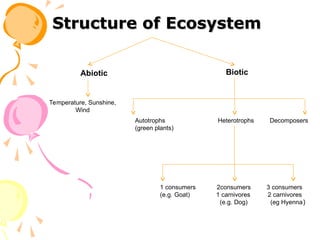
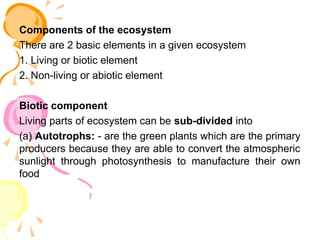
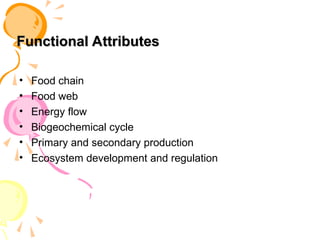
The document outlines the structure of ecosystems, detailing biotic components like autotrophs (primary producers) and heterotrophs (consumers), alongside abiotic elements such as climate and geographical factors. It explains functional attributes including food chains and energy flow, and describes the Earth's hydrosphere, atmosphere, lithosphere, and biosphere, highlighting the significance of these layers for sustaining life. Key atmospheric layers are also described, each with distinct characteristics and functions.