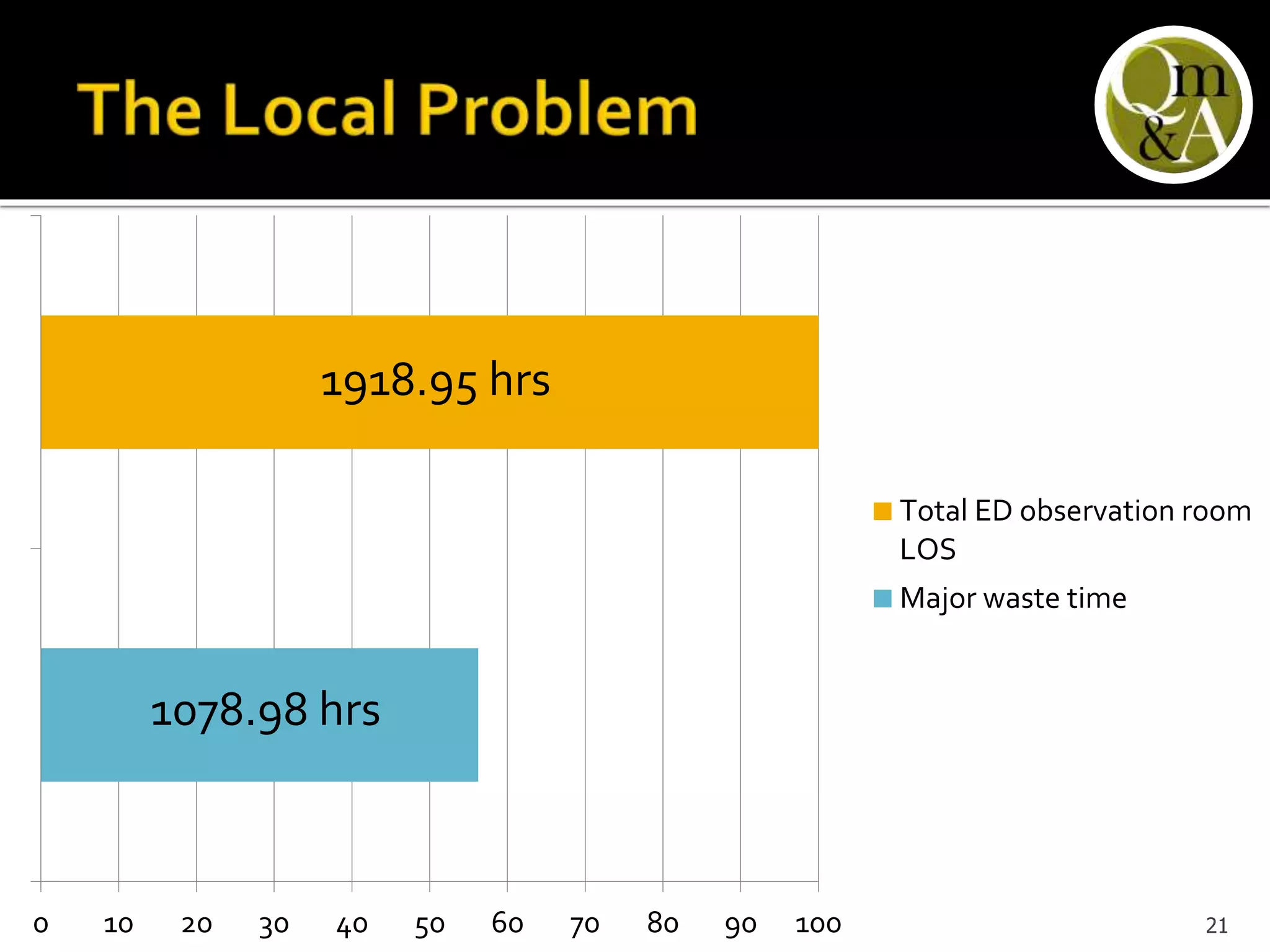
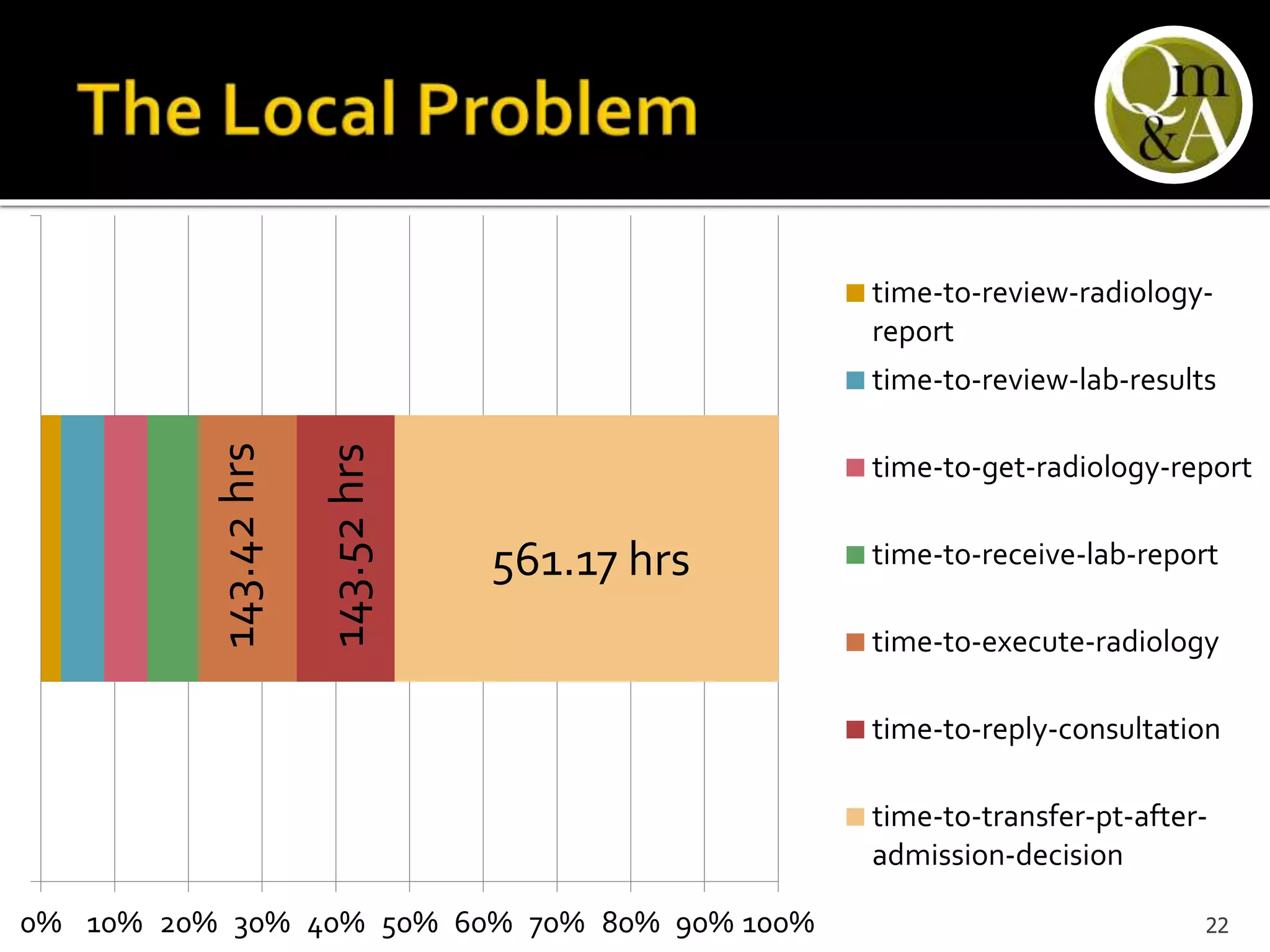
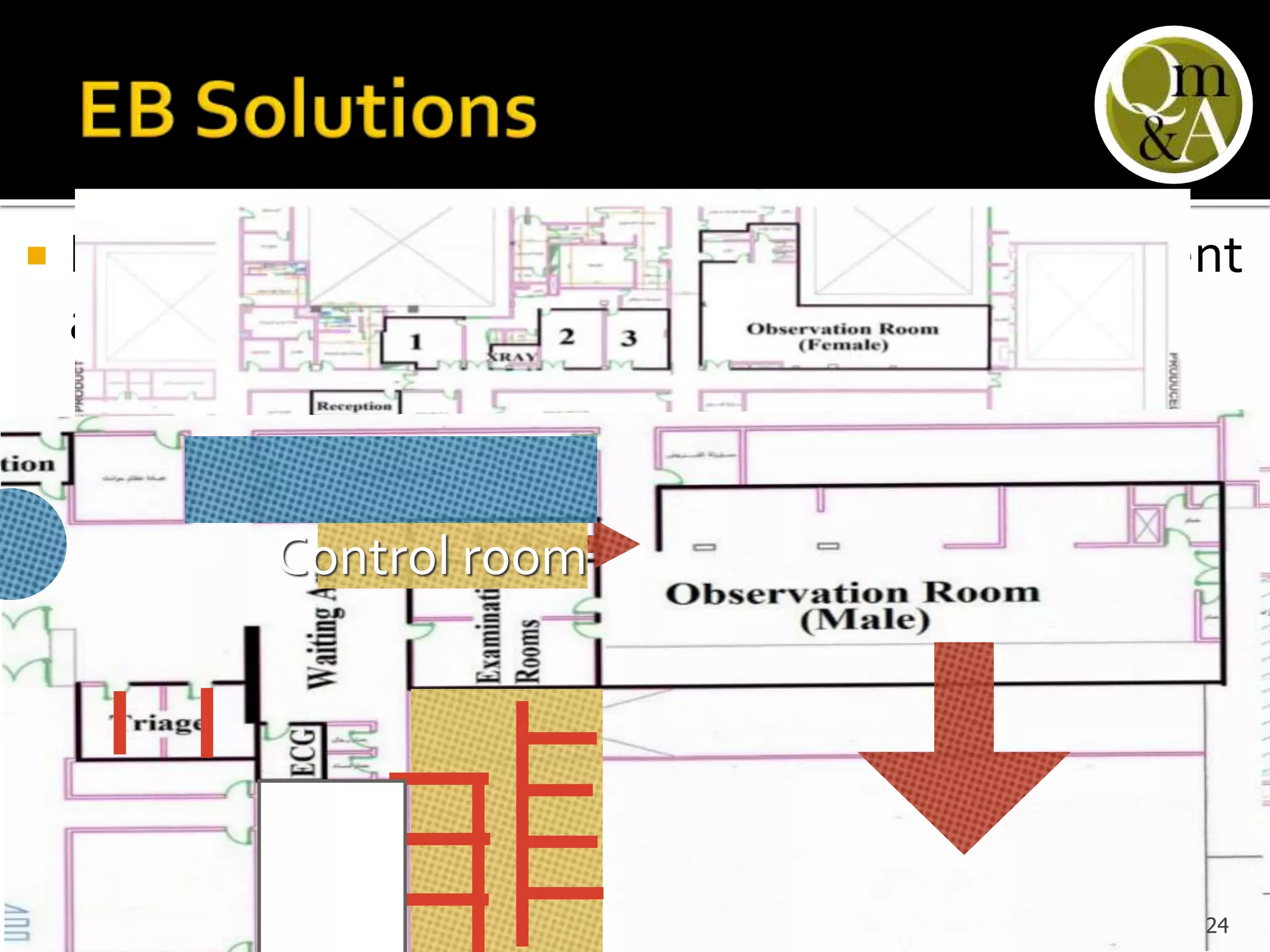
This document discusses quality issues in emergency departments, including access block and prolonged length of stays. It analyzes patient flow data from an emergency department, finding that 27% of visits were for issues that could be handled in primary care centers. Various waste and inefficiencies were identified, including long wait times for imaging reports, consultations, and patient transfers. The document proposes solutions like improving patient triage and routing, making processes more efficient, and implementing bed management protocols to address access block issues.