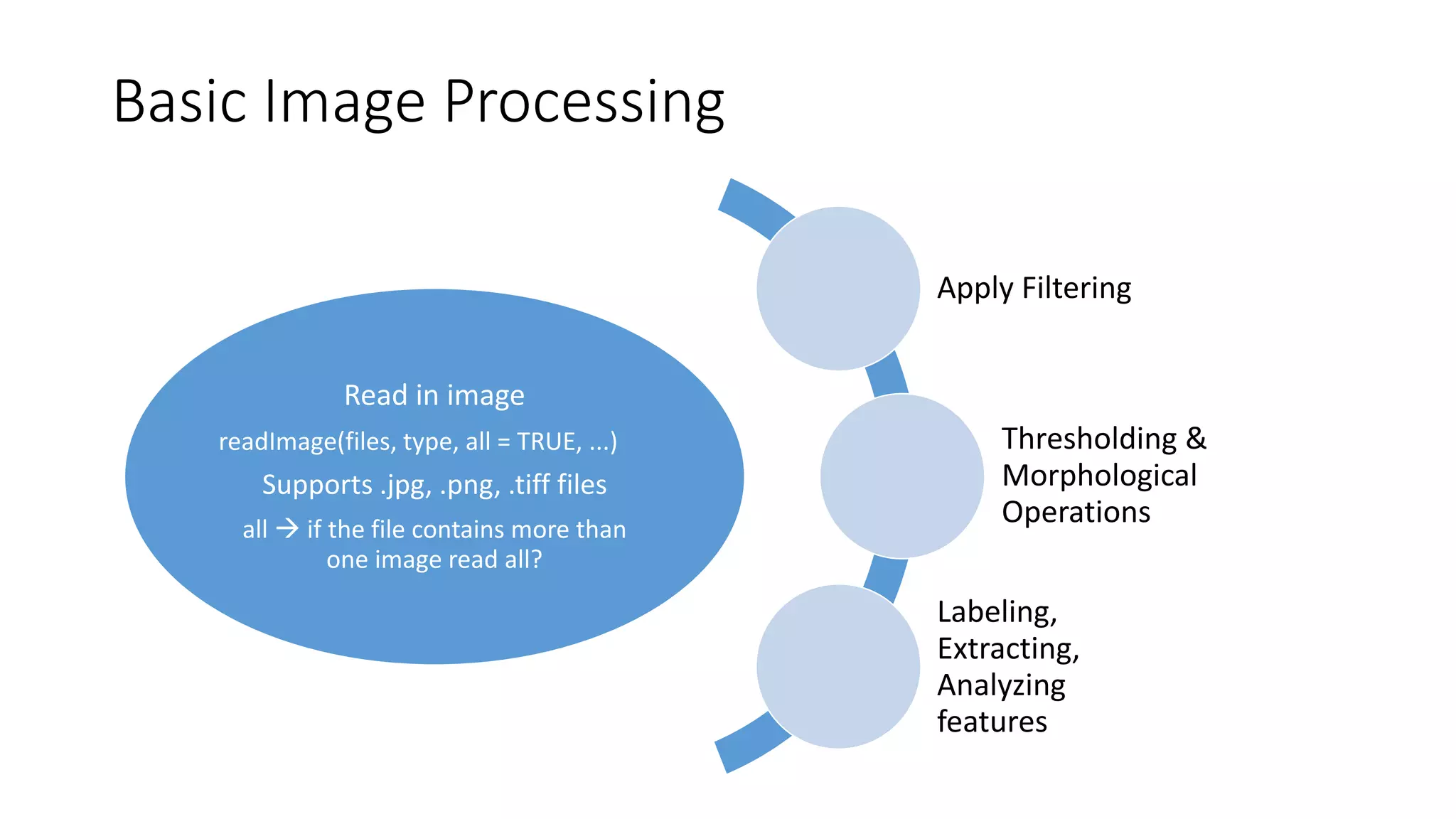
- EBImage is an image processing and analysis toolbox for R that was developed for segmenting cells and extracting quantitative descriptors
- It allows users to read images, apply filters like thresholding and morphological operations, label features, and extract statistics
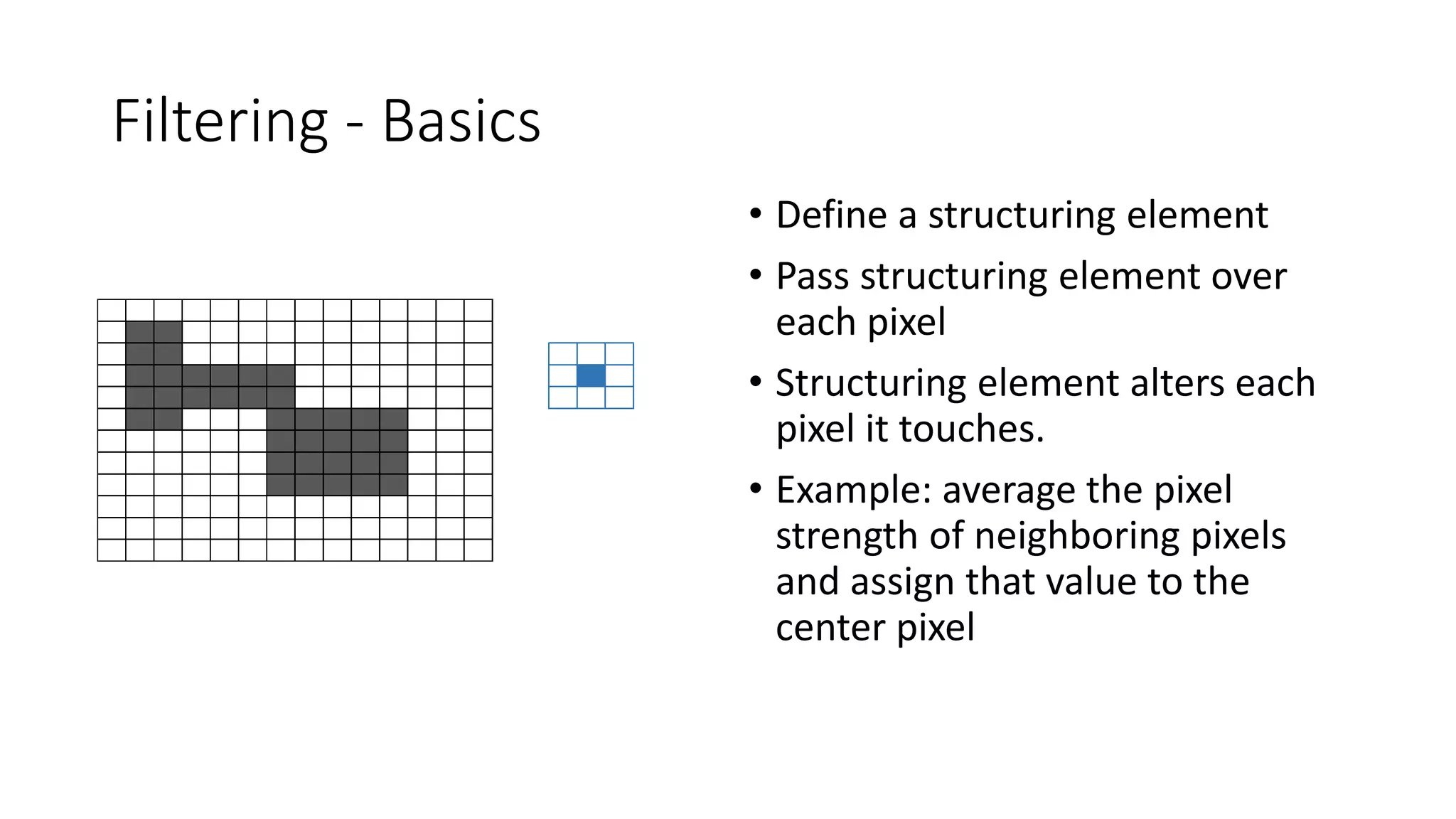
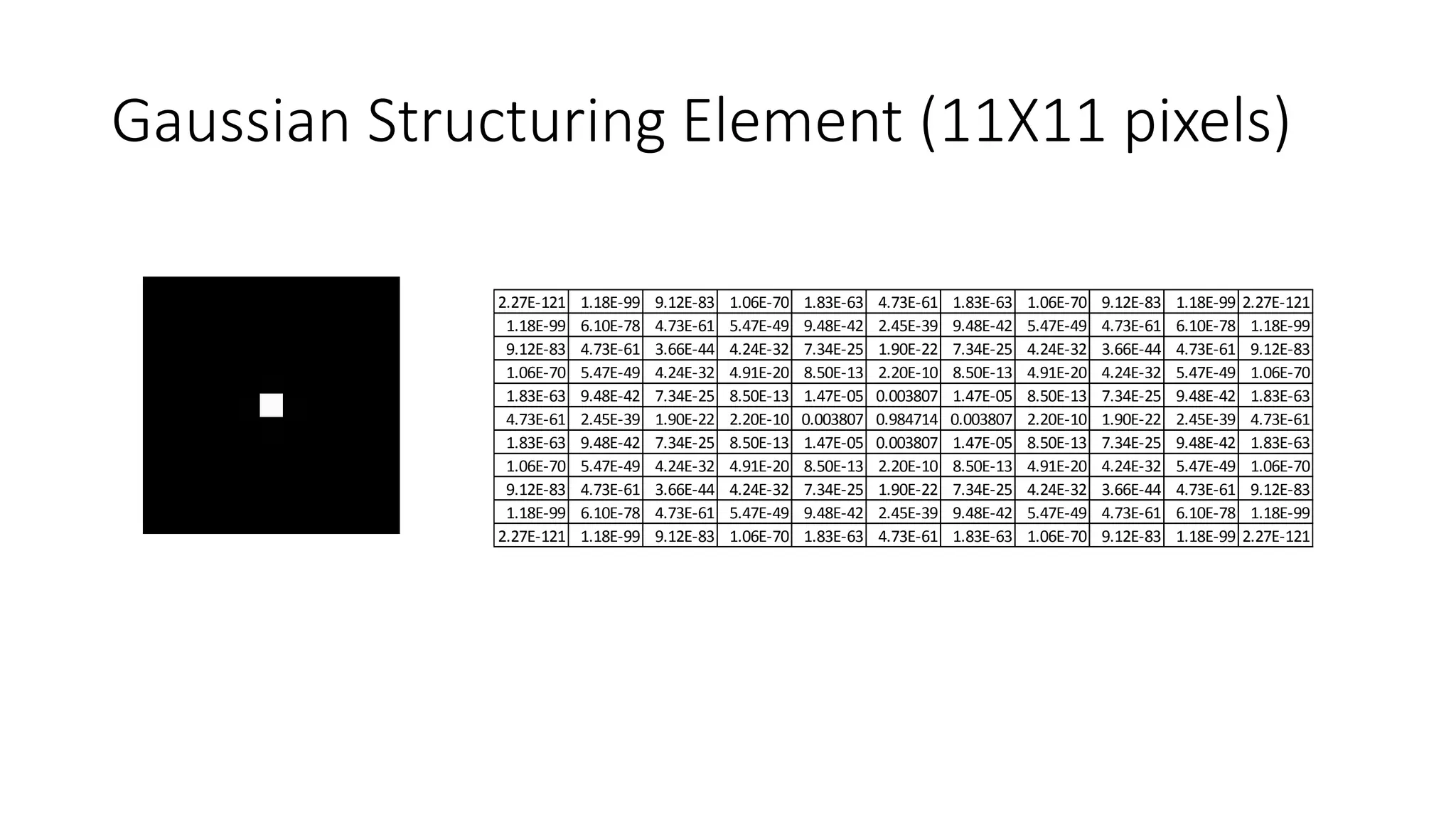
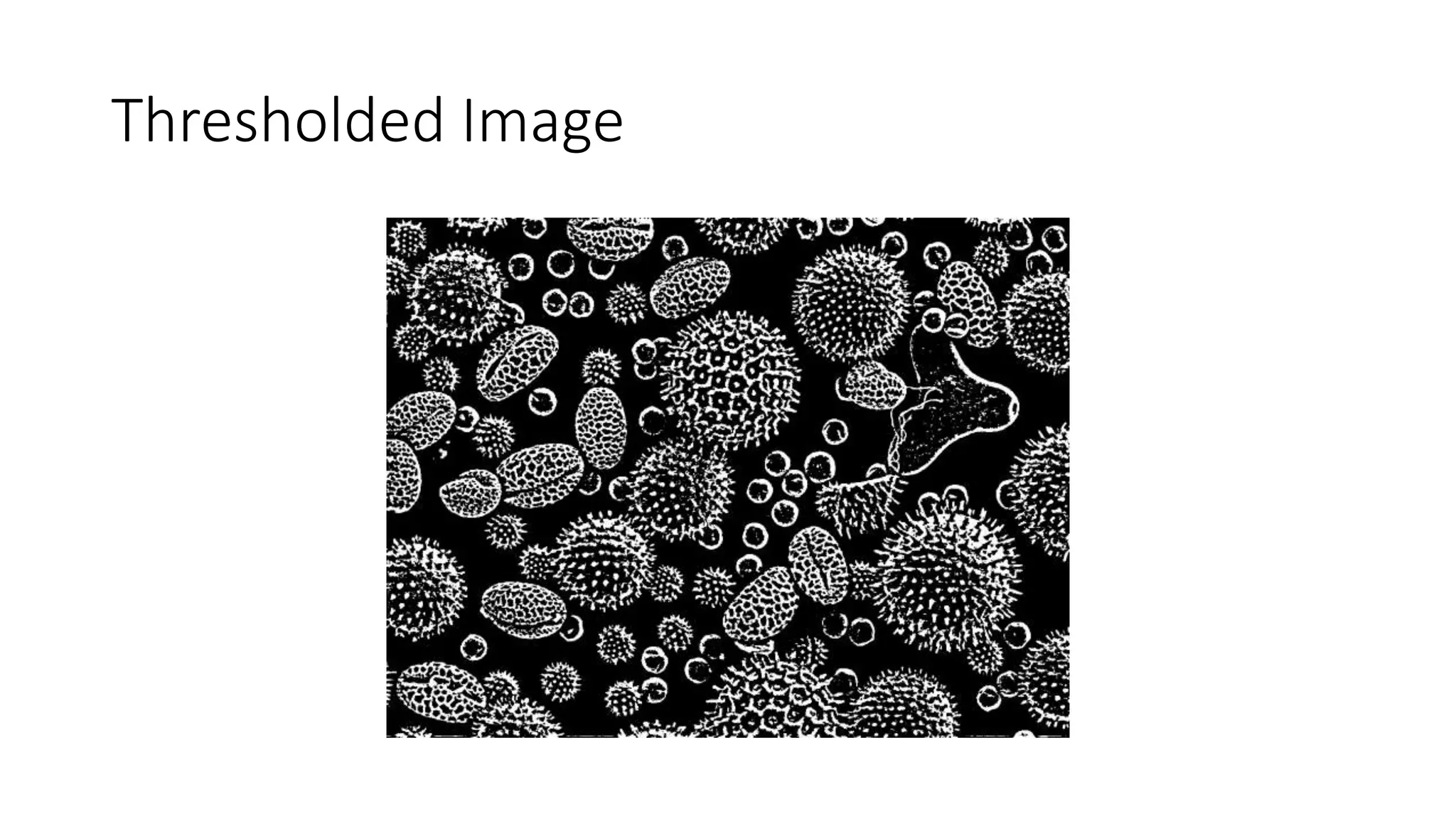
- Filters like Gaussian blurring can be applied using structuring elements of varying sizes to smooth an image, while thresholding and morphological operations like openings and closings can be used to find edges and extract binary features for analysis










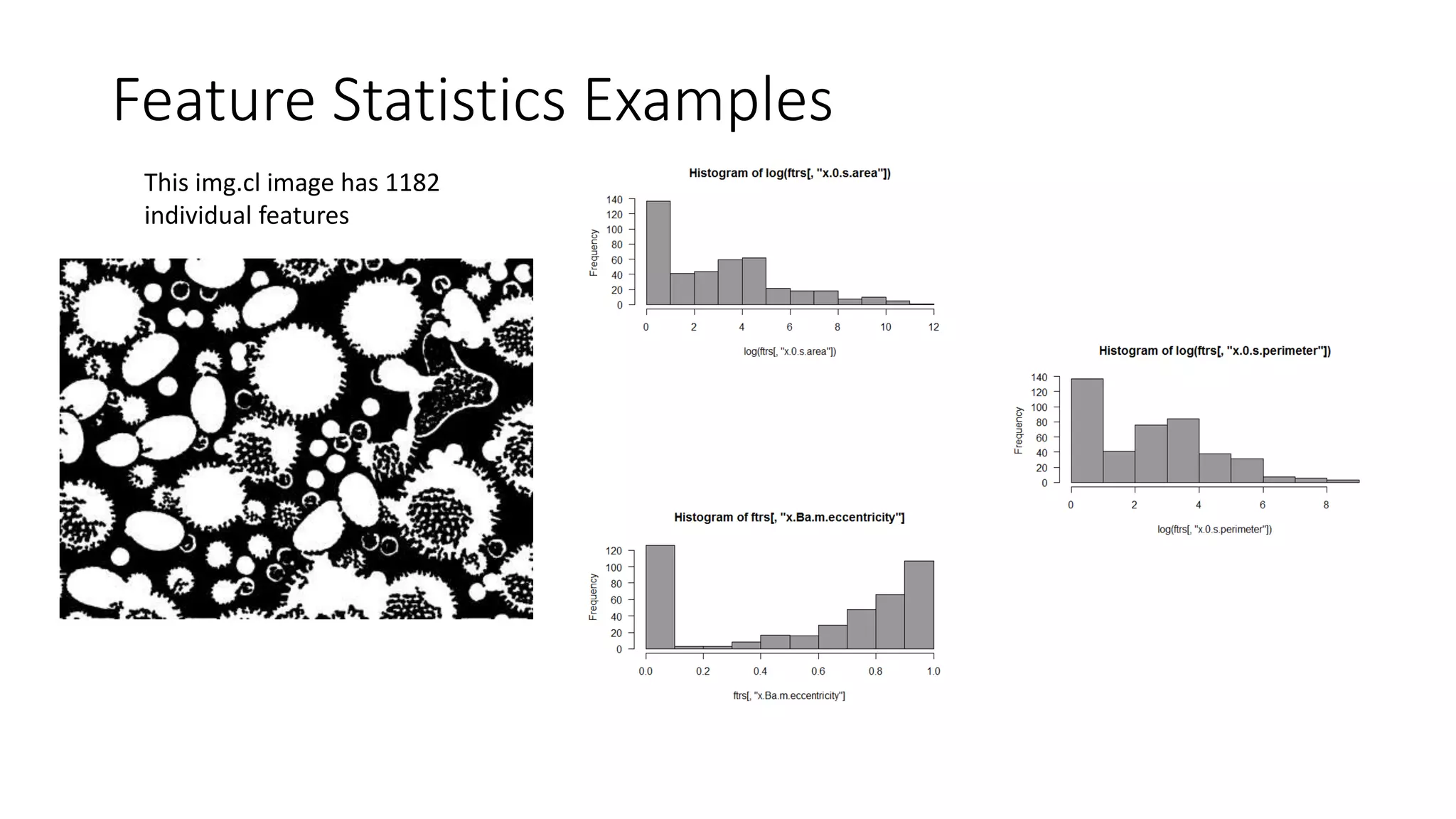
![Feature Statistics Examples
• What are the 0.4-0.5 eccentricity features?
ecc.ftrs<-which(ftrs[,'x.a.m.eccentricity']>0.4 & ftrs[,'x.a.m.eccentricity']<=0.5)
ecc.img<-Image(0,dim=dim(img))
ecc.img[which(imgcl.lab %in% ecc.img)]<-img[which(imgcl.lab %in% ecc.img)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ebimage-150920141207-lva1-app6891/75/EBImage-Short-Overview-17-2048.jpg)
