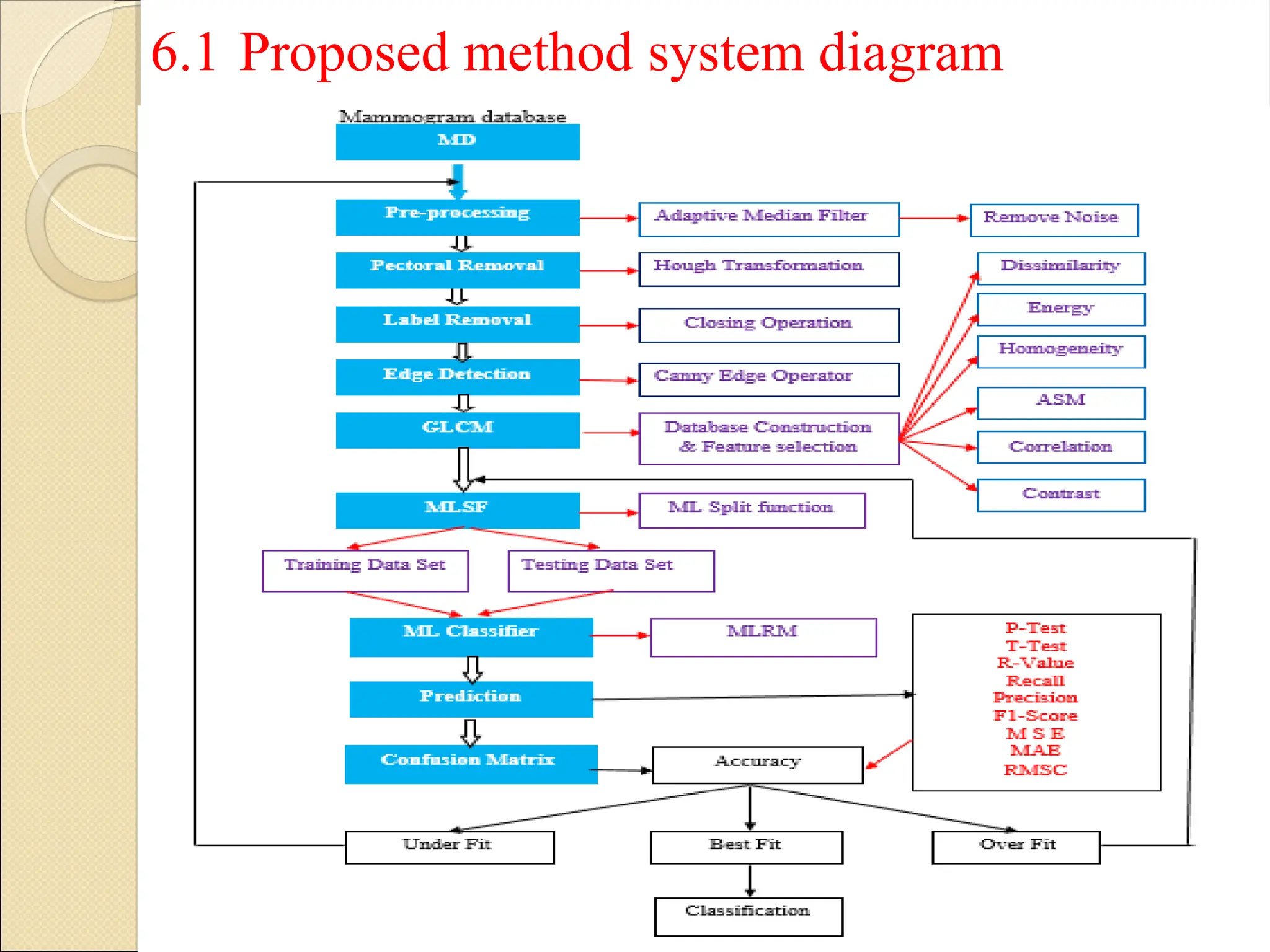
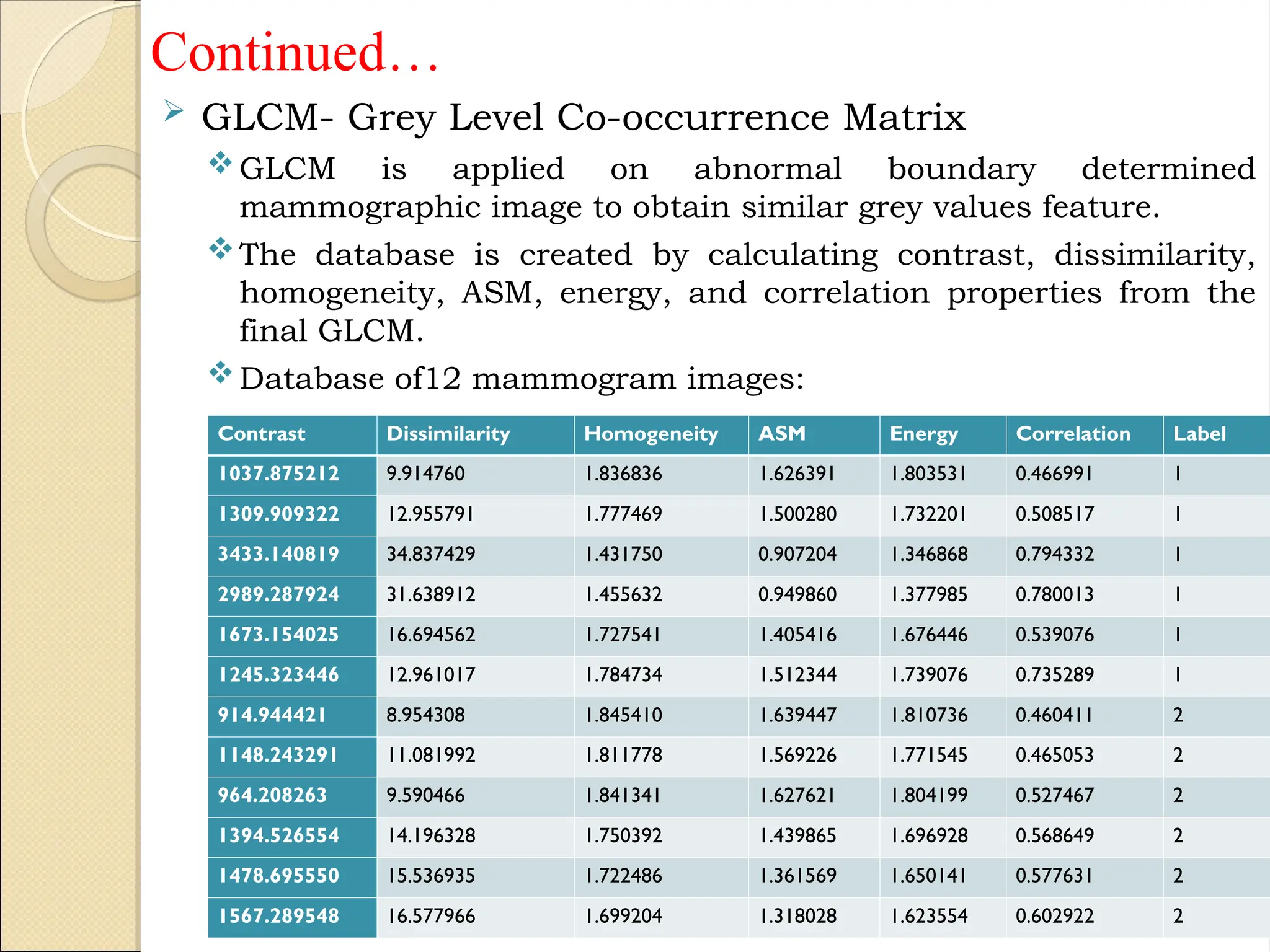
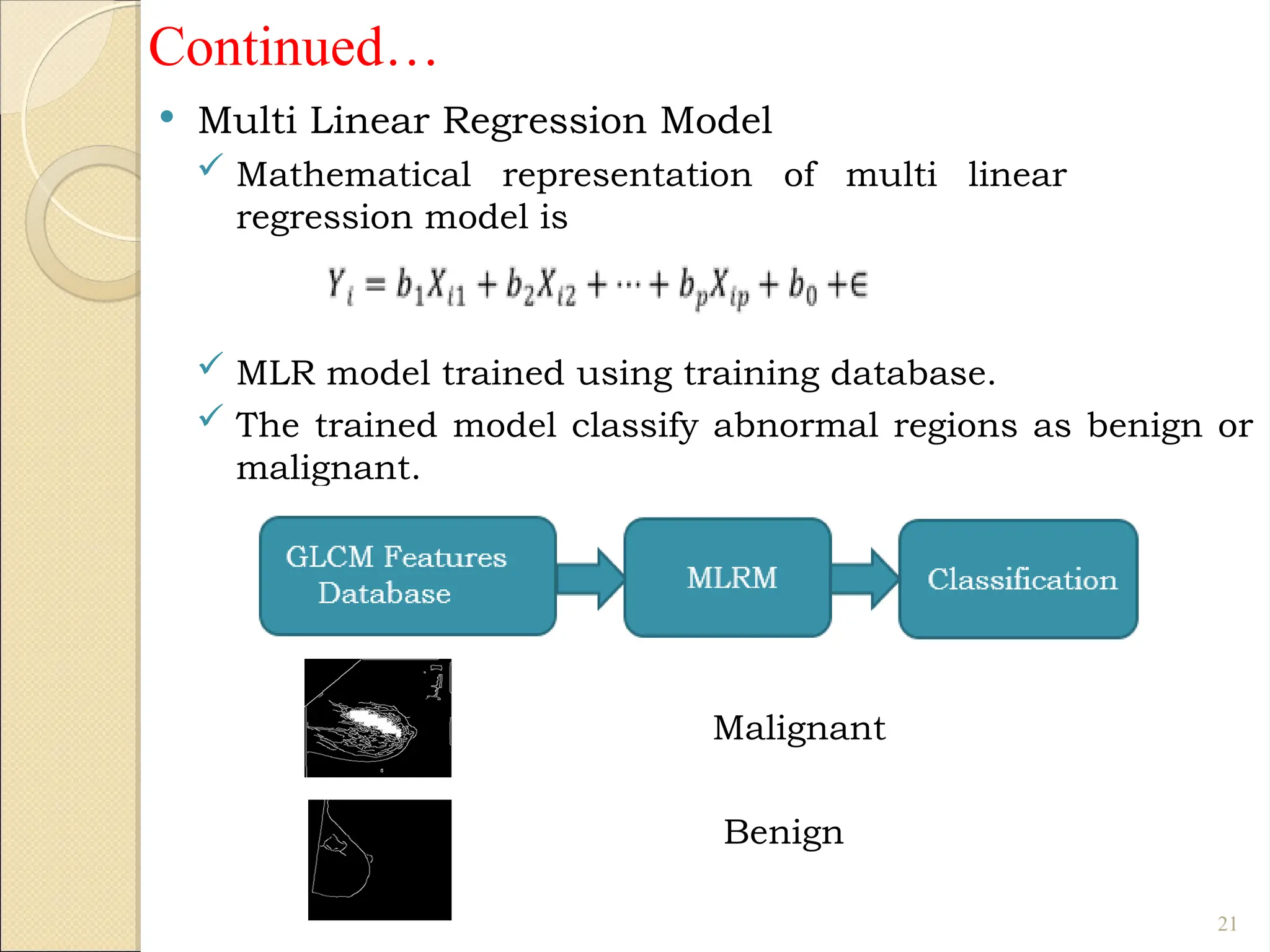
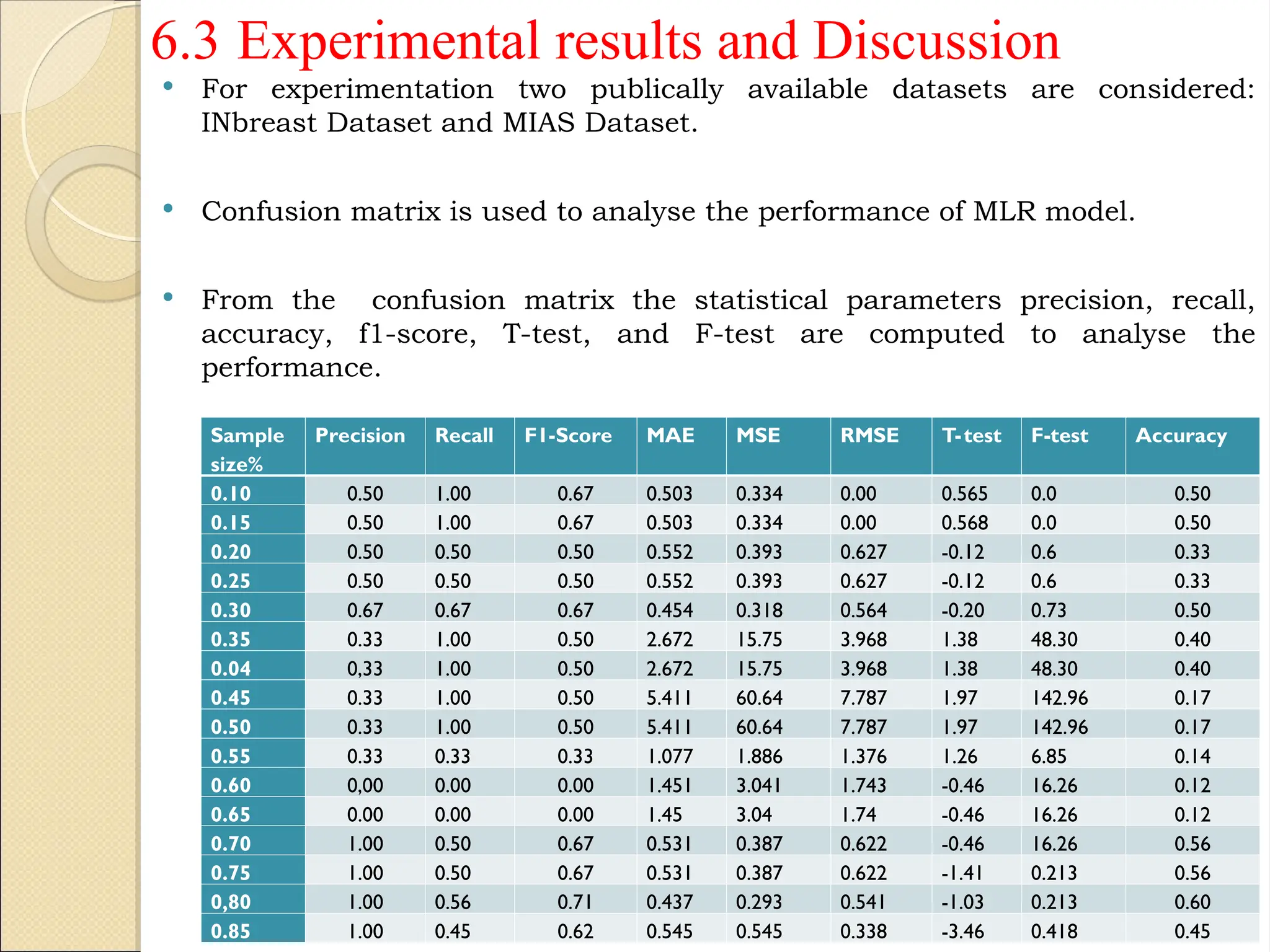
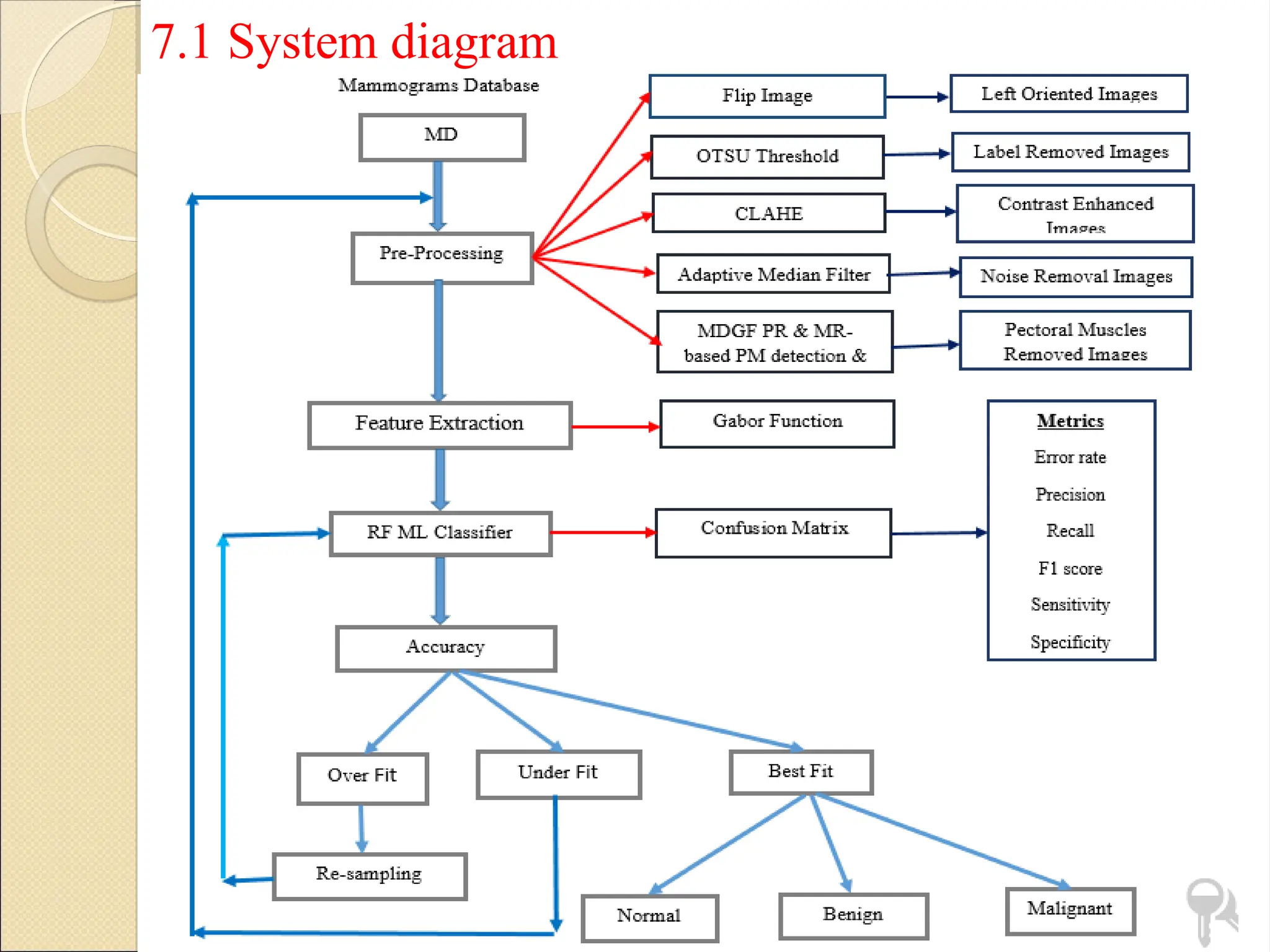
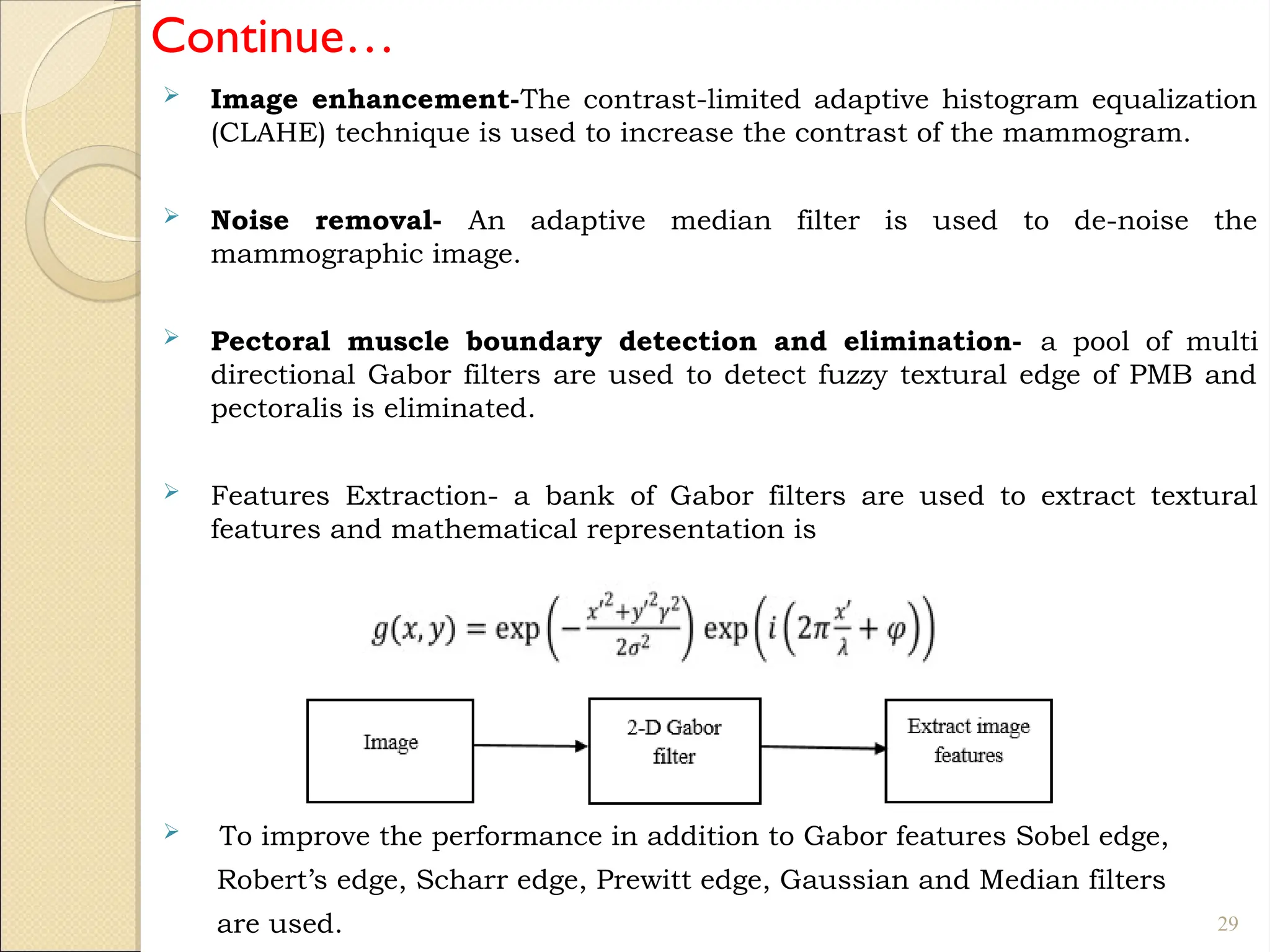
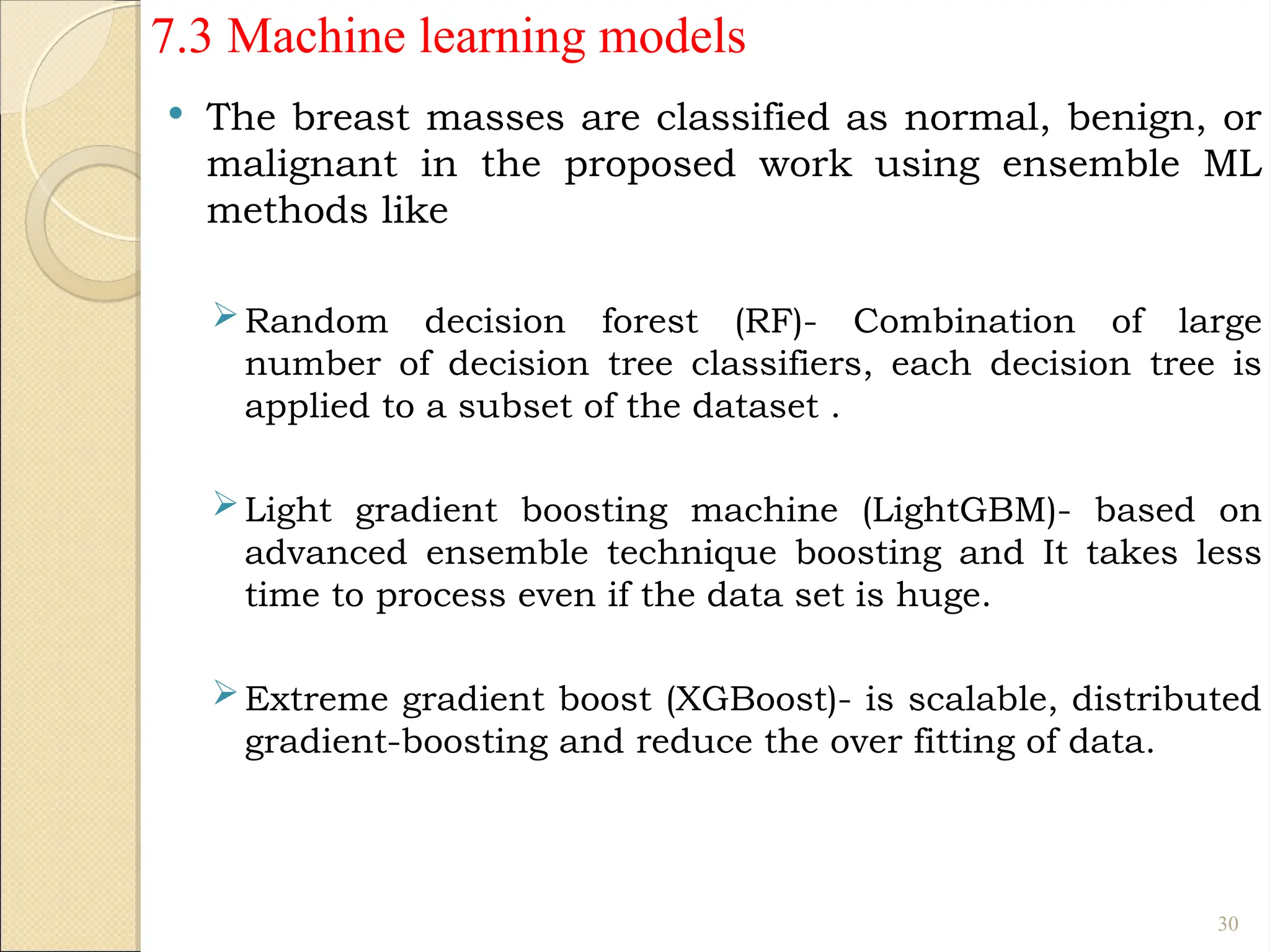
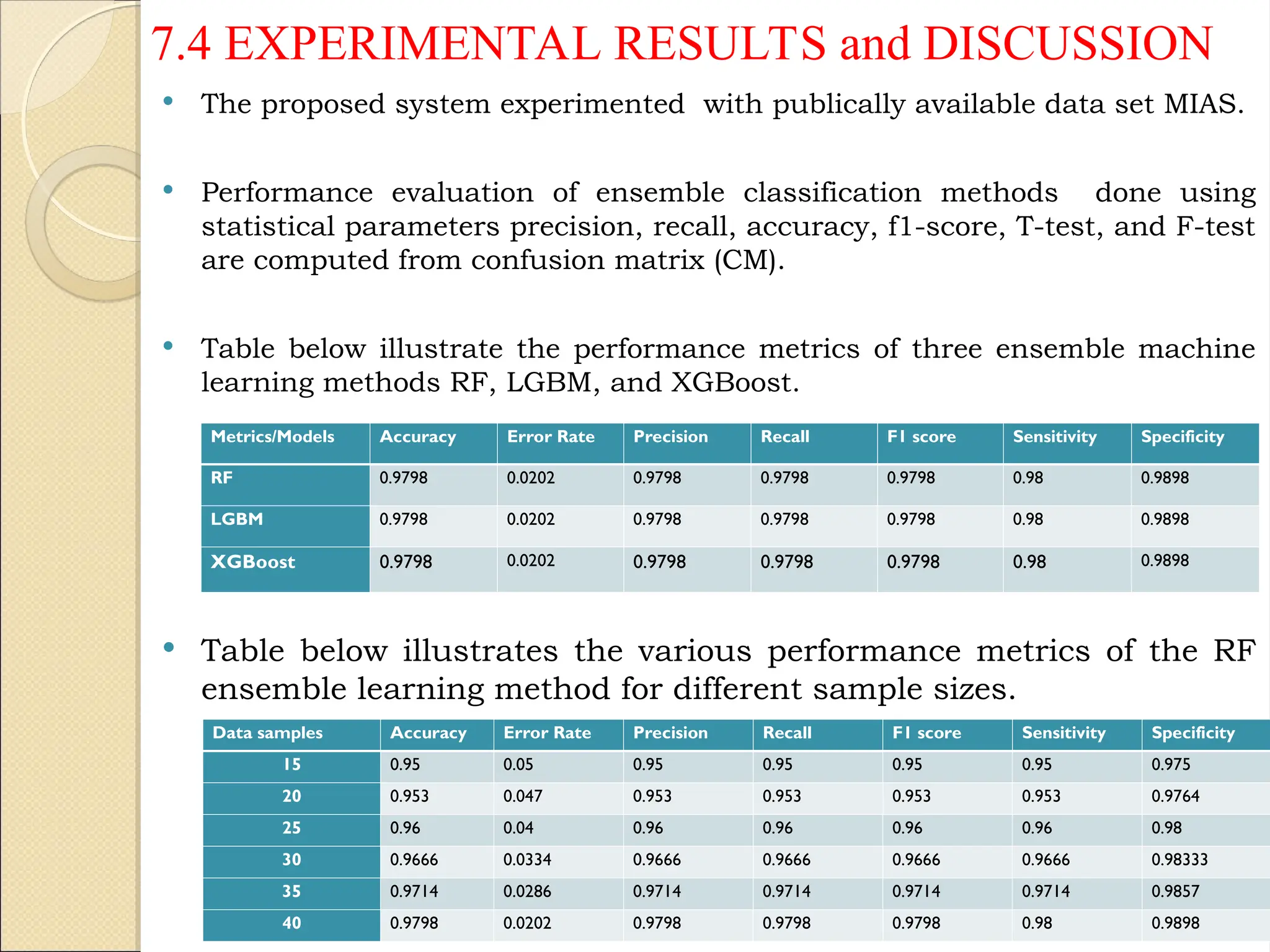
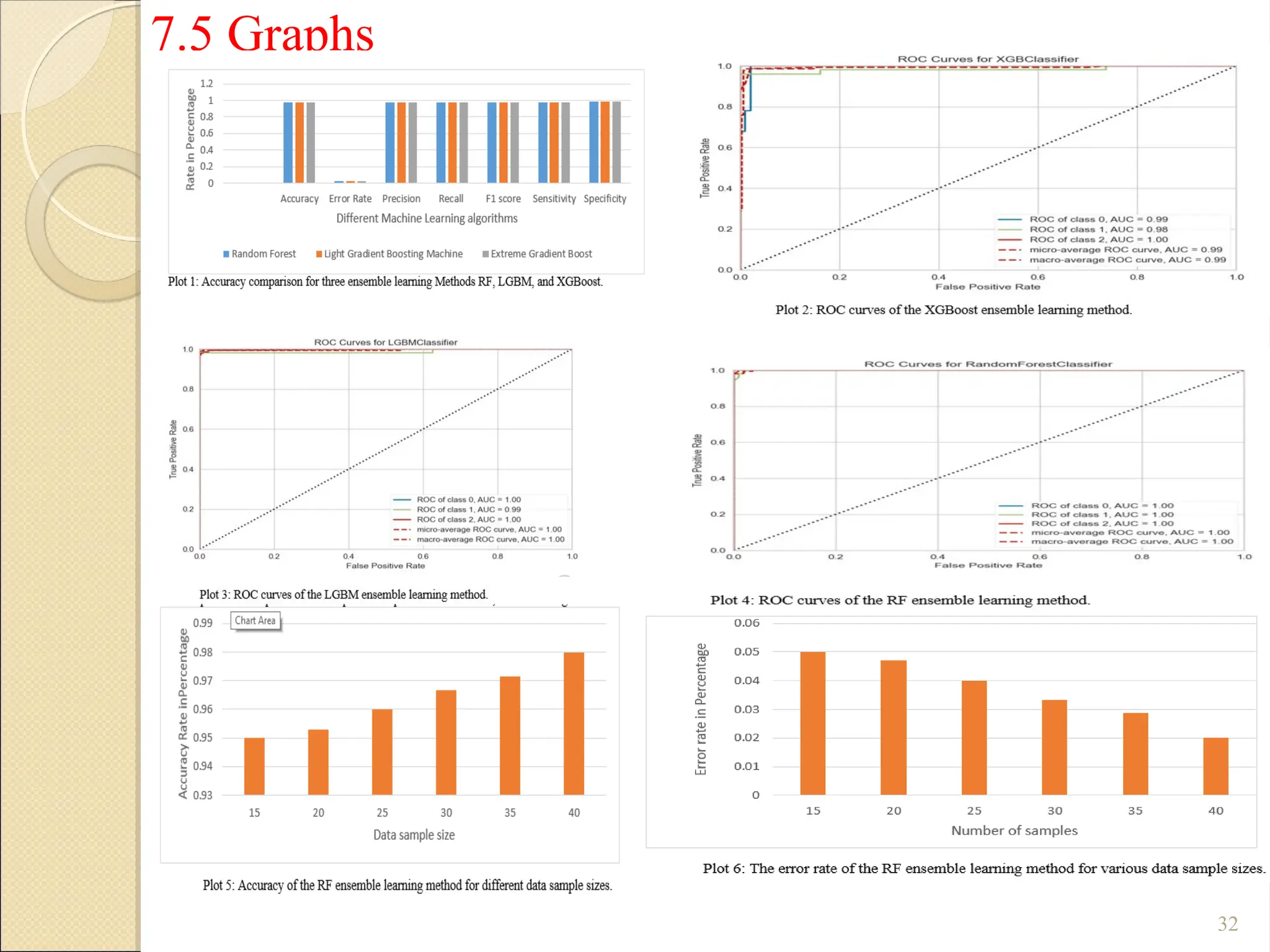
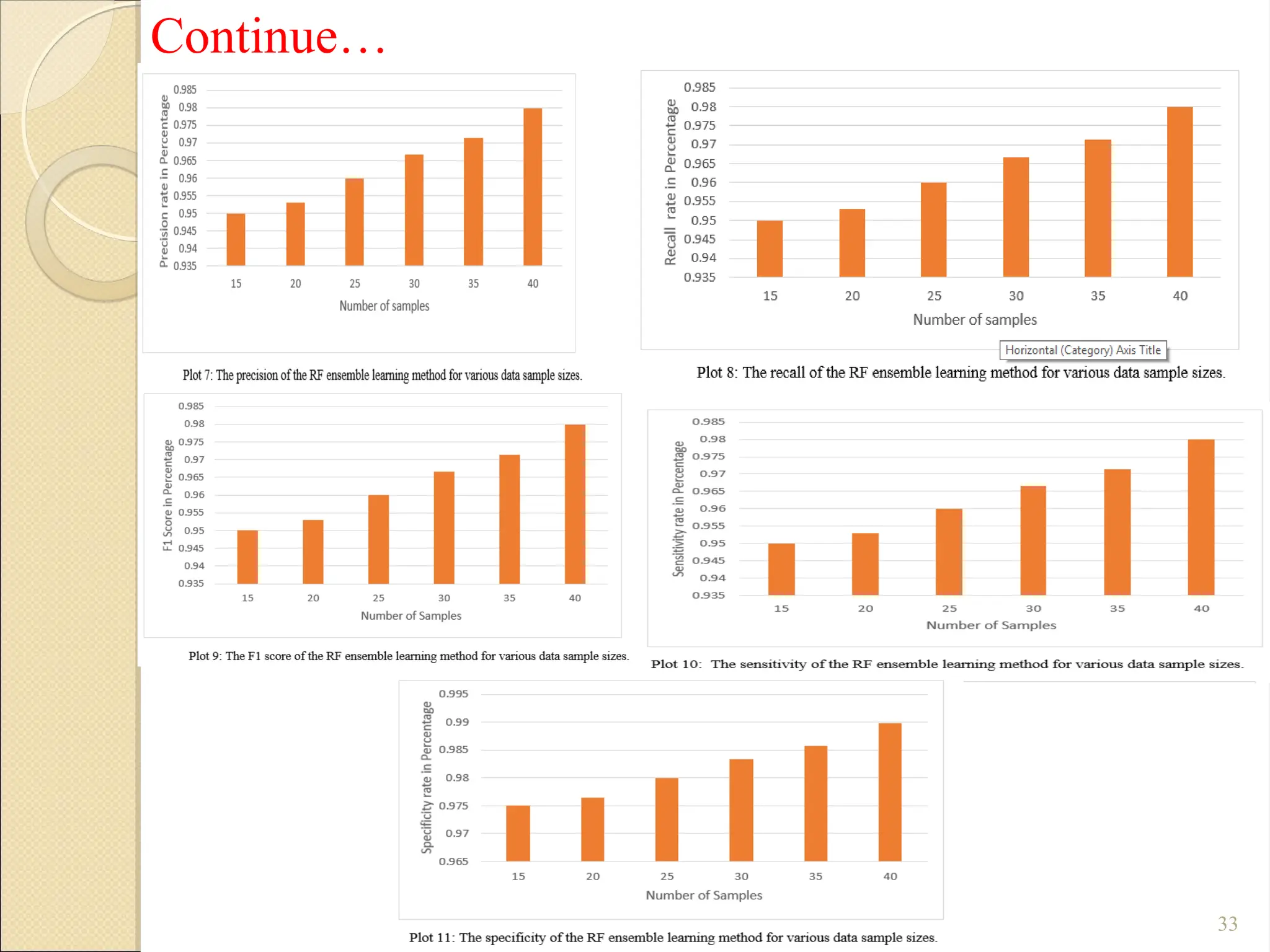
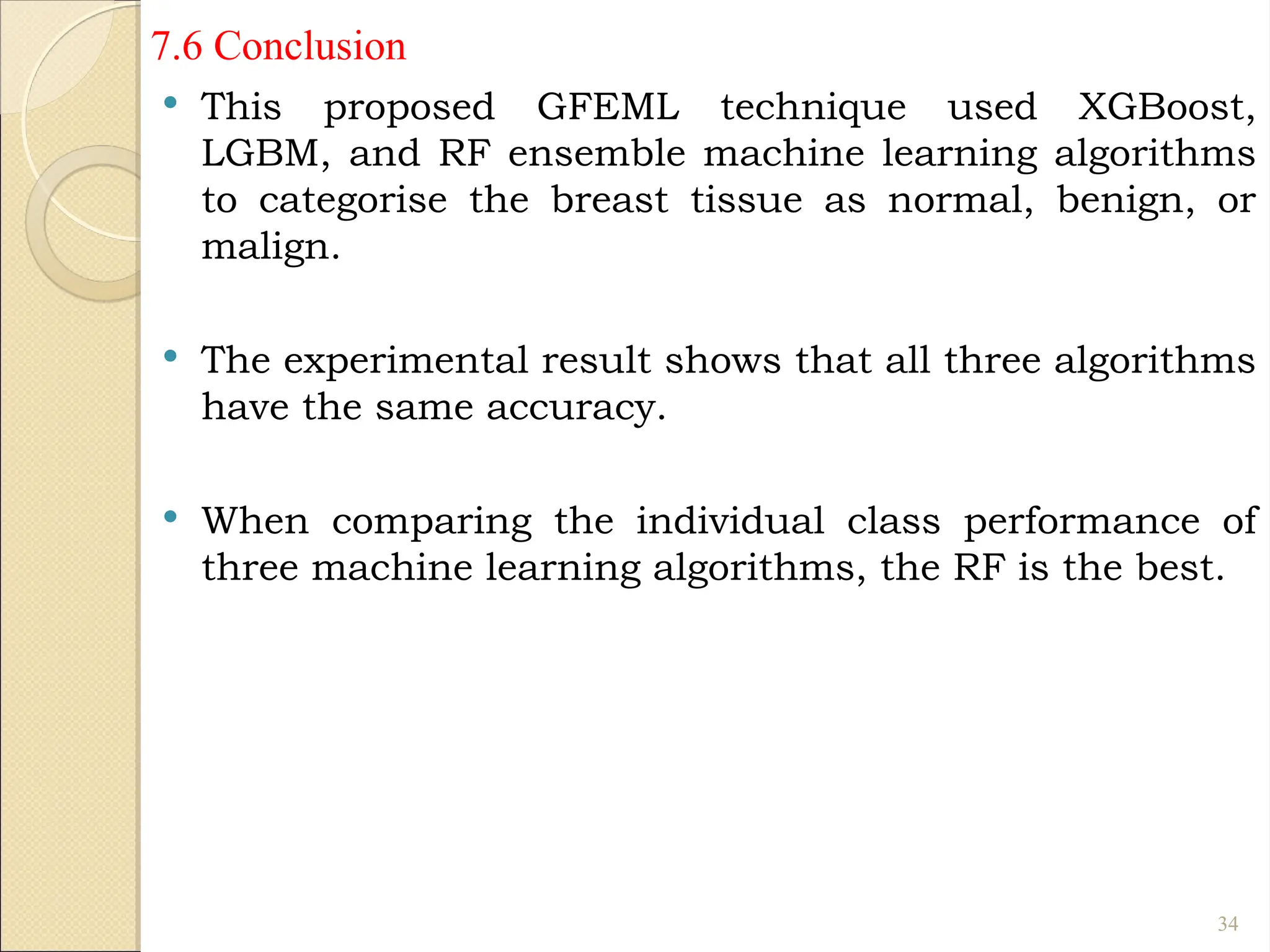
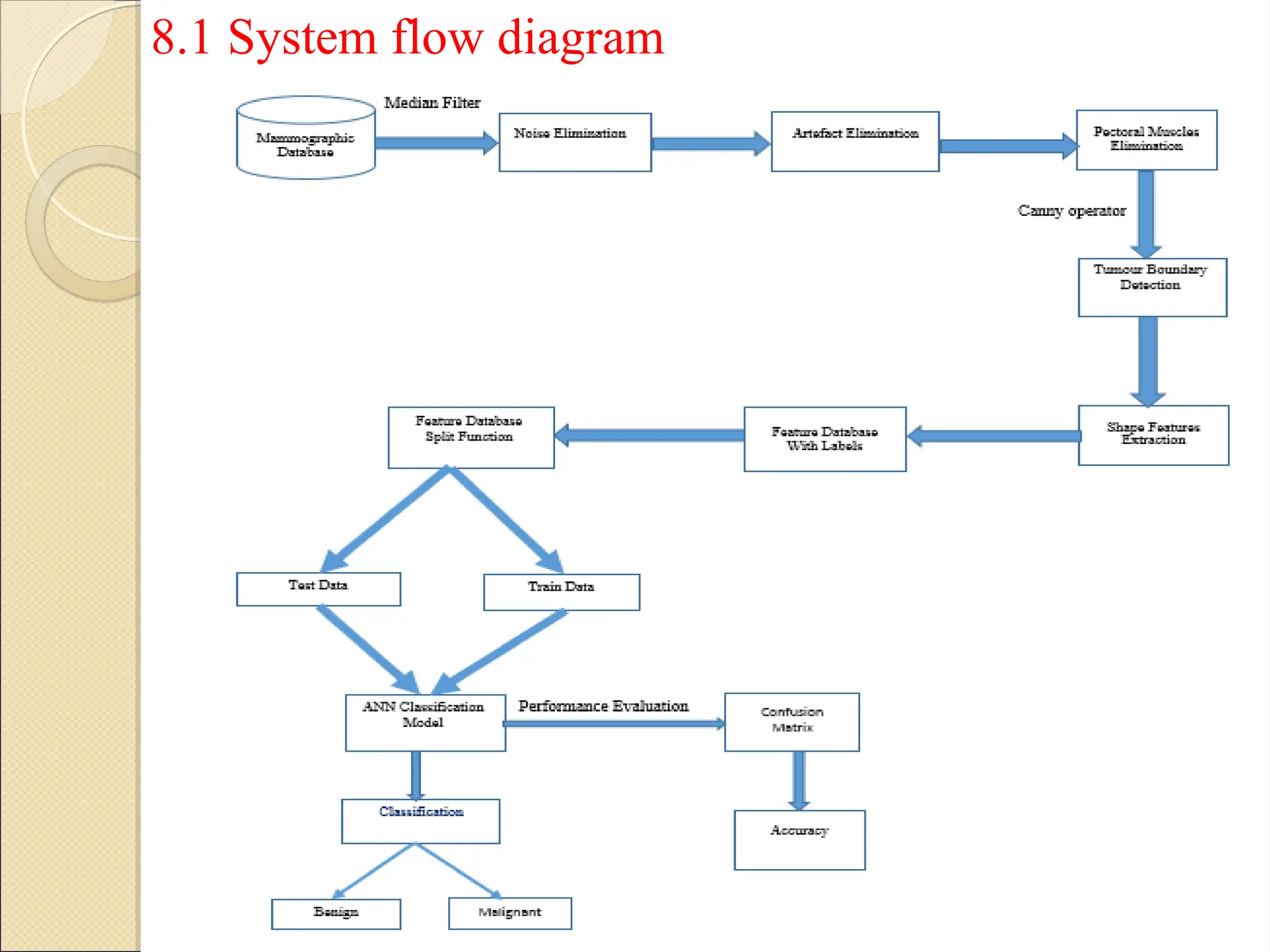
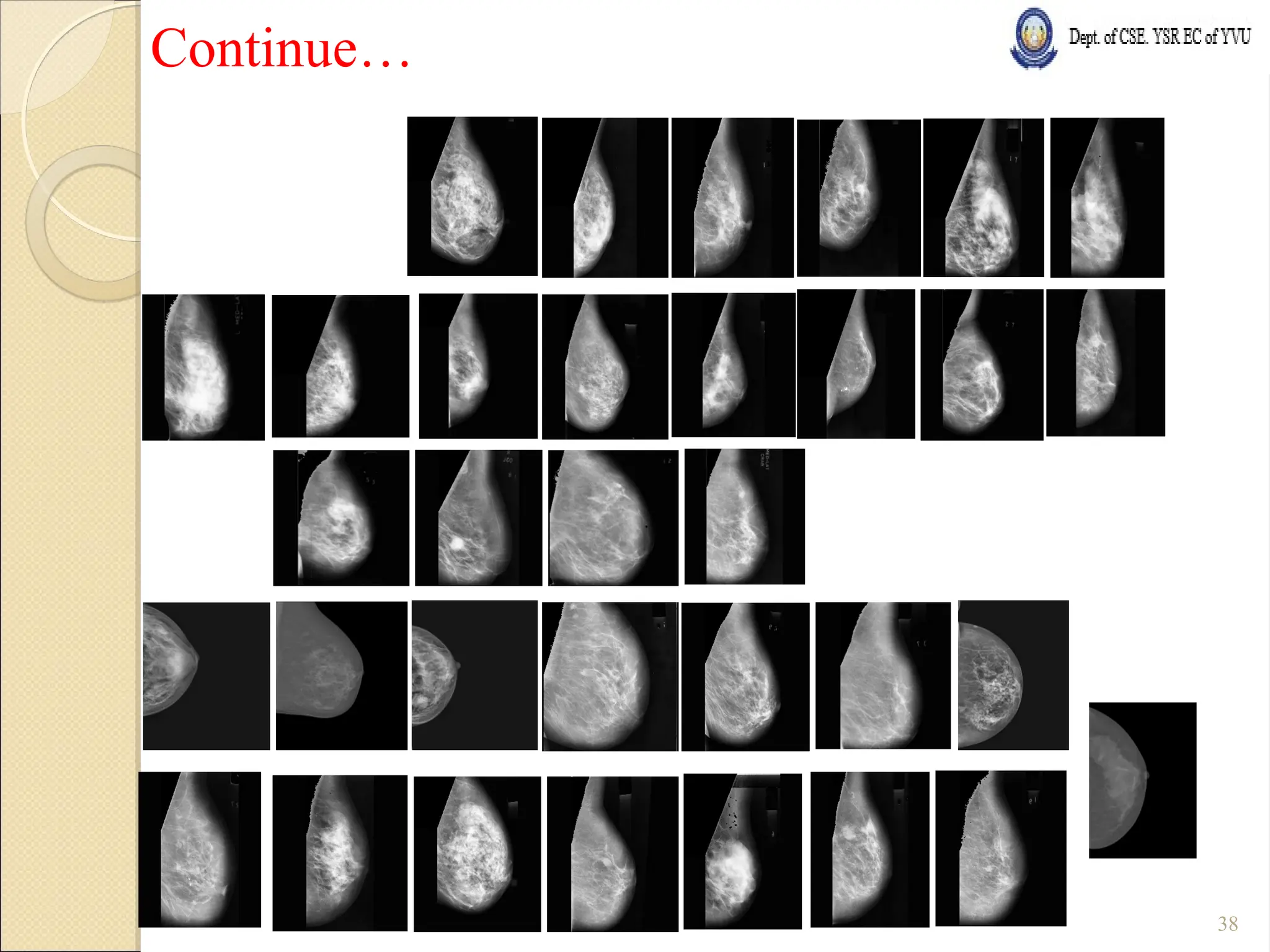
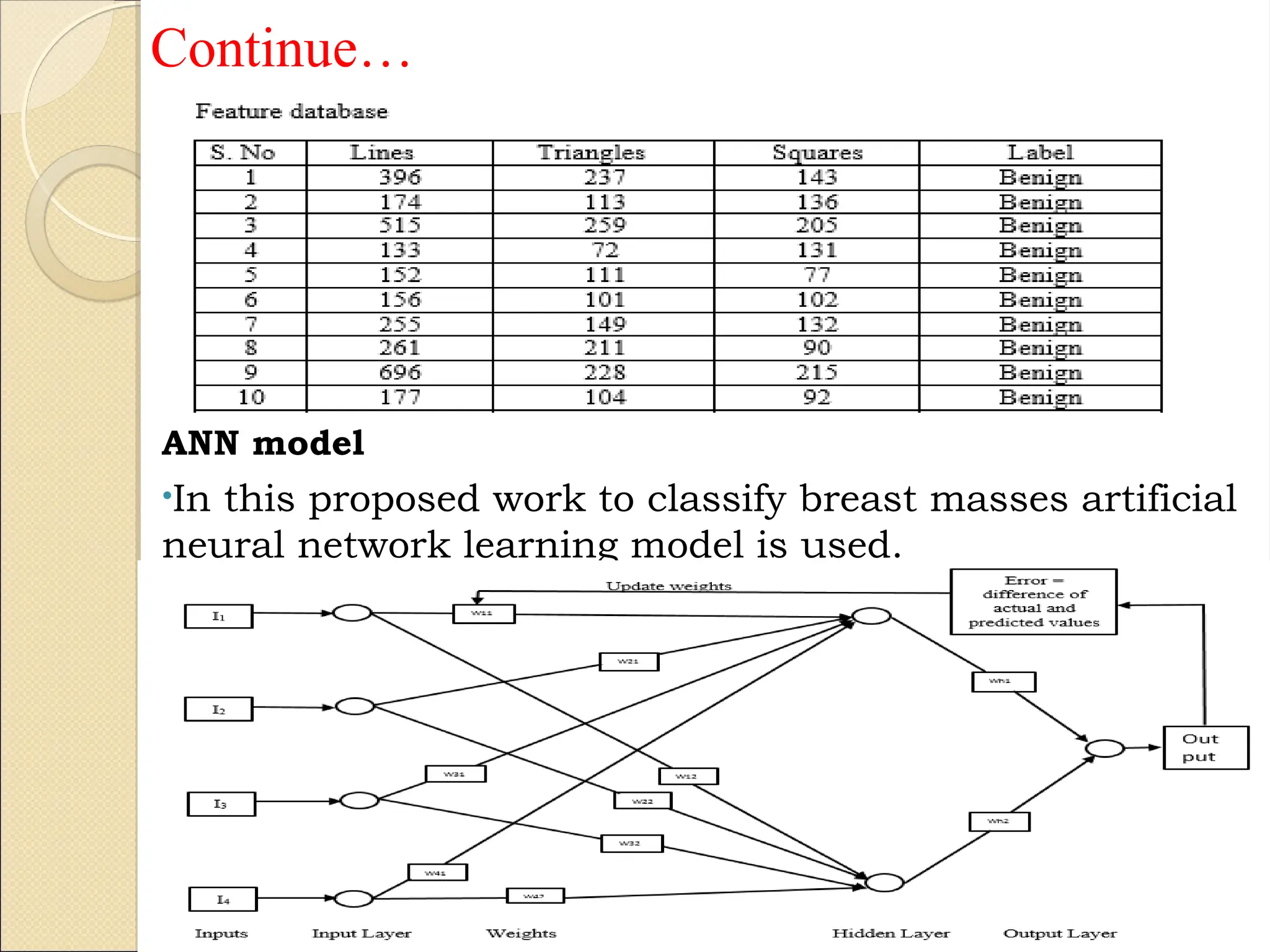
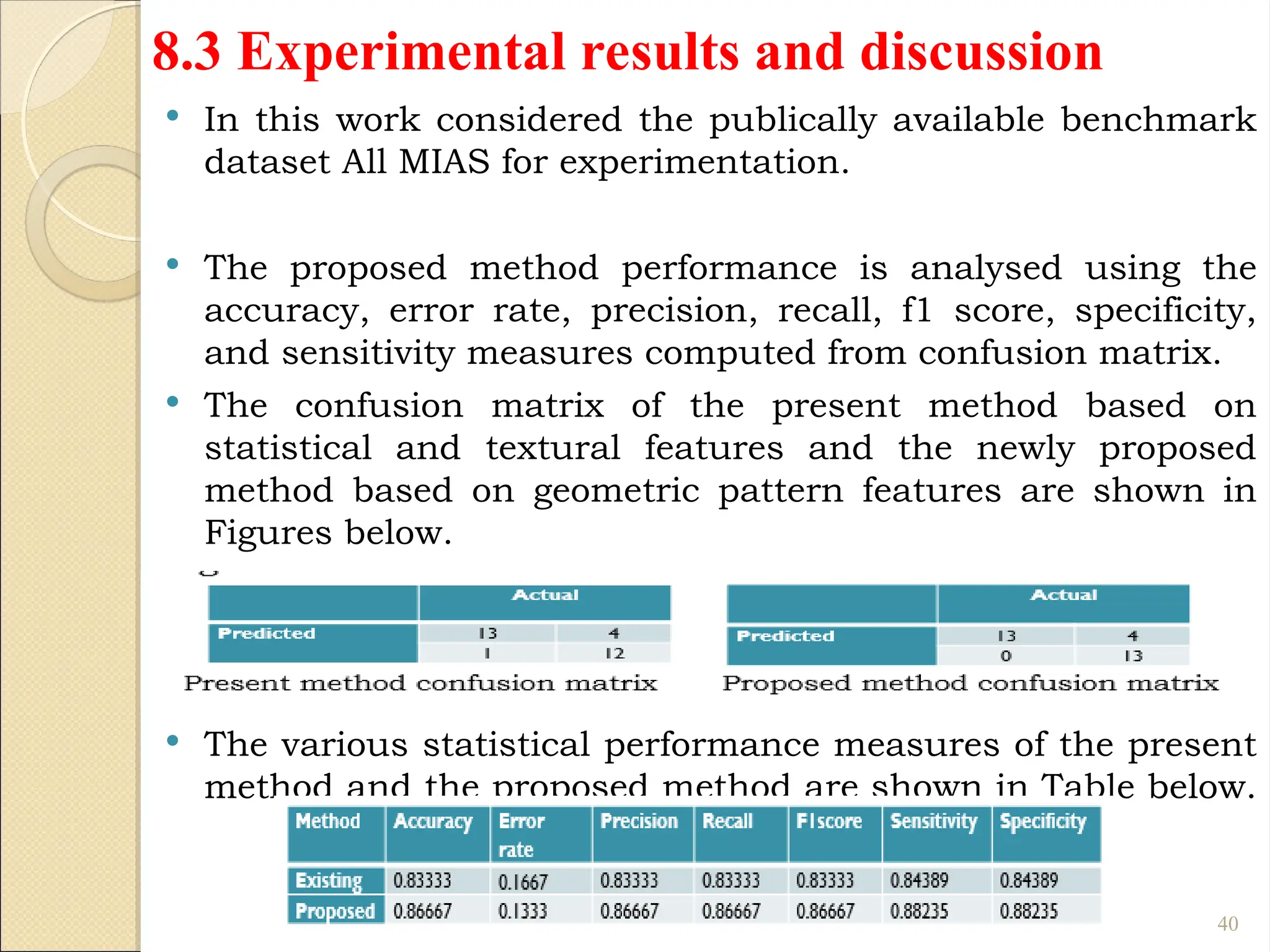
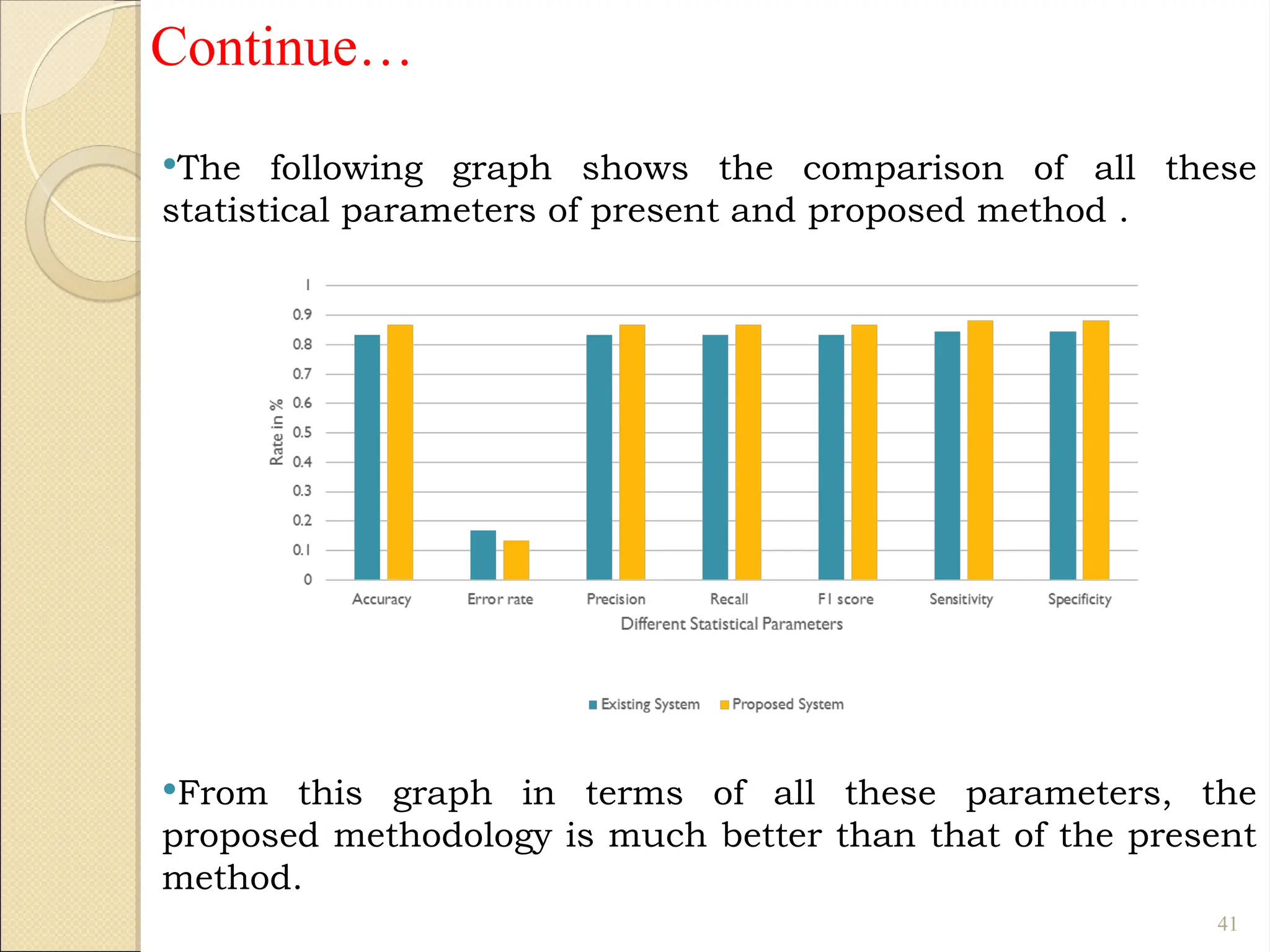
Breast Cancer comprises 16% of all cancers in women- WHO Report.
The number of cases of Breast Cancer is more in developed countries while the incident rates are low.
On the contrary the incidence rates are high in developing nations while the number of cases currently are relatively low.