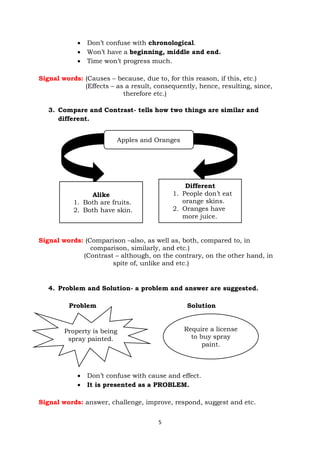
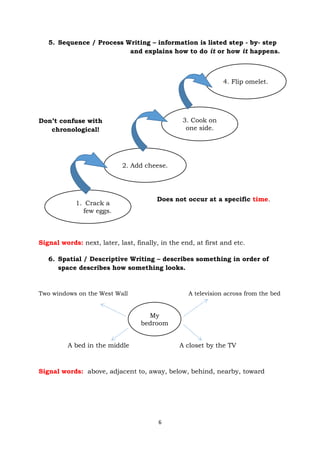
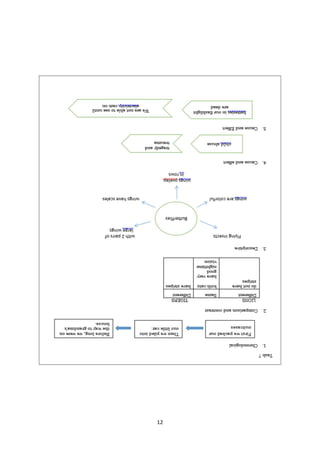
The document provides information about an English for Academic and Professional Purposes module for grade 11/12 students. It includes a title page with learning competencies, a table of contents, introductory messages, and various sections on text structure, including examples and activities. The document discusses identifying different types of text structures such as chronological, cause and effect, compare and contrast, problem and solution, and more. It provides tips for determining the organizational structure of a text.