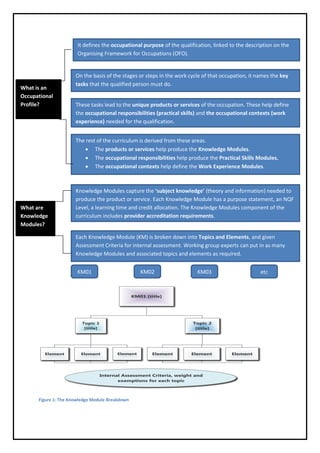
The document outlines the qualification development process for occupational profiles, detailing the roles of the Quality Council for Trades and Occupations (QCTO), development quality partners (DQPs), and working group experts. It describes the components of the curriculum, including knowledge modules, practical skills modules, and work experience modules, each with specific assessment criteria and requirements. The process ensures feedback from the sector at key stages and the qualifications are registered on the National Qualifications Framework (NQF).